EUR/USD clings to gains above 1.1100 ahead of Fed policy decision
- EUR/USD holds gains above 1.1100 as the US Dollar remains under pressure ahead of the Fed’s policy decision at 18:00 GMT.
- Traders seem more confident that the Fed will reduce interest rates by 50 basis points.
- ECB’s Villeroy sees the policy-easing cycle continuing further.
EUR/USD steadies above 1.1100 in Wednesday’s European session ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy announcement at 18:00 GMT. The major currency pair gains as the US Dollar (USD) remains under pressure as the Fed is poised to deliver its first interest rate cut in more than four years.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, struggles to hold its recovery to near 101.00, a rebound fuelled by better-than-expected United States (US) monthly Retail Sales data for August.
The confidence of market participants that the Fed will start the policy-easing cycle aggressively has increased as officials said they remain concerned over a slowdown in job growth. Also, they are confident that inflation is declining towards the bank’s target of 2%.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, 30-day Federal Funds Futures pricing data shows that the probability of the central bank cutting rates by 50 basis points (bps) to 4.75%-5.00% is at 65%, while the rest favors a 25-bps rate cut.
In addition to the Fed’s decision itself, the US Dollar will also be influenced by the Fed’s dot plot, economic projections, and the press conference of Fed Chair Jerome Powell, which will provide fresh guidance on interest rates. The Fed’s dot plot indicates where policymakers see the federal fund rate heading in the medium and long term.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD gains even though Euro struggles
- EUR/USD remains firm at the US Dollar’s expense as the Euro (EUR) is underperforming against other major peers on Wednesday. The Euro faces pressure amid growing uncertainty over the European Central Bank’s (ECB) interest-rate path and the Eurozone’s economic performance.
- ECB officials seem split over the interest rate-cut path due to diverging opinions over the inflation outlook. On Friday, the comments from ECB Governing Council member and Bank of France President, François Villeroy de Galhau indicated that more rate cuts are needed to avoid the risk of inflation coming in too low despite a dovish decision on Thursday. In Wednesday’s Asian session, Villeroy said the ECB “is likely to continue to cut rates.”
- On the contrary, ECB Governing Council member Peter Kazimir said on Monday in a blog post: "We will almost surely need to wait until December for a clearer picture before making our next move," Reuters reported. Kazimir emphasized the need to be certain that price pressures continue to decline as projected, “otherwise policymakers might regret rushing to cut borrowing costs before inflation has been sustainably defeated”, he said.
- Financial market participants expect that the ECB will deliver one more interest rate cut in one of its remaining meetings of the year, either in October or December.
- In the Eurozone calendar, Eurostat will publish at 09:00 GMT the final reading of the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) for August. Economists expect the figures to be aligned with the preliminary estimates, with annual headline inflation at 2.2% and core inflation at 2.8%.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD holds gains above 1.1100
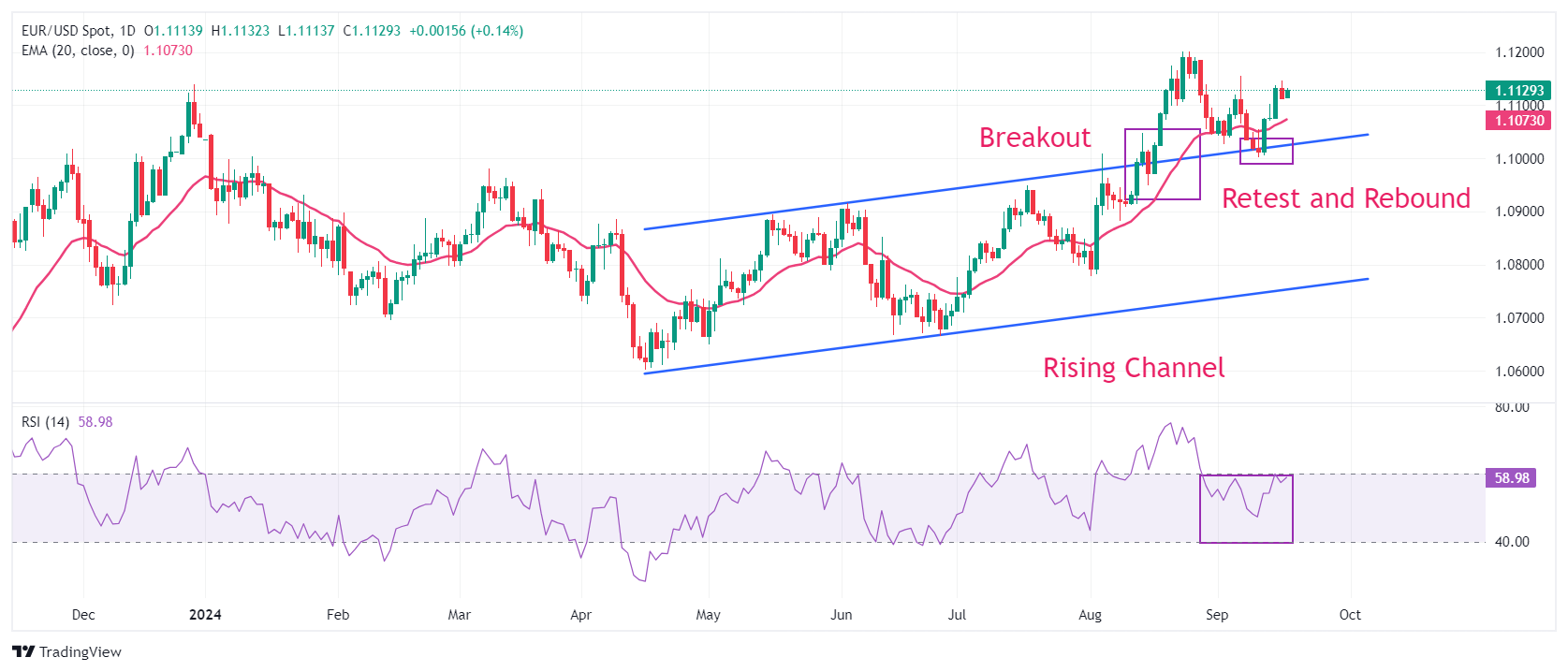
EUR/USD steadies above 1.1100 in European trading hours. The major currency pair strengthened after retesting the breakout of the Rising Channel chart pattern formed on a daily time frame near the psychological support of 1.1000. The near-term outlook of the major currency pair has strengthened as the asset steadies above the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.1060.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) moves higher to near 60.00. A bullish momentum would trigger if it sustains above the aforementioned level.
Looking up, the high of 1.1155 from September 6 and the round-level resistance of 1.1200 will act as major barricades for the Euro bulls. On the downside, the psychological level of 1.1000 and the July 17 high near 1.0950 will be major support zones.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.


