EUR/USD falls sharply as diminished Fed large rate cut bets boost US Dollar
- EUR/USD dives below 1.1050 as the US Dollar strengthens on expectations that the Fed will opt for a small-size interest rate cut this month.
- Investors await the US CPI on Wednesday for fresh guidance on interest rates.
- The ECB is expected to cut interest rates this week.
EUR/USD extends its downside below 1.1050 in Monday’s European session. The major currency pair declines as the US Dollar (USD) strengthens after mixed cues over current labor market health from Friday’s United States (US) Nonfarm payrolls (NFP) report for August, which diminished market expectations for the Federal Reserve (Fed) to reduce interest rates aggressively this month.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, jumps to near 101.50.
The official employment report showed that fresh payrolls were fewer than expected, the Unemployment Rate fell expectedly, and the Average Hourly Earnings, a key measure of wage growth, grew at a faster-than-projected pace.
Market participants were mainly focusing on the employment numbers as the Fed appeared to be confident that price pressures are on track to return to the desired central banks’ rate of 2%. Slower job demand increased evidence that the US economic growth is moderating. Still, the pace of decline was lesser than July’s impression, which diminished recession fears and the Fed’s large rate-cut bets.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, the probability of the Fed reducing interest rates by 50 basis points (bps) to 4.75%-5.00% in September is 27%, while the rest favors a 25-bps interest rate cut.
Going forward, the US Dollar is expected to witness more volatility this week as the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for August is lined up for release on Wednesday.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD drops as US Dollar gains sharply
- EUR/USD performs weakly against its major peers on Monday, with investors focusing on the European Central Bank (ECB) policy decision, which will be announced on Thursday. The ECB is expected to cut its key borrowing rates again by 25 basis points (bps). This would be the second dovish interest rate decision by the ECB in its current policy-easing cycle, which it started in the June meeting but kept interest rates unchanged in July.
- The ECB is almost certain to reduce interest rates this week as Eurozone price pressures have significantly contained and growing uncertainty over the economic outlook. Eurozone’s preliminary headline Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) fell to 2.2% in August, the lowest reading since July 2021. The Eurozone economic prospects are poor due to subdued demand from domestic and overseas markets.
- The German economy has been exposed to a technical recession, given that the nation’s growth contracted in the second quarter of this year, and the outlook for the third quarter remains uncertain.
- Meanwhile, ECB policymakers have also acknowledged growing weakness in the German economy and see more interest rate cuts as appropriate in the remainder of the year. Last week, ECB board member Piero Cipollone said, "There is a real risk that our stance could become too restrictive."
- On the economic data front, Eurozone Sentix Investor Confidence has worsened further to -15.4 in September from -13.9 in August. This appears to be the outcome of the deteriorating economy’s health amid a slowdown in the German economy.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD slips below 1.1050
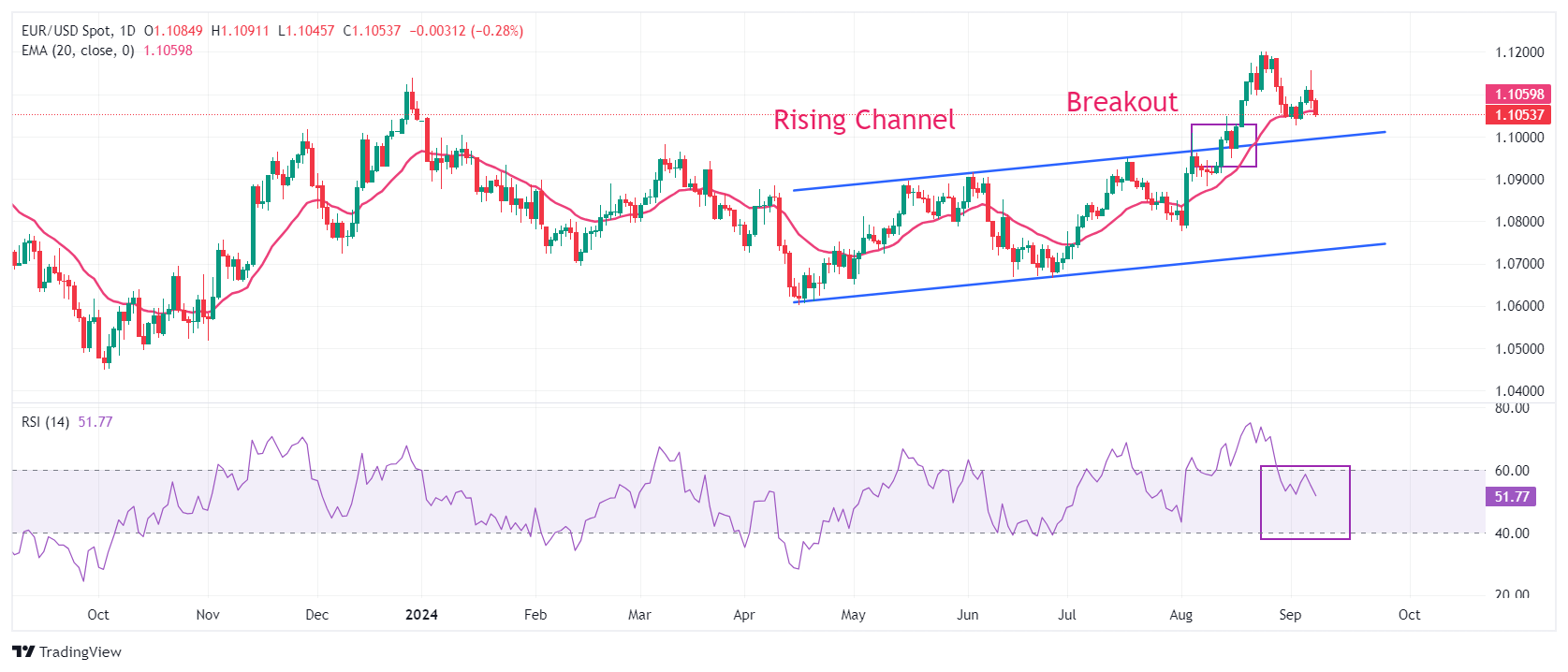
EUR/USD dips below 1.1050 in Monday’s European trading hours. The major currency pair weakens after failing to sustain above the crucial resistance of 1.1100. The near-tern outlook of the shared currency pair has become uncertain as it has dropped below the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.1060.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls further to 50.00, suggesting a lack of bullish momentum.
The pair is expected to find support near the psychological level of 1.1000. On the upside, last week’s high of 1.1155 and the round-level resistance of 1.1200 will act as major barricades for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

