Gold rallies amid US yields plunge fueled by signs of lower core prices
- Gold extends gains as US core inflation was better than expected, sparking a drop in Treasury yields.
- Traders now anticipate the Fed might cut rates by 40 basis points by the end of 2025, adjusting market expectations.
- Potential tariffs by the upcoming Trump administration could counter disinflationary trends, impacting gold's trajectory.
Gold climbed for the second straight day due to a plunge in United States (US) yields following data that hinted at fading core inflation. This suggests that the Federal Reserve (Fed) could ease policy due to the disinflation trend. The XAU/USD trades at $2,690.
The golden metal resumed its uptrend after the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed that underlying consumer inflation dipped compared to estimates and the previous month’s reading. The data sent US yields tumbling, as there is an increasing chance that the Fed will not exclude interest rate cuts following the December meeting.
After the data, traders estimate the US central bank to deliver 40 basis points (bps) of easing towards the end of 2025.
However, Gold is not out of the woods yet, as the upcoming Donald Trump administration has on its agenda applying tariffs, which could stoke inflation and prevent the Fed from lowering borrowing costs.
If the upcoming administration does indeed proceed with tariffs, this could boost the US Dollar (USD) to the detriment of the non-yielding metal.
Meanwhile, financial markets focus on US Retail Sales, unemployment claims and Fed speaking.
Daily digest market movers: Gold’s jump sponsored by plummeting US real yields
- Gold extended its gains as real yields dropped. Measured by the 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) yield, tumbled nine and a half basis points (bps) from 2.33% to 2.234%.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the dollar's performance against six currencies, rose 0.09% to 109.29, recovering from a daily low of 108.62.
- In December, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 2.9% YoY as expected, above the previous month’s 2.7%. Core CPI for the same period expanded by 3.2% YoY, less than the 3.3% registered in November,
- Ahead in the calendar, Retail Sales are expected at 0.6% MoM, down from 0.7% in November. Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending January 11 are projected to jump from 201K to 210K.
- New York Fed President John Williams said the neutral rate is much higher due to the country’s high debt levels. He added that inflation has retreated, yet the Fed is awaiting what elected officials might do on fiscal policy.
- The CME FedWatch Tool shows investors are eyeing the first rate cut for the June 18 meeting.
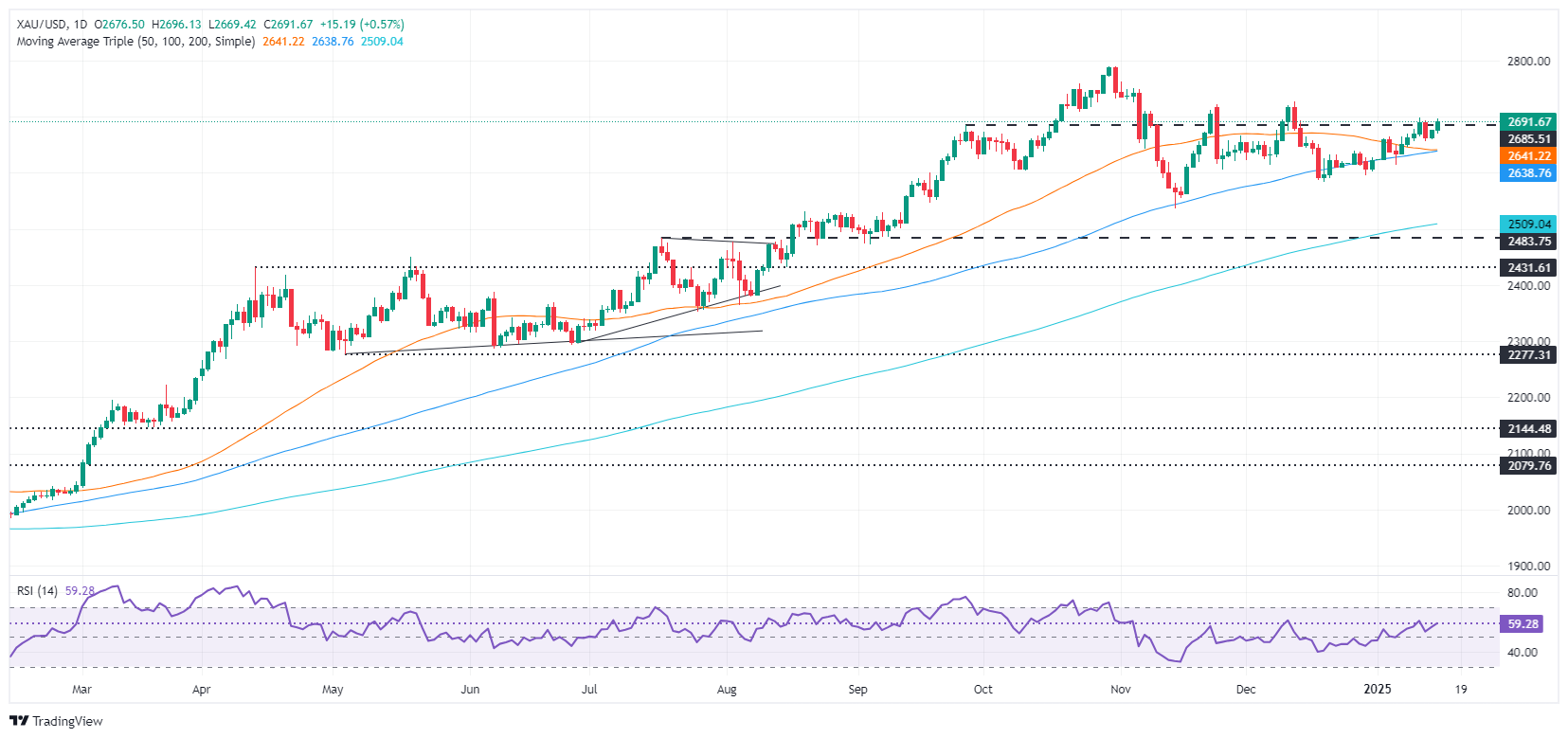
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price surges towards $2,700 as US yields drop
Gold’s uptrend remains intact, with buyers eyeing a clear break of $2,700. Bulls are gathering steam, as depicted by the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and aiming up indicates that momentum favors higher prices. Once XAU/USD clears $2,700, the next resistance would be the December 12 peak of $2,726, followed by the record high at $2,790.
Conversely, if XAU/USD drops below $2,650, the next support would be the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $2,643, followed by the 100-day SMA at $2,633.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

