USD/INR holds positive ground on a rise in month-end US Dollar demand
- The Indian Rupee weakens in Wednesday’s Asian session.
- A rise in month-end US Dollar demand and higher crude oil prices weigh on the INR.
- Positive domestic equity trends and fresh foreign investments might cap the pair’s upside.
The Indian Rupee (INR) loses momentum on Wednesday. Month-end US Dollar (USD) demand from local oil companies and importers, coupled with the Greenback's recovery against major currencies, undermines the Indian currency. Additionally, extended gains in crude oil prices might weigh on the INR as India is the world's third-largest oil consumer.
On the other hand, the rise in Indian stock markets with foreign institutional investors (FIIs) back into buying mode lifts the local currency. The US MBA’s Mortgage Applications and Durable Goods Orders are due later on Wednesday. Also, the Federal Reserve (Fed) officials are scheduled to speak, including Neel Kashkari and Alberto Musalem.
Indian Rupee against the USD edges lower amid firm US Dollar demand
- “There was month-end demand, particularly from oil companies, and likely dollar demand from the Reserve Bank to close its open short positions due in March,” said Anil Bhansali, head of treasury, Finrex Treasury Advisors.
- US President Donald Trump said early Wednesday that he is set to implement copper import tariffs within weeks, per Bloomberg.
- The US Consumer Confidence Index has fallen for the fourth consecutive month to a 12-year low, dropping to 92.9 in March, the Conference Board showed Tuesday. This figure came in lower than the estimation of 94.5.
- The US New Home Sales rose 1.8% to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 676,000 units in February, the Commerce Department's Census Bureau revealed on Tuesday. The sales pace for January was revised up to a rate of 664,000 units from the previously reported 657,000 units.
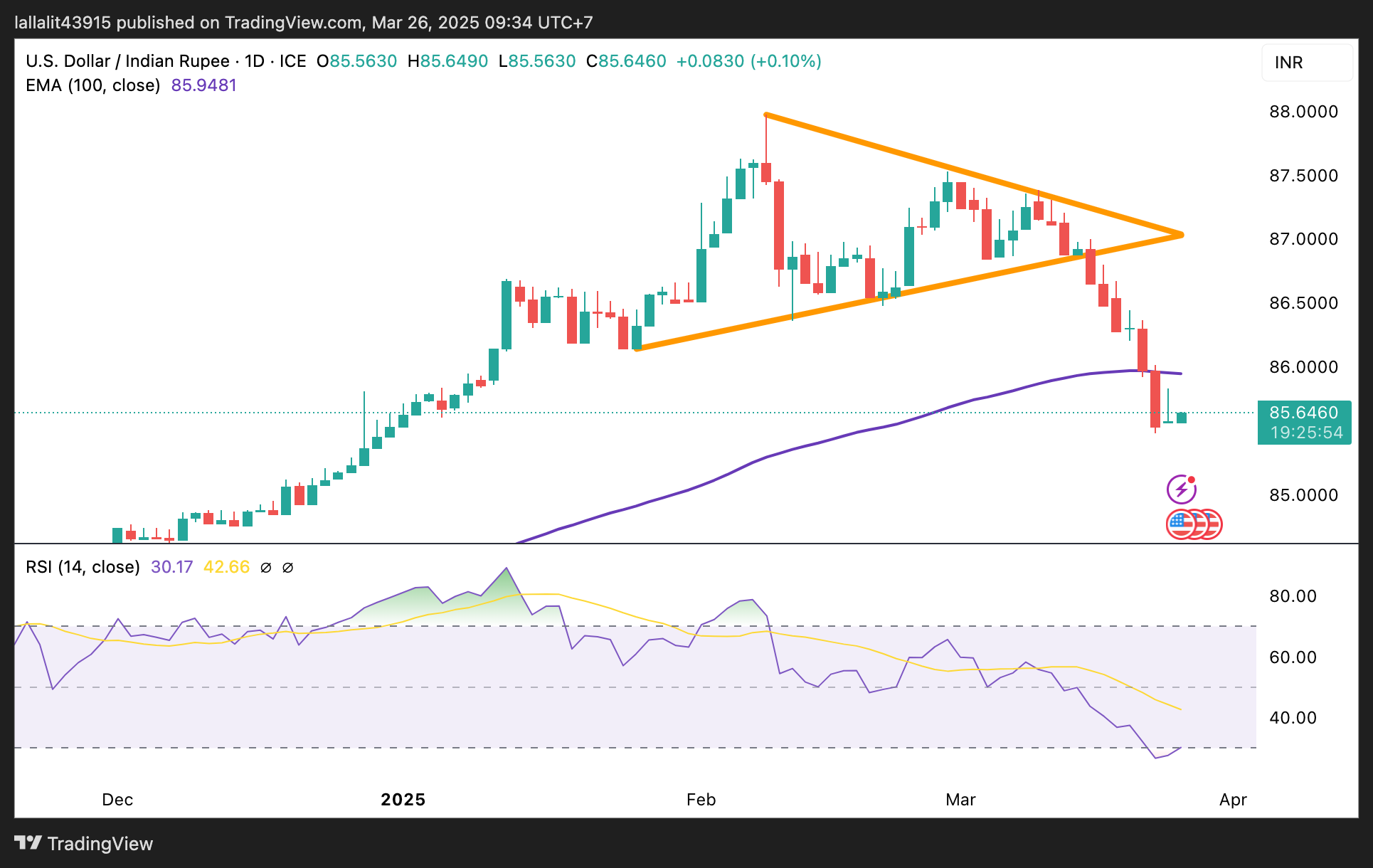
USD/INR’s bearish outlook remains in play under the 100-day EMA
The Indian Rupee softens on the day. The USD/INR pair keeps the bearish vibe, characterized by the price holding below the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average on the daily timeframe. However, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) moves below the 30.00 mark, indicating oversold conditions and warranting some caution. This suggests that further consolidation or a temporary recovery is on the cards.
The low of January 6 at 85.60 acts as an initial support level for USD/INR. Sustained bearish pressure could drag the pair lower to 84.84, the low of December 19, 2024. Further south, the additional downside filter to watch is 84.22, the low of November 25, 2024.
On the upside, the psychological level and the 100-day EMA in the 85.95-86.00 zone appear to be a tough nut to crack for bulls. A decisive break above this level could set its sights on the next upside targets at 86.48, the low of February 21, en route to 87.00, the round figure.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



