Mexican Peso plunges as Trump confirms March tariffs, Peso faces weekly losses
- USD/MXN rises 0.22% to 20.52 as tariff fears weigh on sentiment.
- Mexico’s trade deficit widens and unemployment ticks higher, adding to economic concerns.
- Banxico’s dovish stance and US trade policies could push USD/MXN toward 21.00.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) prolonged its agony and depreciated against the Greenback on Friday, set to achieve weekly losses of over 0.59% as the President of the United States (US) Donald Trump emphasized that tariffs on Mexico are moving forward on March 4. USD/MXN trades at 20.52, up 0.22%.
The emerging market currency remains pressured by US trade policies to be enacted next week. Mexico’s current week’s data showed the Balance of Trade registered a deficit in January, in contrast to December surpluses. Meanwhile, the Unemployment Rate rose two tenths, which could weigh on economic growth.
Traders continued to digest US President Trump's tariffs, saying that 25% duties on Mexico and Canada would start next week, alongside an additional 10% on China. Meanwhile, Mexican Economy Secretary Marcelo Ebrard will meet with Trade Representative Jamieson Greer on Thursday and Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick on Friday.
Across the border, the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) preferred inflation gauge, the Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, dipped annually, showing progress in monthly and yearly figures.
Given the fundamental backdrop, the USD/MXN pair could rise in the short term. Trade policies, geopolitics, and Banxico's dovish stance could push the pair to challenge the 21.00 level.
Cleveland Fed Beth Hammack stated that a rate hike is not in the outlook and added that the potential economic impact of tariffs and how they might influence monetary policy is uncertain.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso treads water as Trump’s tariff deadline approaches
- The Peso remains adrift to discussions between Mexican and US officials in Washington.
- Mexico’s Balance of Trade witnessed a more pronounced deficit than the $3.8 billion expected in January. It widened to $4.55 billion after sustaining a surplus of $2.576 billion in December.
- The Unemployment Rate in Mexico rose by 2.7% as expected in January, up from December’s 2.4%.
- The US Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, the Fed’s preferred inflation gauge, rose 0.3% Month over Month in January, matching expectations and accelerating from December. On a year-over-year (YoY) basis, core PCE eased to 2.6%, down from December’s 2.9%.
- US headline inflation expanded 2.5% YoY, in line with forecasts but slightly lower than December’s 2.6%. Monthly, it remained unchanged at 0.3%, as projected.
- The swaps markets hint that the Federal Reserve might ease policy by 58 basis points, up from last week's 70 bps in 2025, via data from the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT).
- Trade disputes between the US and Mexico remain front and center. Although the countries found common ground previously, USD/MXN traders should know that the 30-day pause is about to end, and tensions could trigger volatility in the pair during the rest of the week.
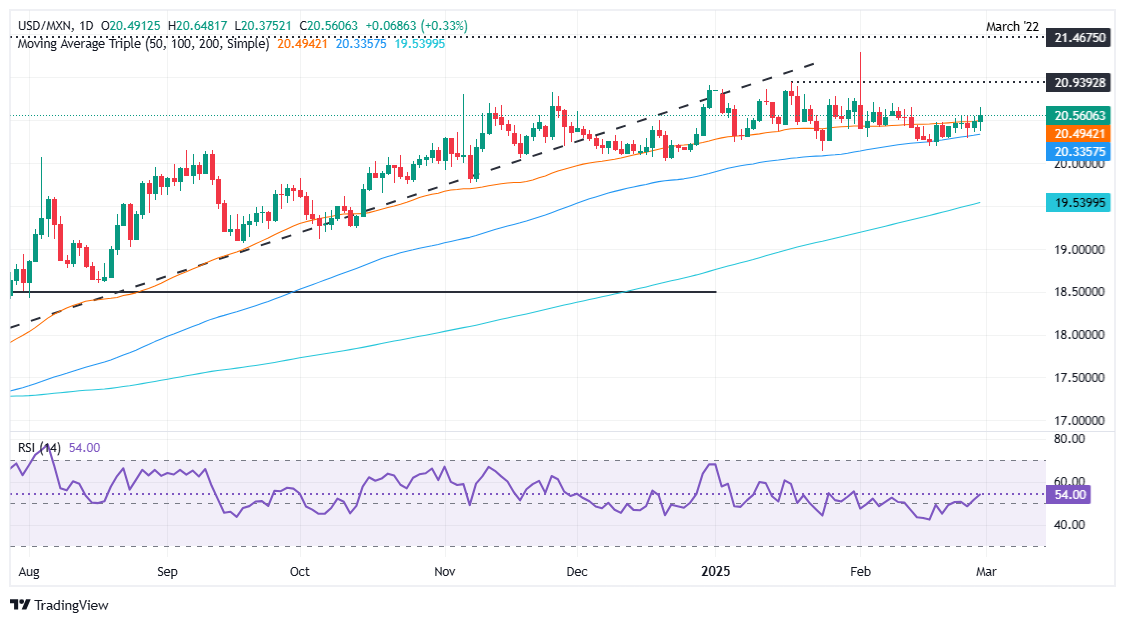
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso falls as USD/MXN hurdles 50-day SMA
USD/MXN maintains a bullish bias and a break above the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 20.45 would pave the way for a push toward 20.50. The Relative Strength Index (RSI), now above 50, reached its highest level in February, signaling strong bullish momentum. Buyers will aim to clear the January 17 high of 20.93, followed by 21.00, and the year-to-date (YTD) high of 21.28.
On the downside, failure to hold above the 50-day SMA could trigger a pullback toward the 100-day SMA at 20.24. Further weakness could be seen in the pair breaking below this dynamic support, potentially testing the psychological 20.00 level.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.

