Canadian Dollar continues to drift higher on Wednesday
- The Canadian Dollar added a thin 0.5% as the Greenback drifts lower.
- Upbeat US employment data is sending risk appetite higher.
- Meaningful Canadian data remains limited until Friday.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) tested higher against the Greenback on Wednesday, chalking in a scant one-fifth of one percent gain following the early week’s sharp recovery from multi-decade lows. Us data dominated market headlines during the midweek market session, and a general improvement in trader risk appetite is stepping down on the US Dollar, giving the Loonie a leg up.
Economic data from Canada is strictly low-tier until Friday’s labor print. US Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) figures missed the market on Wednesday, but the key reading for US data came from ADP jobs change data, which showed a potential upswing in US net job gains. Traders are keeping a close eye on employment preview numbers in the run-up to Friday’s Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar gains ground on sentiment uptick
- The Canadian Dollar gained a few points on easing Greenback flows.
- Canadian Trade Balance numbers for December rebounded, but less than expected. Markets overwhelmingly overlooked the data print.
- US ISM Services PMI survey results from January softened to 52.8 from a revised 54.0, missing the forecast 54.3.
- US ADP Employment Change swung higher to 183K, stepping over the previous revised 176K and beating the 150K forecast.
- Canadian labor figures are due on Friday, but market attention will be fully focused on US NFP jobs figures due at the same time.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) managed to eke out thin gains on Wednesday, dragging USD/CAD back down to the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near the 1.4300 handle. Loonie traders remain aware that any gains on the CAD side are coming from generalized weakness in USD flows, but gains are gains and the Loonie has recovered solidly from 21-year lows set earlier this week.
The downside of the CAD’s rebound is USD/CAD is once again back into a congestion range as the pair grinds through a volatile but immovable sideways channel. Momentum is unlikely to meaningful break through the bottom near 1.4000, and the technical ceiling remains in place near 1.4500, albeit with some new holes.
USD/CAD daily chart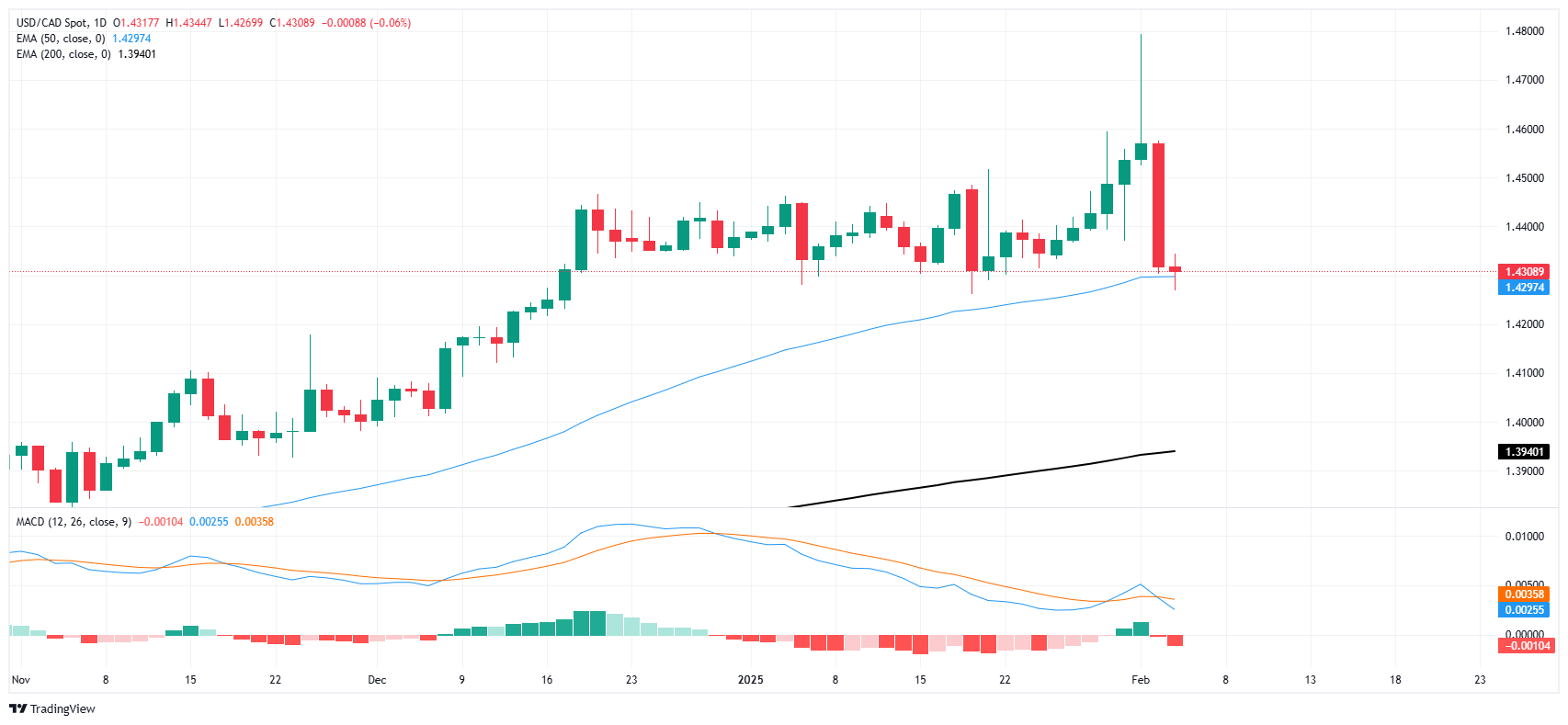
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

