Canadian Dollar slams back into familiar territory as markets recover
- The Canadian Dollar recovered a steep 1.55% on Tuesday.
- US threats of tariffs on Canadian goods have evaporated.
- US NFP and Canadian labor figures loom ahead late in the week.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) surged on Tuesday after market sentiment recovered from a bout of tariff fears, sending the Canadian Dollar just high enough to crash back into familiar consolidation territory after a brief test of two-decade lows.
A stiff 25% tariff on all Canadian goods and a 10% import fee on Canadian energy products was waved off for 30 days by US President Donald Trump on Monday. The US has agreed to temporarily suspend its plans to tax its own citizens for demanding Canadian-made goods, which includes approximately 60% of all US-consumed fuel and roughly 40% of all vehicles purchased. With a third kick of the can on President Trump’s tariffs, investors will likely view any further threats of import tariffs as simply a strongarm measure for Donald Trump to secure concessions from key trade allies with the US, most of which were already agreed to with the previous US administration.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar recovers ground post-tariff rout
- The Canadian Dollar rebounded 1.55%, sending USD/CAD back into consolidation range.
- US trade tariffs on Canada have been waived for 30 days.
- Investors are likely to disregard future tariff threats as pure posturing, limiting their effectiveness in the future.
- Canadian labor figures are due later this week, slated for Friday. The Canadian Unemployment Rate is expected to tick higher to 6.8% from 6.7%, and the Net Change in Employment is expected to ease to 25K from 90.9K in January.
- Canadian labor prints are likely to be entirely overshadows by US Nonfarm Payrolls figures due at the same time. US NFP net job gains are expected to ease to 170K from 256K, and back-dated revisions are also expected.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
The Canadian Dollar’s crash-and-bounce sent USD/CAD briefly to two-decade highs near 1.4800 before correcting sharply back below the 1.4400 handle on Tuesday. Despite firm gains behind the Loonie, Tuesday’s correction was only enough to plant USD/CAD back into its recent consolidation range between 1.4300 and 1.4500.
Price action continues to grind into a familiar pattern, albeit with quick spikes in either direction as the pair muddles along the midrange.
USD/CAD daily chart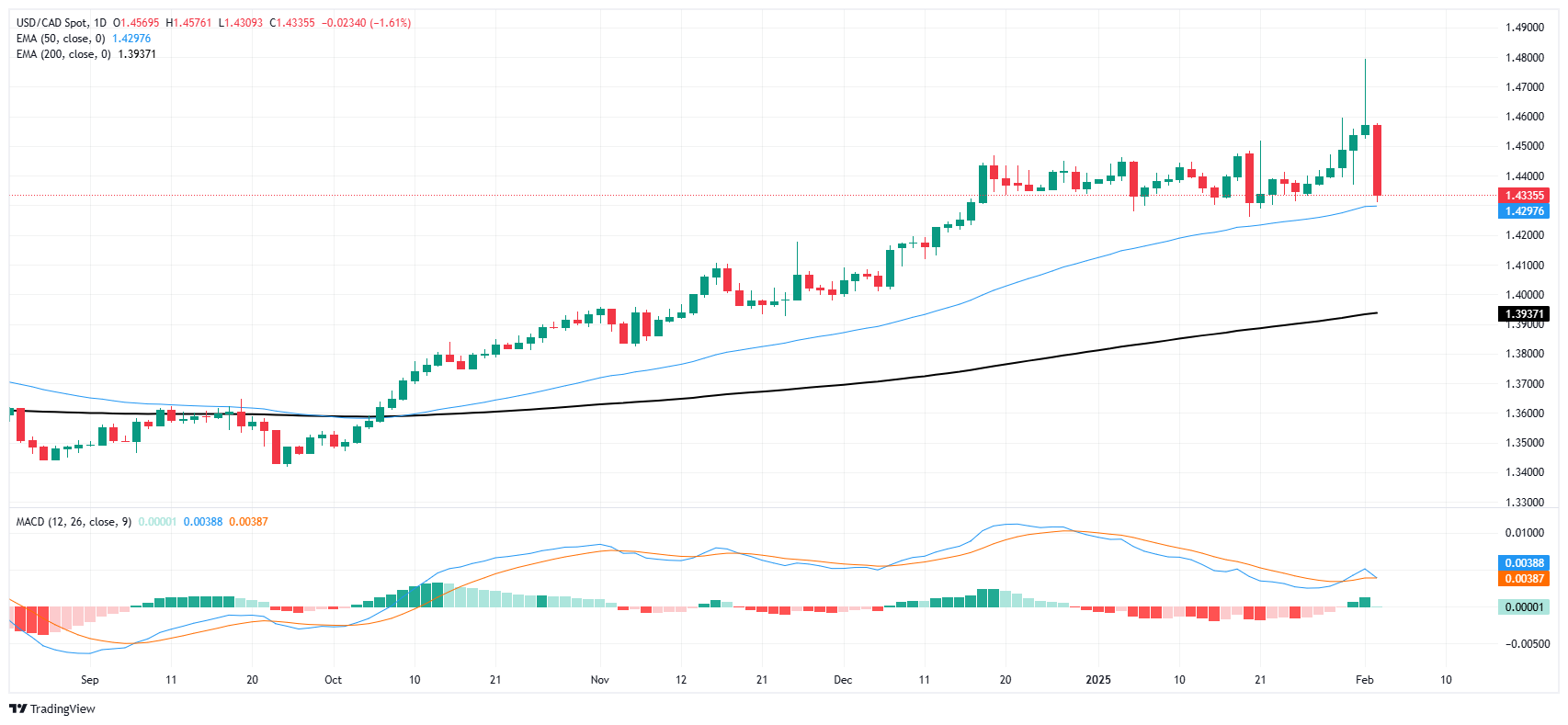
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

