USD/INR softens ahead of US Core PCE release
- The Indian Rupee rebounds in Friday’s Asian session.
- Lower crude oil prices and RBI’s intervention could support the INR, but more cautious stance from the Fed might cap its downside.
- The US Core PCE Price Index report will be the highlight on Friday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) recovers on Friday after depreciating to an all-time low of 85.12 in the previous session. The decline in crude oil prices might help limit the local currency’s losses as India is the world's third-largest oil consumer. Additionally, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) could intervene in the market to prevent excess volatility.
However, a hawkish rate cut from the US Federal Reserve (Fed) could spark the US Dollar (USD) broadly and exert some selling pressure on emerging market currencies, including the INR. Looking ahead, traders will focus on the US Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index data, which is due later on Friday. Also, the US Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index for December will be released.
Indian Rupee rebounds amid multiple challenges
- "We expect the rupee to trade with a negative bias on global equities following a hawkish Fed and a strong dollar. Concerns over a slowdown in the economy may further weigh on the rupee," said Anuj Choudhary Research Analyst at Mirae Asset Sharekhan.
- India's foreign exchange reserves fell in nine out of the past 10 weeks, hitting a multi-month low. The reserves had been falling ever since reserves touched an all-time high of USD 704.89 billion in September, and now last week the forex stood at USD 654.857 billion, according to the RBI data.
- The US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) grew at a 3.1% annualized rate in the third quarter (GDP), compared to a previous projection of 2.8%, the third estimate of the figures from the Bureau of Economic Analysis showed Thursday.
- The US weekly Initial Jobless Claims in the US declined to 220,000 in the week ending December 14, compared to the previous week's print of 242,000, and came in above the market consensus of 230,000.
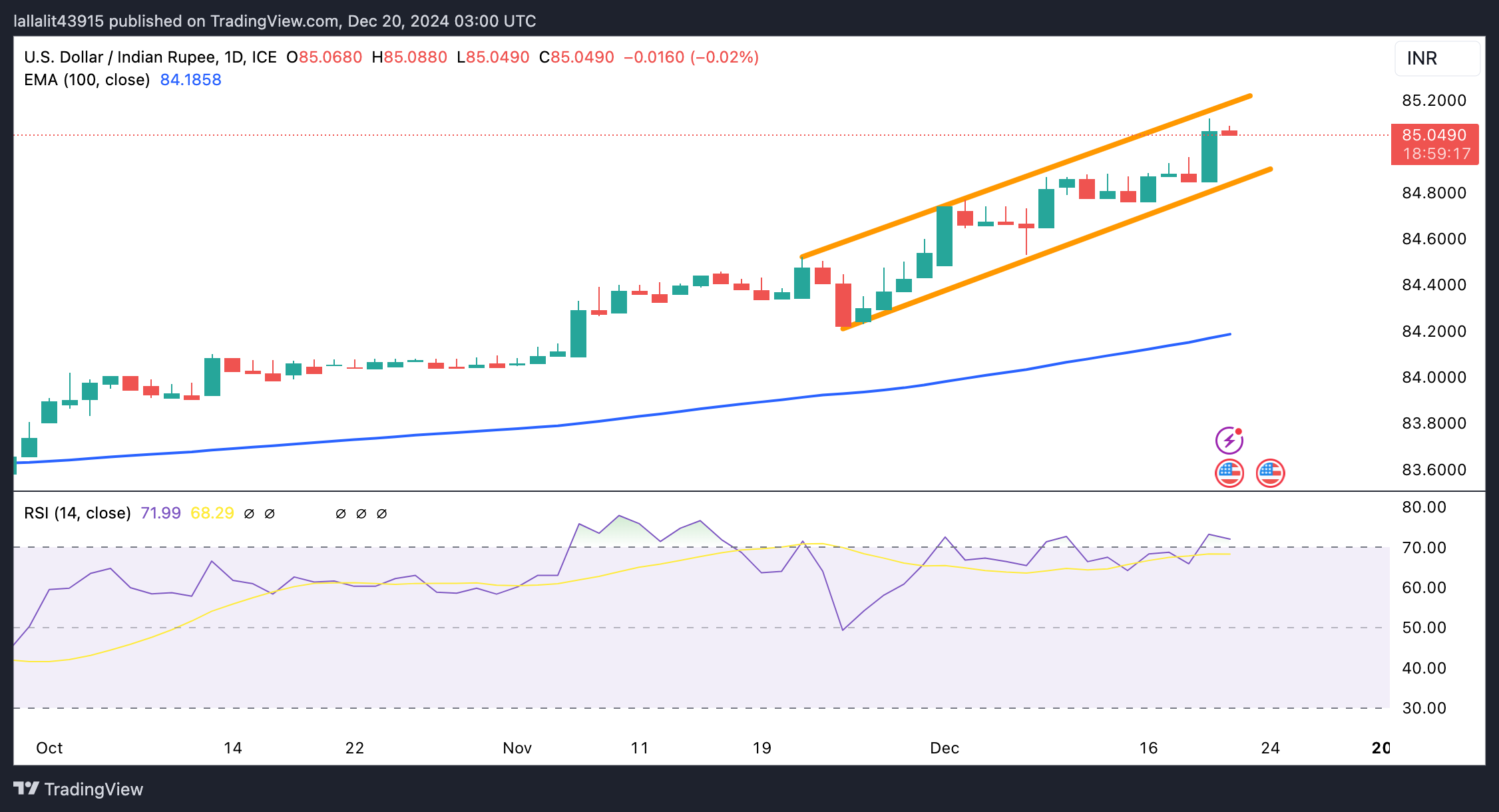
USD/INR maintains a strong uptrend in the longer term
The Indian Rupee trades firmer on the day. The constructive outlook of the USD/INR pair remains intact on the daily chart as the pair holds above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Nonetheless, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is over the midline near 70.95, suggesting an overbought condition. This means that additional consolidation should not be ruled out before positioning for any short-term USD/INR appreciation.
The ascending trend channel at 85.20 acts as an immediate resistance level for USD/INR. A decisive break above this level could see a rally to 85.50.
On the flip side, the first downside target is seen at 84.86, the lower boundary of the trend channel. A breach of this level could pave the way to 84.16, the 100-day EMA.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



