Mexican Peso trims gains with all eyes on US inflation
- The US Dollar is gaining momentum with investors wary of risk ahead of the release of US CPI data for November.
- US inflation is expected to have ticked up above the Fed’s 2% target.
- Technically, the USD/MXN maintains the short-term negative trend intact.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) has been capped again near the 20.00 level and is pulling back on Wednesday. The US Dollar (USD) appreciates across the board buoyed by higher US Treasury yields as traders are growing wary of risk heading into the release of US November’s Consumer Prices Index (CPI) data.
US inflation is expected to have ticked up slightly at levels above the Fed’s 2% target rate. This, coupled with expectations that Donald Trump’s government will implement inflationary policies, is likely to limit the scope of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) easing cycle.
Economic data from Mexico revealed that consumer confidence deteriorated in November to its weakest reading since September. On Monday, November’s CPI cooled beyond expectations, which endorses the view that the Bank of Mexico will cut interest rates again next week.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso hesitates against a stronger US Dollar
- US CPI inflation is expected to have accelerated at a 0.3% pace in November and 2.7% from the same month last year from 0.2% and 2.6%, respectively, in October.
- The US core CPI, more relevant regarding monetary policy expectations, is seen growing steadily at 0.3% on the month and 3.3% year on year.
- Futures markets are now pricing an 85% chance that the Fed will cut interest rates by 25 basis points in December, up from below 70% last week, according to data from the CME Group’s Fed Watch tool.
- Former US Treasury Secretary and Fed Chair, Janet Yellen, warned at a Wall Street Journal's Summit that Donald Trump’s sweeping tariffs could “significantly raise costs to households” and derail progress on inflation.
- Data released on Tuesday revealed that Mexico’s Consumer Confidence dropped 1.5 points in November, to 47.4 points. The report reflected a deterioration in the households’ and the country’s economic expectations in the next 12 months.
- Mexico’s CPI eased at a 4.55% pace in the last twelve months to November, from 4.76% in the previous month. The market was expecting a 4.59% reading.
- Likewise, the core CPI dropped to 3.58% year-on-year from 3.8%, below the market consensus of a 3.6% reading.
- These figures boost hopes that the Bank of Mexico will cut rates by 25 bps for the fourth consecutive time after their December 19 meeting.
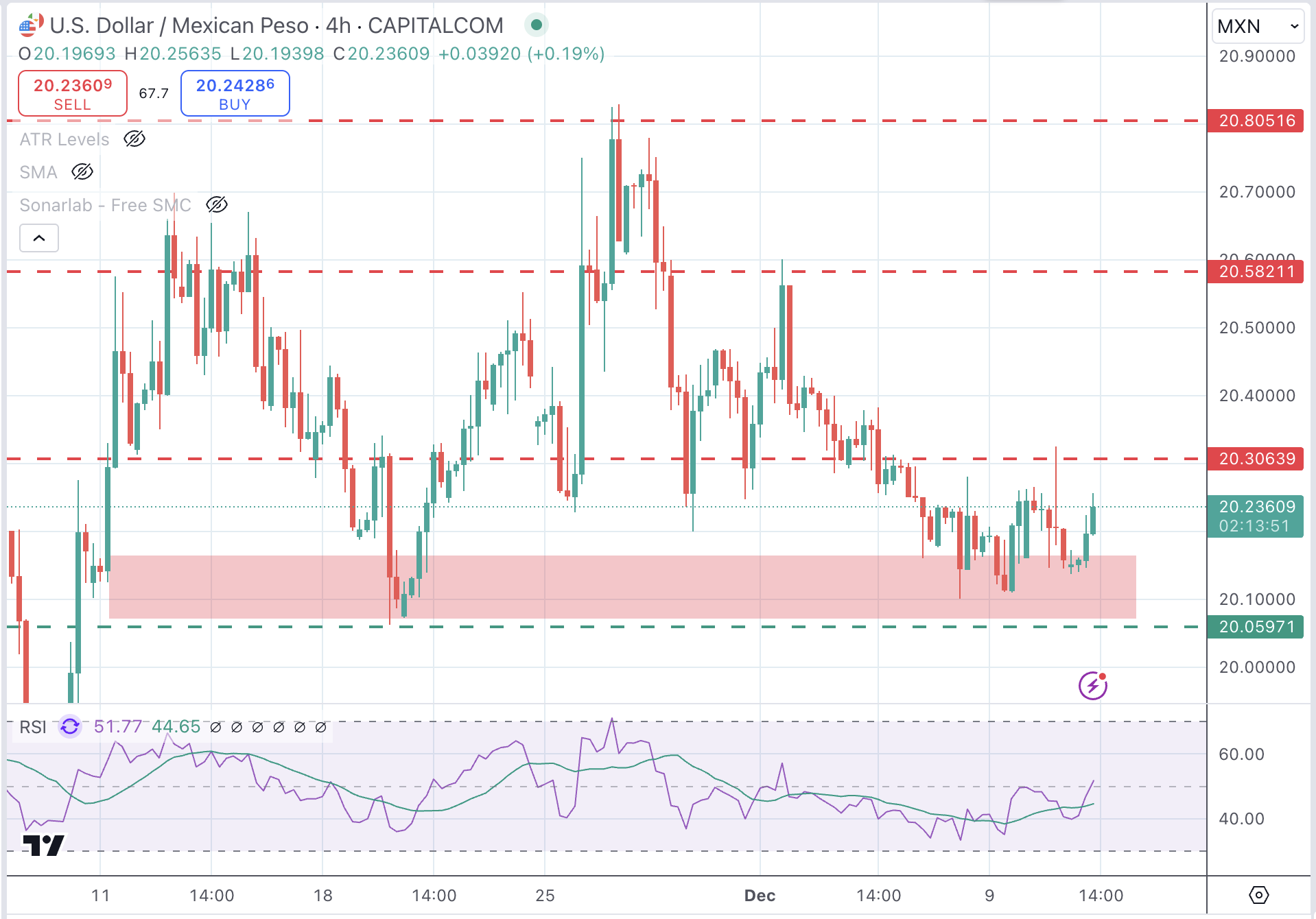
Mexican Peso technical outlook: USD/MXN has strong support at 20.00
The USD/MXN pair remains steady above the 20.00 support area, with upside attempts limited below the December 5 high at the 20.30 area so far.
The technical picture shows the US Dollar is building up heading into the release of the US CPI report. The 4-hour Relative Strength Index (RSI) has popped up above the 50 level, suggesting an incipient bullish momentum. The broader perspective, however, remains bearish with the double top at 20.80 suggesting the possibility of a deeper correction.
Immediate resistance is at the mentioned December 5 high at 20.30, ahead of the December 2 high at 20.60 and November’s peak at 20.80.
On the downside, the 20.00 psychological level is the neckline of the mentioned double top ahead of November’s low at 19.75.
USD/MXN 4-hour Chart
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.


