Gold price slips following 50 bps Fed cut as Powell speaks
- Gold prices fall following a 50 bps Fed rate cut; officials project fed funds rate to reach 4.4% by 2024.
- Fed expresses confidence in nearing 2% inflation target, despite economic uncertainties and balanced mandates.
- US Treasury yields climb to 3.67%; US Dollar Index dips 0.54% to 100.49, hitting new yearly low of 100.24.
Gold prices fluctuated within the $2,565-$2,600 range during the North American session after the Federal Reserve (Fed) cut rates by 50 bps. The Fed also projected that the fed funds rate would end 2024 around 4.4%, according to the median estimate. At the time of writing, XAU/USD had erased its previous gains and is down by over 0.20%.
Fed policymakers decided to lower borrowing costs as they grew confident that inflation is moving “sustainably” toward the bank’s 2% goal. However, they acknowledged that the dual mandate on price stability and maximum employment are roughly balanced while noting that the economic outlook is uncertain.
It is worth noting that there was a dissenter in the vote as Governor Michelle Bowman voted to lower rates by a quarter of a percentage point.
The Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) shows officials estimate interest rates to end at 4.4% in 2024 and 3.4% in 2025. Meantime, inflation as measured by the Core Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCE) is foreseen reaching its target in 2026, though it’s projected to end at 2.6% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
Fed officials project that the economy will grow at a 2% pace in 2024 and the Unemployment Rate to edge up to 4.4% by the end of the year.
In the meantime, Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference is underway. He said that risks to inflation have diminished and reaffirmed that the economy is strong. Powell added that if inflation persists, “we can dial back policy more slowly,” and he added that, according to the SEP, the Committee is not in a rush to normalize policy.
In the meantime, US Treasury yields are rising two-and-a-half basis points at 3.67%, while the Greenback plunges. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s performance against six currencies, tumbles 0.54% to 100.49 after reaching a new yearly low of 100.24.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price drops on volatile session
- December 2024 fed funds rate futures contract suggests that the Fed might lower rates by at least 108 basis points, implying that in the following two meetings, they expect two 25 bps rate cuts left in 2024.
- US Building Permits in August grew by 4.9% MoM from 1.406 million to 1.475 million.
- Housing Starts expanded by 9.6% and rose from 1.237 million to 1.356 million.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price hits $2,600, then retreats amid Powell’s press conference
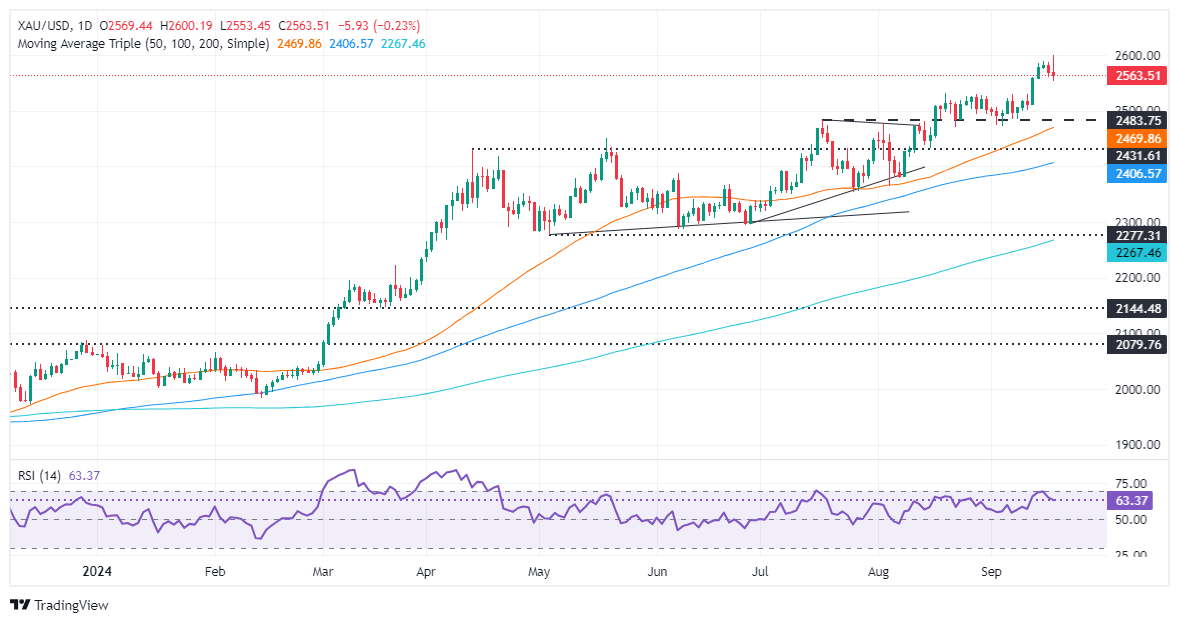
Gold price remains volatile during the North American session, but it remains bullish after hitting a new all-time high of $2,600. However, buyers failed at the latter, which could pave the way for a pullback.
Momentum favors buyers, though short-term sellers are in control, as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) aims lower.
If XAU/USD drops below the September 13 low of $2,556, the next support would be $2,550. Once cleared, the next stop would be the August 20 high, which turned into support at $2,531, before aiming toward the September 6 low of $2,485.
On the upside, if Gold continues to rally, the first resistance would be $2,600. A breach of the latter will expose the psychological levels $2,650 and $2,700.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.




