EUR/USD struggles to extend recovery amid fears of potential Eurozone-US tariff war
- EUR/USD faces pressure while reclaiming 1.1000 as investors await the meeting of Eurozone finance ministers to discuss measures against Trump’s tariffs.
- Trump threatened to impose additional 50% tariffs on China for taking countermeasures against reciprocal levies announced last week.
- The Fed is almost certain to cut interest rates in June.
EUR/USD trades higher in Tuesday’s European trading session but struggles to reclaim the psychological figure of 1.1000. The major currency pair tussles for more upside as the US Dollar Index (DXY) strives to extend its two-day recovery move above Monday’s high of 103.50.
Broadly, the US Dollar (USD) is under pressure in the aftermath of the reciprocal tariff announcement by United States (US) President Donald Trump last week. He swept new levies in addition to a 10% universal baseline on Wednesday in an attempt to fix trade imbalances and ‘make America great again.’
Financial market participants expect that the new suite of Trump tariffs and likely countermeasures by US trading partners could lead to an economic recession. On Monday, Trump threatened to hike import duty on China by 50% if the country doesn’t withdraw its retaliatory response of 34% reciprocal tariffs on US goods already announced last Friday and coming into effect this Thursday.
Earlier in the day, a spokesperson for the Chinese Ministry of Commerce warned that the US president’s new tariff threats were "a mistake on top of a mistake" and China will “fight to the end” to protect its interest.
This has also led to traders raising bets supporting an interest rate reduction by the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the June policy meeting. According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders are confident that the central bank will cut its key borrowing rates in June.
Going forward, investors will focus on the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) data for March, which will be released on Thursday and Friday, respectively.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD gains as the US Dollar faces pressure
- EUR/USD gains at the expense of the US Dollar. Meanwhile, the outlook of the Euro (EUR) has become uncertain as investors become increasingly concerned that countermeasures by the European Union (EU) in the face of reciprocal tariffs by Donald Trump could lead to a trade war between regions situated on the opposite sides of the Atlantic.
- Finance ministers of all Euro area countries are scheduled to meet in Warsaw on Friday to discuss measures to contain the likely consequences of tariffs imposed by the US. Ahead of the meeting, Poland Finance Minister Andrzej Domański said, "Disrupted supply chains and rising costs for companies will affect European growth ratios and currencies." He added that such a scenario will have “adverse social consequences” and “increasing prices for consumers”, leaving citizens more vulnerable, Reuters report.
- On Monday, European Union trade commissioner Maroš Šefčovič also stated that our continent has offered to the US “zero-for-zero tariffs” for “cars and all industrial goods". Investors considered the statement positive for the Euro as a cooperative deal would be prosperous for the Eurozone.
- Additionally, escalating European Central Bank (ECB) dovish bets have also put some pressure on the Euro. Some ECB officials, including Bank of Italy Governor Piero Cipollone, Bank of France Governor François Villeroy de Galhau and Governor of Bank of Greece Yannis Stournaras, have all supported further policy easing. Stournaras said last week that US tariffs will not be an “obstacle to April rate cut” as the inflation path remains “unchanged”. He guided that US tariffs will “negatively impact” the Euro area Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate by “0.3%-0.4%” in the first year.
- During European trading hours, Stournaras said that the monetary policy needs to be less “restrictive in 2025”. However, he warned of the possibility that the inflation rise might “delay the normalisation of monetary policy”.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD tussles around 1.1000
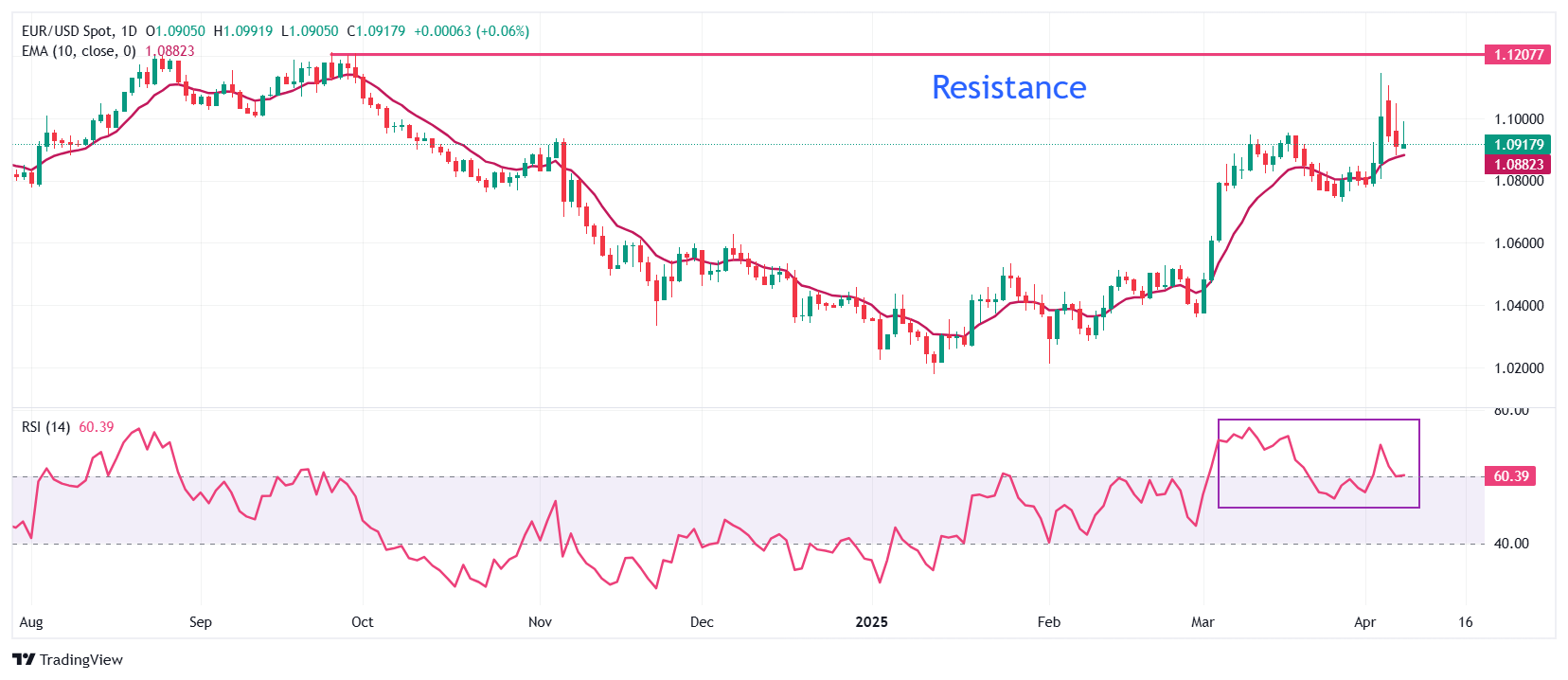
EUR/USD struggles to break above 1.1000 during European trading hours on Tuesday. The major currency pair rebounded from the 10-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on Monday, which trades around 1.0883.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) holds the 60.00 level, suggesting that the bullish momentum is intact.
Looking down, the March 31 high of 1.0850 will act as the major support zone for the pair. Conversely, the September 25 high of 1.1214 will be the key barrier for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

