US Dollar stronger on Fed keeping its projections for 2025
- The US Dollar trades stronger against most major peers on Thursday.
- Traders see the Fed sticking to its projected cutting cycle for 2025.
- The US Dollar Index is still stuck between 103.00 and 104.00 for now.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar (USD) against six major currencies, rallies towards 104.00 on Thursday after the Federal Reserve (Fed) kept borrowing costs unchanged and projected two interest rate cuts for 2025. During Wednesday’s Fed meeting, Chairman Jerome Powell said that any tariff-driven bump in inflation will be “transitory.” However, he added later that it will be very challenging to say with confidence how much inflation stems from tariffs versus other factors. He also said recession odds have moved up, though are not high, Bloomberg reports.
On the economic data front, the US jobless claims and the Philadelphia manufacturing data will be key. After Powell highlighted that the US economy might start to ease, traders will look for proof of that. Any data that comes in far below the benchmark could trigger some US Dollar weakness.
Daily digest market movers: Back to data-driven to determine interest rate cuts
- At 12:30 GMT, the most important data for this Thursday will be released:
- US Initial Jobless Claims are expected to tick up to 224,000, coming from 220,000. The US Continuing Jobless Claims are expected to come in at 1,890 million against 1,870 million last week.
- The Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Survey for March is expected to fall to 8.5 from the previous 18.1.
- At 14:00 GMT, US Existing Home Sales month-on-month for February will be released. Expectations are for a contraction to 3.95 million compared to 4.08 million the previous month.
- Equities are struggling with European indices facing big profit-taking. The German Dax is down over 1%, while US futures are flat to marginally positive.
- According to the CME Fedwatch Tool, the probability of interest rates remaining at the current range of 4.25%-4.50% in May’s meeting is at 80.5%. For June, the odds for borrowing costs being lower stand at 71.1%.
- The US 10-year yield trades around 4.22%, heading back to its five-month low of 4.10% printed on March 4.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Contradictions and correlations
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is trying to break out of a short-term technical descending triangle pattern. The tilted side of a triangle should act as strong resistance while the flat base of the triangle at 103.18 should act as strong support. Normally, the textbook logic is that sellers will build up positions alongside the tilted descending trend line in order to break through that flat base, which will result in more downturn.
The fact that currently the DXY is trying to break out of that pattern could be a sign for a turnaround, though heavy resistance is awaiting just around the corner at 104.00.
If bulls can avoid a technical rejection at 104.00, a large sprint higher towards the 105.00 round level could happen, with the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) converging at that point and reinforcing this area as a strong resistance. Once broken through that zone, a string of pivotal levels, such as 105.53 and 105.89, could limit the upward momentum.
On the downside, the 103.00 round level could be considered a bearish target in case US yields roll off on deteriorating US data, with even 101.90 on the table if markets further capitulate on their long-term US Dollar holdings.
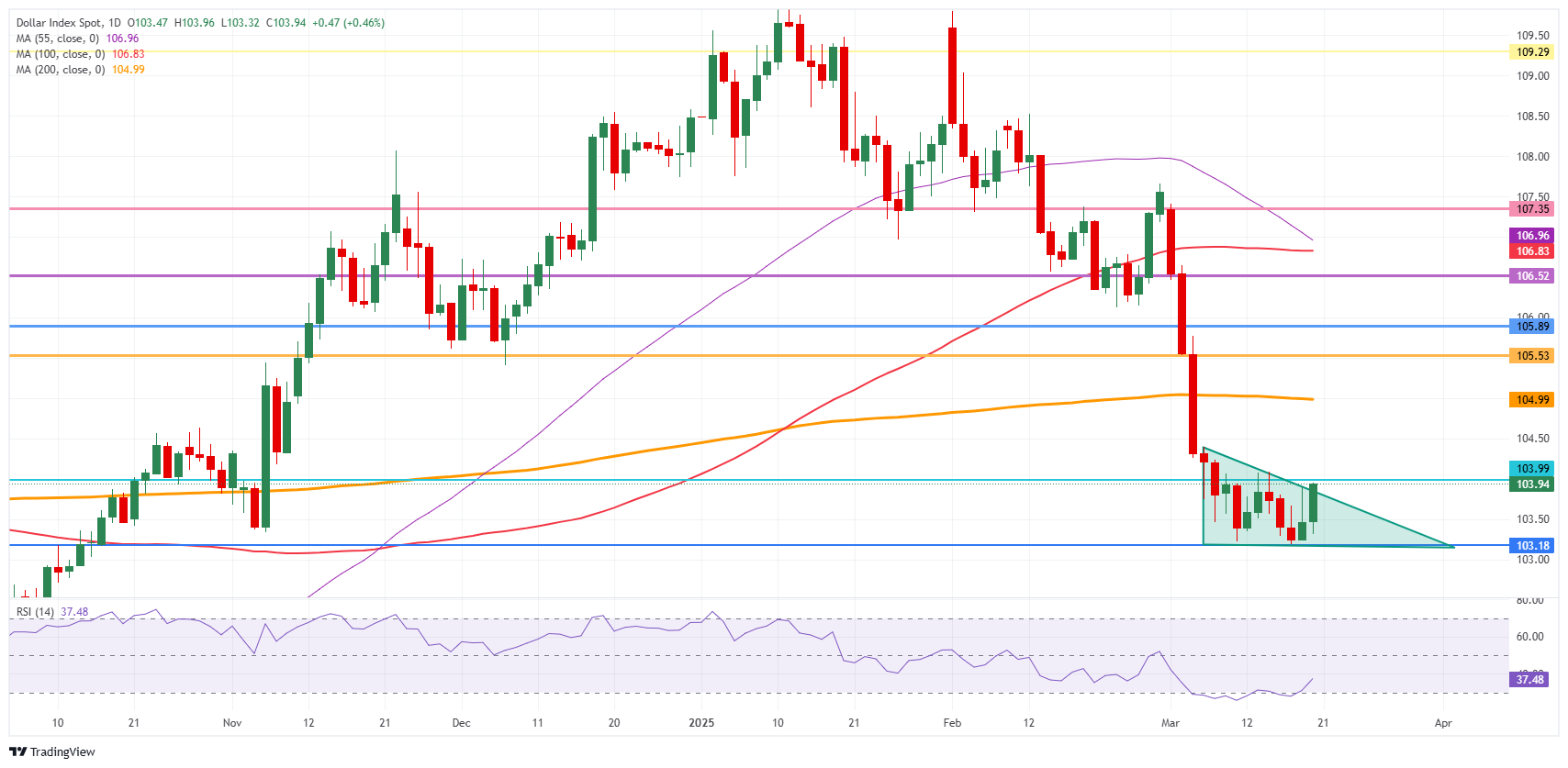
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.

