Dow Jones Industrial Average churns to kick off new year
- The Dow Jones cycled near familiar levels on the first trading day of 2025.
- Tepid intraday flows crimp hopes for a ‘Santa Clause rally’.
- Initial Jobless Claims improved, but not enough to spark a firm risk-on bid.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fizzled on Thursday, kicking off the 2025 trading year with a flat performance and churning chart paper near 42,500. Equities were middling overall during the US market session, with early gains reversing through the day.
The first week of 2025 remains thin on the economic calendar overall, though US ISM Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) survey results are due on Friday. US Initial Jobless Claims rose 211K through the week ended December 27, below the forecast uptick to 222K from the previous week’s revised print of 220K.
Dow Jones news
Roughly a third of the Dow Jones’ constituent stocks are in the green on Thursday, with Nvidia (NVDA) rebounding 1.8% after a near-term dip and rising toward $137 per share. Despite the upswing in 2024’s tech rally darling, concentrated losses in other market favorites including Boeing (BA) and Apple (AAPL) are keeping the DJIA hobbled for the new year, with both companies falling 3.5% and 3%, respectively.
Dow Jones price forecast
The Dow’s mixed performance on Thursday has chalked a wide range into the intraday chart with the major equity index starting the day with a 300-point gain before reversing course and backsliding to a -300 loss. The DJIA peaked just north of 42,800 before falling back below 42,250.
Bearish flows from the tail-end of 2024 are continuing into the new year, keeping the Dow capped below the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) which is rolling over into a bearish stance below 43,270. If bearish momentum accelerates, it’ll put the DJIA on pace for a fresh challenge of the 200-day EMA near 42,120.
Dow Jones daily chart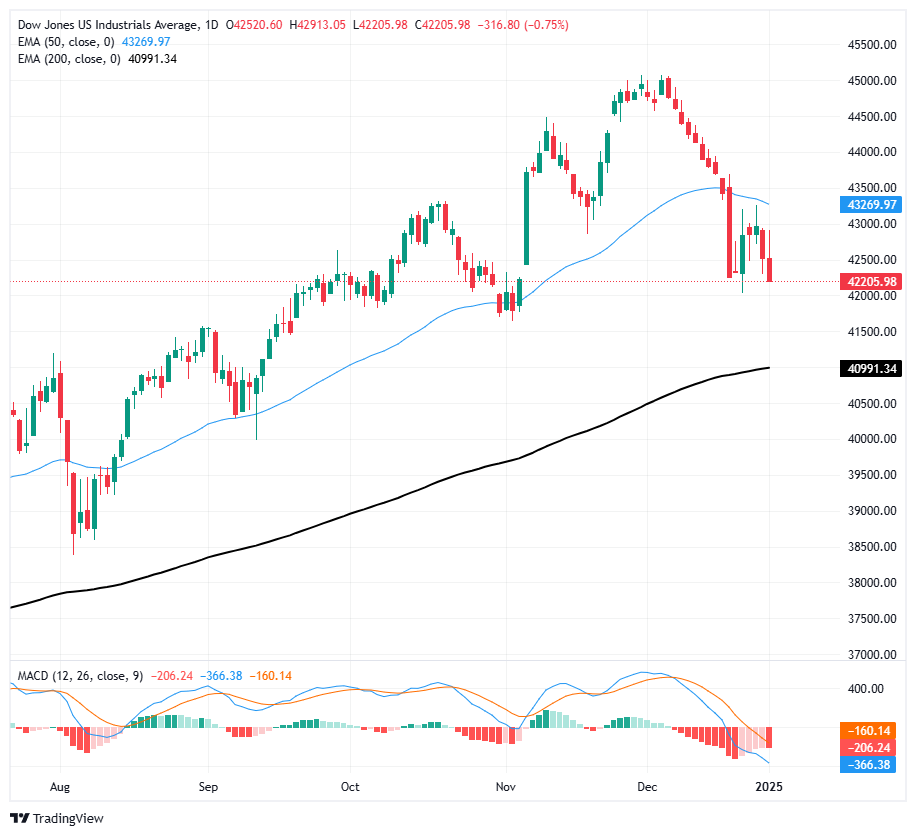
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.

