ADP report expected to show US private employment rose by 120,000 in September
- The ADP Employment Change report is expected to show a modest improvement in the number of private jobs created in September.
- The United States will publish the Nonfarm Payrolls report on Friday.
- The US Dollar consolidates post-Fed losses and is at risk of falling further.
The Automatic Data Processing (ADP) Research Institute will release its monthly report on private-sector job creation for September on Wednesday. The so-called ADP Employment Change report is expected to show that the United States (US) added 120,000 new positions in September after creating 99,000 jobs in August.
The data is usually released two days ahead of the official Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report for the same month and is usually seen as an advanced indicator of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) jobs report, despite a doubtful correlation between both indicators.
ADP Jobs Report: Employment and the Federal Reserve
US employment data has been in the eye of the storm for over a year amid its impact on the latest Federal Reserve (Fed) monetary policy decisions. The Fed’s dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability has been under siege in the pandemic aftermath, and the central bank opted to tighten monetary policy to put things back in balance.
The main issue was inflation, as price pressures skyrocketed throughout 2022. The Fed pushed rates to record highs and maintained them there amid the risks of a tight labor market further fuelling price pressures. Nevertheless, indicators have come into a better balance in the last few months, and the Fed finally decided to trim interest rates. US policymakers cut the benchmark rate by 50 basis points (bps) when they met in September while anticipating additional cuts on the way.
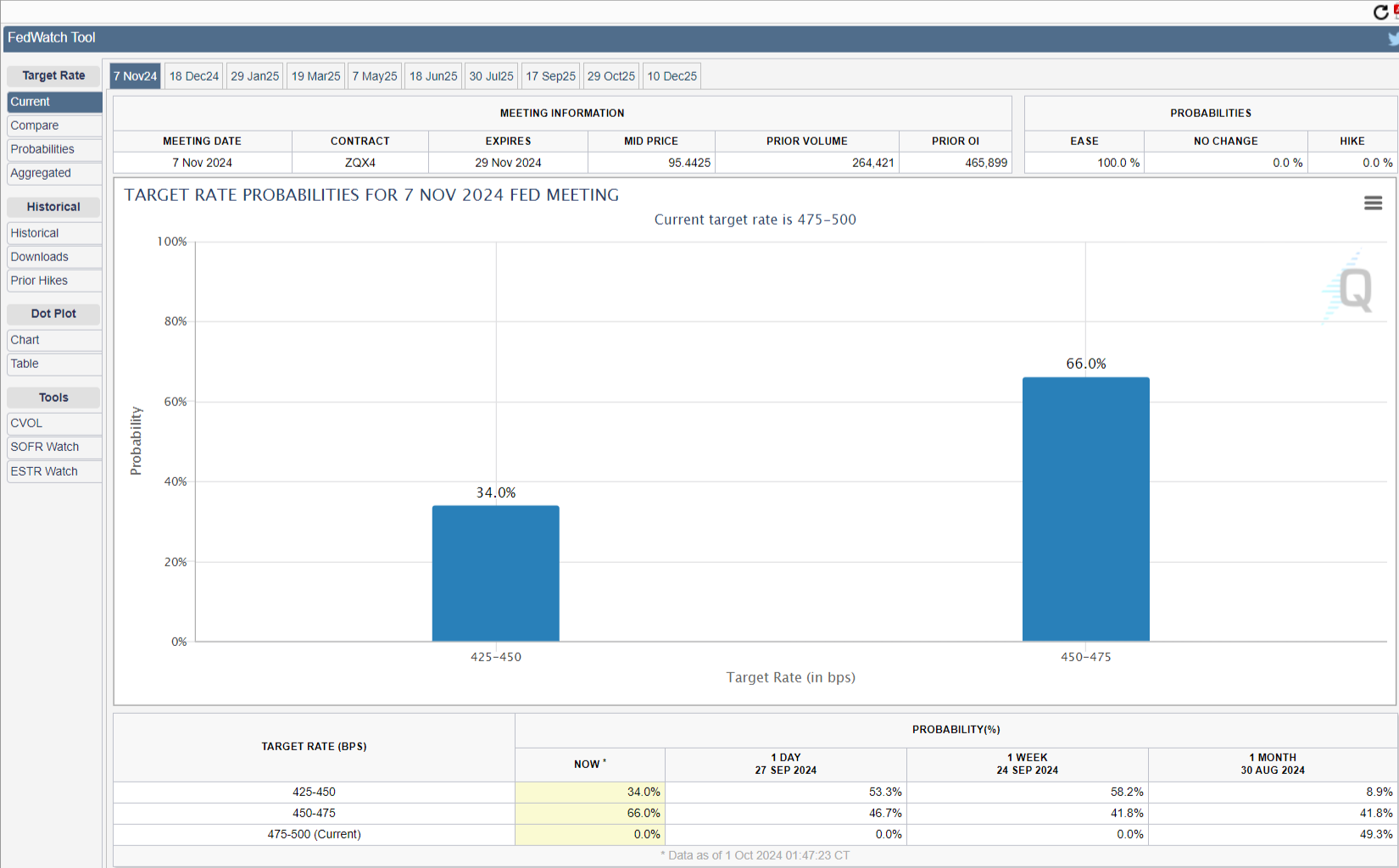
That said, market participants are now wondering whether the central bank will deliver a mode discretionary 25 bps cut when it meets in November or proceed again with a 50 bps trim. Ahead of data releases, the odds for a 25 bps stand at 66%, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
In the meantime, Fed officials have shifted their focus from inflation to employment. With price pressures receding, maintaining a “healthy” labor market is now their main goal.
With that in mind, a stronger-than-anticipated ADP report will likely weigh down the odds for another aggressive interest rate cut in November, giving near-term support to the US Dollar. On the contrary, a disappointing reading may force speculative interest to increase bets for another 50 bps interest rate cut, resulting in a weaker USD. Finally, it is worth remembering the report could have a short-lived impact, as market players will most likely wait until the NFP release scheduled for Friday.
When will the ADP Report be released, and how could it affect the USD Index?
ADP will release the US Employment Change report on Wednesday and it is expected to show that the private sector added 120,000 new positions in September.
Ahead of the release, the US Dollar Index (DXY) consolidates below the 101.00 mark after posting a fresh 2024 low of 100.16 by the end of September.
From a technical perspective, Valeria Bednarik, Chief Analyst at FXStreet, says: “The DXY has remained under pressure since the Fed’s monetary policy announcement mid-September, and technical readings in the daily chart suggest its bullish potential remains well-limited. A bearish 20 Simple Moving Average (SMA) provides near-term resistance around the aforementioned threshold, while a bearish 100 SMA gains downward momentum well above the shorter one, and after crossing below a flat 200 SMA.”
Bednarik adds: “Technical indicators, in the meantime, remain within negative levels, lacking directional momentum. Overall, the risk skews to the downside. Resistance beyond the 101.00 threshold comes at 101.47, followed by the daily low at 102.17 posted on August 5. Supports, on the other hand, can be found at 100.41 and the year-to-date low of 100.16. A break below the latter could anticipate a steeper decline towards the 99.00 figure.”
Economic Indicator
ADP Employment Change
The ADP Employment Change is a gauge of employment in the private sector released by the largest payroll processor in the US, Automatic Data Processing Inc. It measures the change in the number of people privately employed in the US. Generally speaking, a rise in the indicator has positive implications for consumer spending and is stimulative of economic growth. So a high reading is traditionally seen as bullish for the US Dollar (USD), while a low reading is seen as bearish.
Read more.Next release: Wed Oct 02, 2024 12:15
Frequency: Monthly
Consensus: 120K
Previous: 99K
Source: ADP Research Institute
Traders often consider employment figures from ADP, America’s largest payrolls provider, report as the harbinger of the Bureau of Labor Statistics release on Nonfarm Payrolls (usually published two days later), because of the correlation between the two. The overlaying of both series is quite high, but on individual months, the discrepancy can be substantial. Another reason FX traders follow this report is the same as with the NFP – a persistent vigorous growth in employment figures increases inflationary pressures, and with it, the likelihood that the Fed will raise interest rates. Actual figures beating consensus tend to be USD bullish.
Employment FAQs
Labor market conditions are a key element in assessing the health of an economy and thus a key driver for currency valuation. High employment, or low unemployment, has positive implications for consumer spending and economic growth, boosting the value of the local currency. Moreover, a very tight labor market – a situation in which there is a shortage of workers to fill open positions – can also have implications on inflation levels because low labor supply and high demand leads to higher wages.
The pace at which salaries are growing in an economy is key for policymakers. High wage growth means that households have more money to spend, usually leading to price increases in consumer goods. In contrast to more volatile sources of inflation such as energy prices, wage growth is seen as a key component of underlying and persisting inflation as salary increases are unlikely to be undone. Central banks around the world pay close attention to wage growth data when deciding on monetary policy.
The weight that each central bank assigns to labor market conditions depends on its objectives. Some central banks explicitly have mandates related to the labor market beyond controlling inflation levels. The US Federal Reserve (Fed), for example, has the dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank’s (ECB) sole mandate is to keep inflation under control. Still, and despite whatever mandates they have, labor market conditions are an important factor for policymakers given their significance as a gauge of the health of the economy and their direct relationship to inflation.

