Gold price recovers part of Monday’s slide amid trade war fears, sustained USD selling
- Gold price rebounds from a one-week low and draws support from a combination of factors.
- Global trade war fears and geopolitical risks continue to underpin the safe-haven commodity.
- Fed rate cut bets keep the USD depressed and further benefit the non-yielding XAU/USD pair.
Gold price (XAU/USD) attracts some dip-buyers near the $2,880 region during the Asian session on Tuesday and reverses a part of the previous day's downfall to a one-week low. The uncertainty surrounding US President Donald Trump's trade policies and their impact on the global economy continues to weigh on investors' sentiment. This is evident from the prevalent risk-off mood, which, along with geopolitical risks, drives flows toward the safe-haven bullion.
Meanwhile, expectations that a tariff-driven slowdown in US growth might force the Federal Reserve (Fed) to cut interest rates multiple times this year keep the US Dollar (USD) depressed near its lowest level since November. This, in turn, is seen as another factor underpinning the non-yielding Gold price. However, the recent range-bound price action witnessed over the past week or so warrants caution for bulls ahead of the US inflation figures this week.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price continues to be underpinned by rising trade tensions and bearish USD
- Investors continue to take refuge in traditional safe-haven assets amid concerns about US President Donald Trump's trade tariffs, assisting the Gold price to rebound from a one-week trough touched on Monday. In fact, Trump's 25% tariffs on global steel and aluminum imports go into effect on Wednesday. Furthermore, the Trump administration is preparing for other levies planned for April 2.
- Markets remain worried about a potential US recession on the back of Trump's protectionist policies. Adding to this, signs of a weakening US labor market fuel speculations that the Federal Reserve would resume its rate-cutting cycle in June. This keeps the US Treasury bond yields depressed and the US Dollar close to a multi-month low, further lending support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy's meeting with Trump at the Oval Office on February 28 ended in disaster, leading to the US suspending all military aid to Ukraine. Hence, investors brace for more geopolitical action at a meeting between US officials and their Ukrainian counterparts starting today. This, in turn, could play a key role in influencing the XAU/USD pair's price action.
- Later during the North American session, traders will take cues from the release of the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) from the US. The focus, however, will remain on the US inflation figures – the Consumer Price Index (CPI) on Wednesday and the Producer Price Index (PPI) on Thursday. This will drive the USD and determine the near-term trajectory for the precious metal.
Gold price bears need to wait for some follow-through selling below the $2,880 support before placing fresh bets
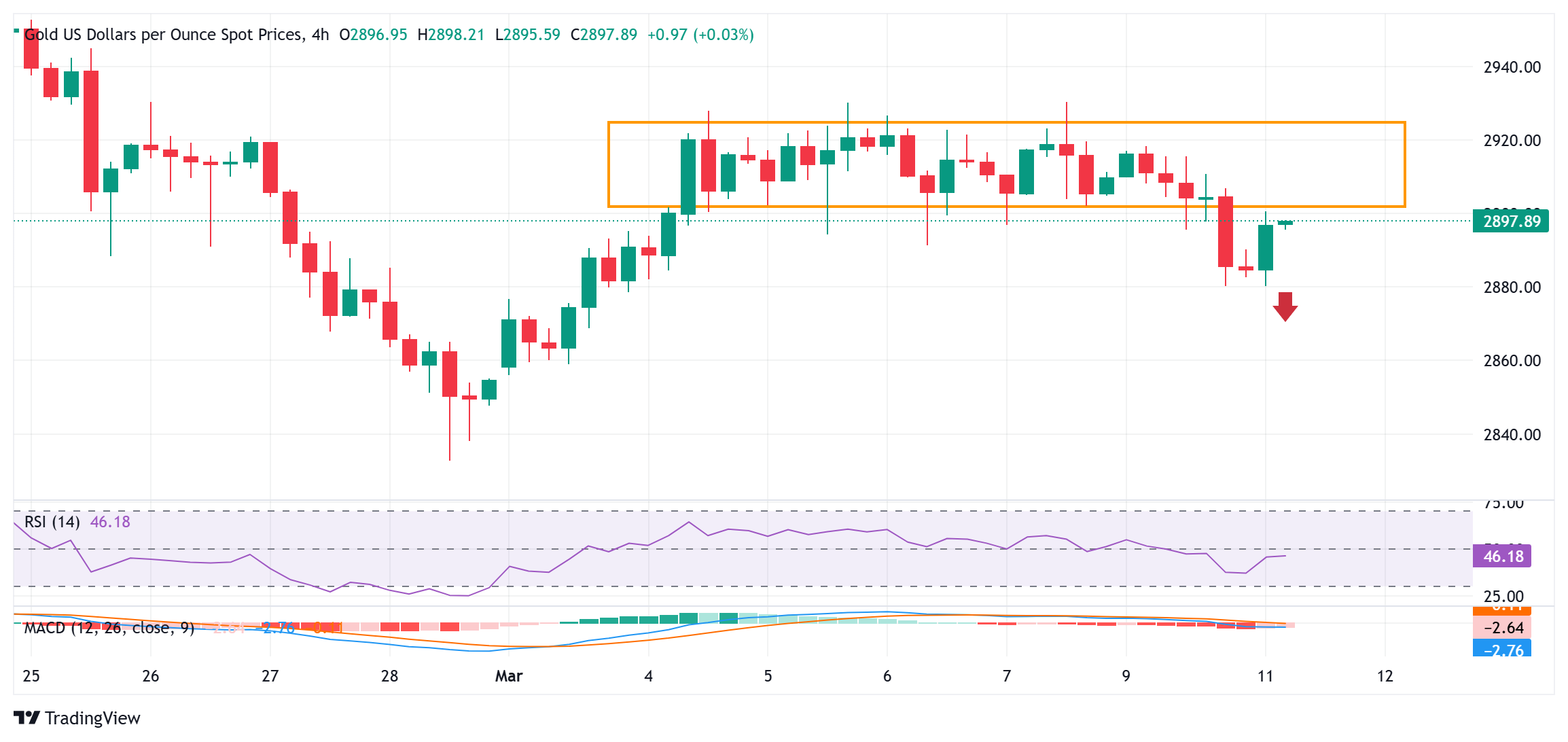
From a technical perspective, the overnight breakdown and close below the $2,900 round figure, or the lower end of a short-term trading range, could be seen as a key trigger for bearish traders. That said, mixed oscillators on the daily chart make it prudent to wait for some follow-through selling below the $2,880 region, or the one-week low, before positioning for further losses. The subsequent downfall could drag the Gold price to the $2,860 intermediate support en route to the late February swing low, around the $2,833-2,832 region, and the $2,800 mark.
On the flip side, any further move up beyond the $2,900 round figure is likely to face some resistance near the $2,922-2,924 area. A sustained strength beyond the said barrier could lift the Gold price beyond the $2,934 resistance, towards retesting the record high, around the $2,956 region touched on February 24.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

