Gold price trades with modest losses; holds above $2,900 amid rising trade tensions
- Gold price drifts lower as an uptick in US bond yields allows the USD to move away from a multi-month low.
- The uncertainty over Trump’s tariff plans and trade war fears should act as tailwinds for the XAU/USD pair.
- Bets that the Fed will cut interest rates further this year might contribute to limiting losses for the yellow metal.
Gold price (XAU/USD) attracts fresh sellers during the Asian session on Thursday, though it manages to hold above the $2,900 round-figure mark. A pickup in the US Treasury bond yields assists the US Dollar (USD) in moving away from its lowest level since December 10 retested on Wednesday and undermines the precious metal. Apart from this, a generally positive tone around the equity markets turns out to be another factor weighing on the safe-haven bullion.
That said, the uncertainty over US President Donald Trump's tariff plans might continue to act as a tailwind for the Gold price. Moreover, signs of a cooling US economy and growth concerns should contribute to limiting losses for the commodity. Traders also seem reluctant and keenly await the release of the US Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index on Friday for cues about the Federal Reserve's interest rate path, which would influence the XAU/USD.
Gold price is pressured by an uptick in US bond yields and modest USD strength
- The US Dollar builds on the overnight bounce from the 11-week low amid a modest bounce in the US Treasury bond yields and exerts some downward pressure on the Gold price during the Asian session on Thursday.
- US President Donald Trump fueled hopes for another pause on steep new tariffs on imports from Mexico and Canada and said on Wednesday that they could take effect on April 2, vs. the previous deadline on March 4.
- A White House official, however, said that the deadline for tariffs on Mexican and Canadian goods remained in effect "as of this moment," pending Trump's review of actions to halt the flow of migrants into the US.
- Furthermore, Trump said that his administration will soon announce a 25% tariff on imports from the European Union, which continues to fuel uncertainty and should act as a tailwind for the safe-haven precious metal.
- Bets for more interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve this year are on the rise in the wake of the recent downbeat US macro data, which pointed to signs of a cooling economy and fueled concerns about the growth outlook.
- Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic noted on Wednesday that the US central bank should hold rates where they are, at a level that continues to put downward pressure on inflation, which has shown a lot of progress but is still high.
- Hence, the focus will remain glued to the release of the US Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index – the Fed's preferred inflation measure – due on Friday for further cues about the central bank's rate-cut path.
- In the meantime, Thursday's US economic docket – featuring the release of the Prelim Q4 GDP print, Durable Goods Orders, Pending Home Sales, and Weekly Initial Jobless Claims – might provide short-term impetuses.
- Apart from this, speeches by influential FOMC members could offer more insights on policy easing this year, which will drive the USD demand and contribute to producing trading opportunities around the XAU/USD pair.
Gold price might continue to attract dip-buyers; $2,860 holds the key for bulls
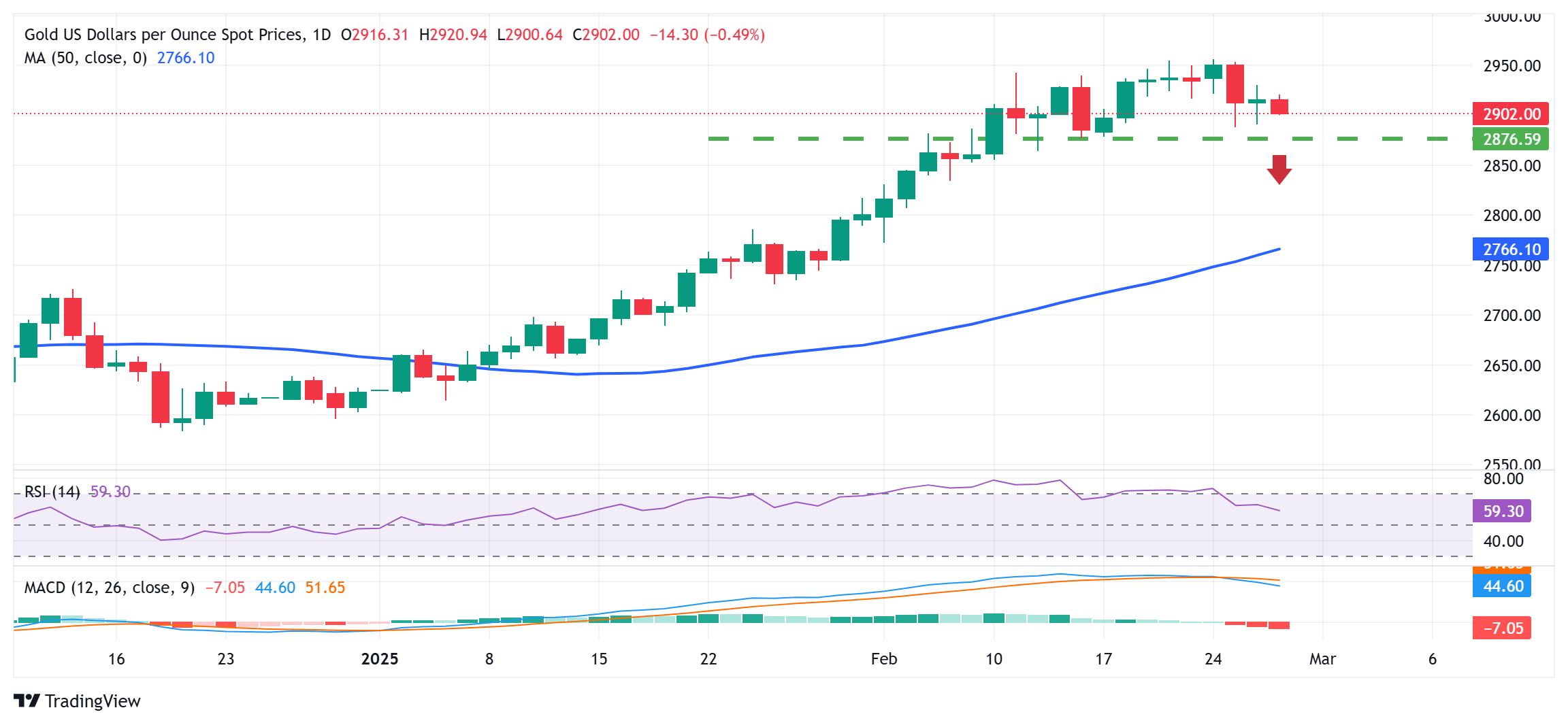
From a technical perspective, the $2,888 area, or over a one-week low touched on Tuesday is likely to act as immediate support ahead of the $2,878 zone and the $2,860-2,855 region. Failure to defend the said support levels could make the Gold price vulnerable to accelerate the corrective decline further towards the $2,834 region en route to the $2,800 round-figure mark.
On the flip side, any positive move beyond the $2,920 immediate hurdle could attract some sellers near the overnight swing high, around the $2,930 region. A sustained strength beyond the latter has the potential to lift the Gold price further toward the $2,950-2,955 horizontal resistance, or the record high touched on the first day of the current week.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.

