Gold already at 11% return for 2025 with more tariffs coming, Fed Powell’s testimony eyed
- Gold hits another fresh all-time high at $2,942 and surges over 11% for 2025.
- Markets got caught by surprise this Monday with countermeasures from China to US President Donald Trump’s tariffs.
- The $3,000 is gaining quickly, though tail risks could grow from here.
Gold’s price (XAU/USD) has set another record high at $2,942 in early Tuesday trading before paring back nearly all the incurred gains for the day. Meanwhile, United States (US) President Donald Trump has imposed 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum imports for all countries as of March 12,, while China has quietly imposed retaliatory tariffs on some US goods. China is only showing its teeth by now and has not gone full blazing, while US President Trump is nowhere near his promised 60% levies on all Chinese products as announced earlier in his campaign, Bloomberg reports.
Meanwhile, traders will focus on Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell’s semiannual testimony to lawmakers on Tuesday and Wednesday for fresh clues about the path the US monetary policy will take. Powell is likely to highlight the resilient economy as a key reason central bankers are in no rush to cut borrowing costs further. This is a big risk for Gold this Tuesday, as it could be a bearish element for bullion.
Daily digest market movers: Tariff safe haven
- At 15:00 GMT, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell testifies before the US Senate Banking Committee
- US President Donald Trump said on Monday that the latest round of levies, which go into effect in March, would bolster domestic production and bring more jobs to the US. He also warned the tariffs “may go higher”, Bloomberg reports.
- The CME FedWatch tool shows a 93.5% chance that interest rates will remain unchanged in March, compared to a slim 6.5% chance of a 25 basis point (bps) interest rate cut.
Technical Analysis: Resistance levels to watch
A whopping 11% of gains so far this year is making bullion already the favorite trade for the first quarter. Tail risks are set to kick in though, with Fed Chairman Powell to speak later this Tuesday at Capitol Hill. If his speech is hawkish, yields are expected to surge, which could spark some sizable profit-taking in the Gold rally.
The Pivot Point level on Tuesday is the first nearby support at $2,891, followed by the S1 support at $2,871. From there, S2 support should come in at $2,835. In case of a correction, the bigger $2,790 level (October 31, 2024, high) should be able to catch any falling knives.
On the upside, the R1 resistance comes in at $2,928, which was already tested earlier this Tuesday. In case the rally recovers again in the European and US sessions, the $2,950 level, which is the confluence of a big figure and the R2 resistance, will be tested for a break to the upside. Further up, the $3,000 psychological level could be next.
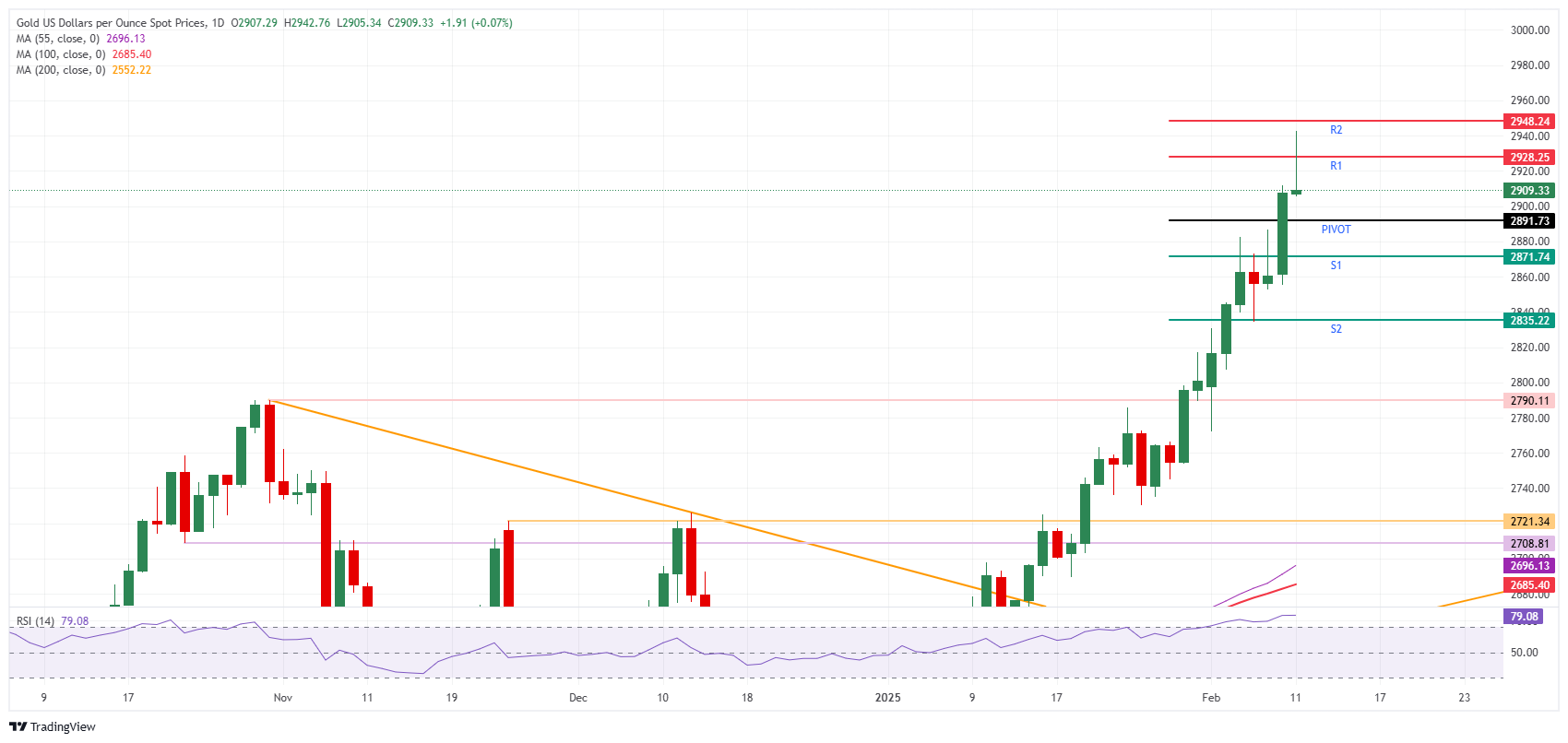
XAU/USD: Daily Chart
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.

