Gold price advances amid safe-haven demand ahead of US NFP
- Gold price rises 0.35% as investors seek safety amid potential US tariffs and soaring UK Gilt yields.
- Fed officials deliver mixed signals on the rate path during a quiet trading session.
- Market focus shifts to upcoming US Nonfarm Payrolls and UoM Consumer Sentiment for further economic cues.
Gold's price surged for the third straight day and edged up 0.35% due to safe-haven demand spurred by concerns over Donald Trump’s proposed policies, while the United Kingdom (UK) dealt with a budget crisis. The XAU/USD trades at $2,671 at the time of writing.
On Wednesday, CNN revealed that United States (US) President-elect Donald Trump might consider declaring a national economic emergency, which would provide him with a legal justification to impose tariffs on adversaries and US allies. Earlier during Thursday’s overnight session, UK Gilt yields at the long end of the curve skyrocketed above 5%, their highest level since 1998.
In the meantime, Federal Reserve (Fed) officials are grabbing the headlines as US financial markets remained closed for former US President Jimmy Carter’s National Day of Mourning.
Fed Governor Michelle Bowman maintained a hawkish stance, saying the central bank should be cautious in adjusting interest rates, while Kansas City Fed Jeffrey Schmid added that rates are “near” neutral.
Earlier, Philadelphia Fed Patrick Harker revealed that the US central bank could pause amid uncertainty, while Boston Fed Susan Collins said the current outlook suggests a gradual approach to rate cuts.
This week, traders are eyeing the release of December US Nonfarm Payrolls data and the University of Michigan (UoM) Consumer Sentiment.
Daily digest market movers: Gold and the US Dollar surge modestly
- Gold price shrugs off higher US real yields, which rose by two bps to 2.29%. At the same time, the US 10-year T-note yield remains unchanged at 4.691%
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against a basket of six currencies, rises 0.16% to 109.18.
- Further labor market data was announced. The US Challenger Jobs report for December showed a significant decline in layoffs, with employers cutting 38,792 jobs compared to November's 57,727.
- Easing expectations of the Federal Reserve continued to edge lower. The December Fed funds futures contract is pricing in 54 basis points of easing.
- The FOMC's December meeting minutes hinted that the central bank is near a point at which it would be appropriate to slow the pace of easing. Participants indicated that if data comes as expected, “it would be appropriate to continue easing.”
- On Wednesday, the World Gold Council said physically backed Gold exchange-traded funds registered their first inflow in four years.
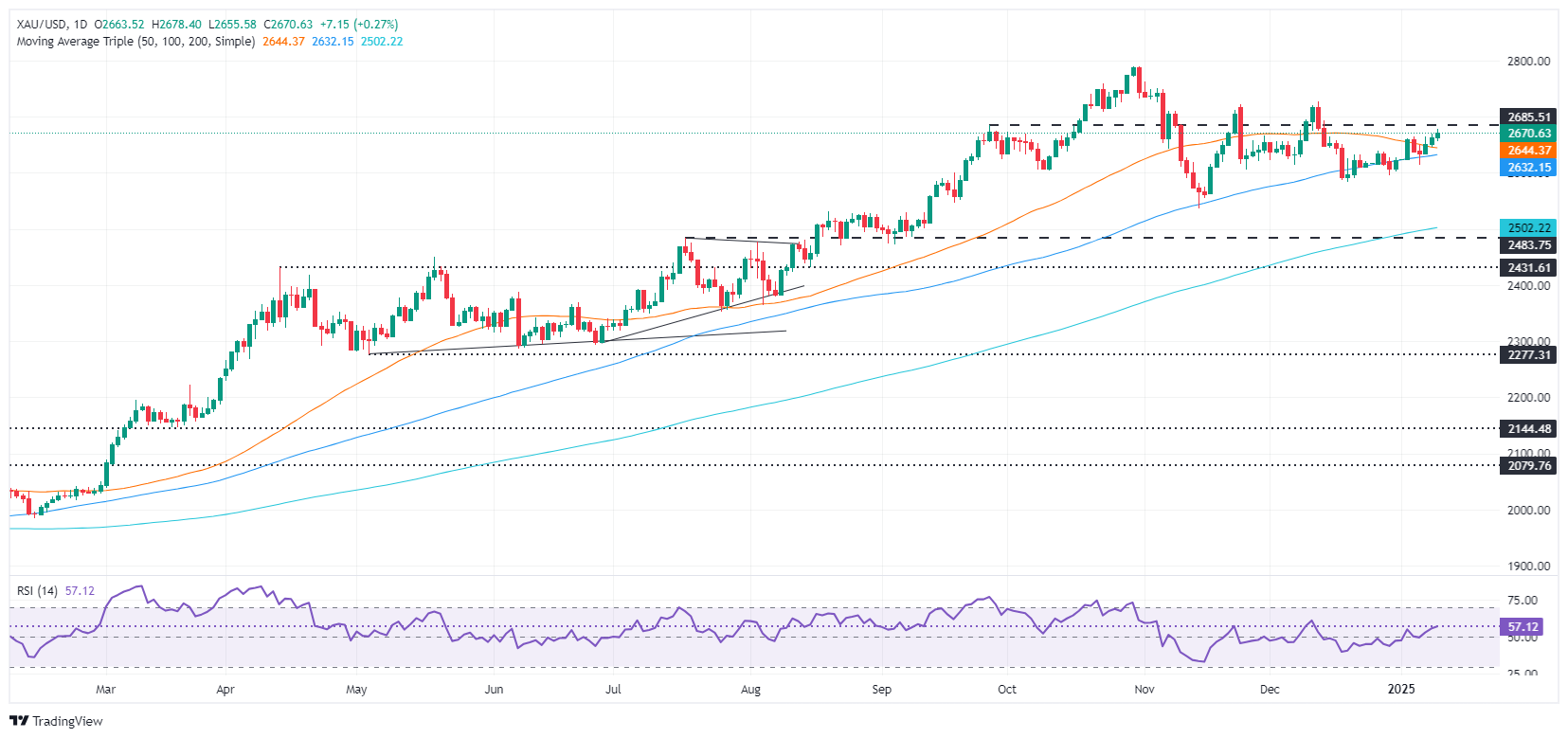
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price soars above $2,650 as bulls stepped in
Gold price steadily advances, carving a successive series of higher highs and higher lows after bouncing off the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) of $2,646, spurring XAU/USD’s jump toward the $2,670 area.
On further strength, Gold's first resistance would be $2,700, followed by the December 12 high of $2,726 and the all-time high (ATH) at $2,790.
On the downside, if sellers push XAU/USD below the 50-day SMA, the path to test the 100-day SMA will be cleared at $2,630. If surpassed, the next key support level would be $2,600, with further losses potentially extending to the 200-day SMA at $2,500.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

