Gold edges up, trimming some recent losses with US PCE inflation on focus
- Gold trims some losses on Friday but upside attempts remain capped amid broad-based US Dollar strength.
- Investors are reluctant to sell US Dollars ahead of the US PCE inflation reading for November.
- XAU/USD remains under pressure, limited below $2,605
Gold (XAU/USD) is trading with a moderate positive tone on Friday following the sharp sell-off earlier this week. However, upside attempts remain limited as investors brace for the release of the US Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index.
On Thursday, an upward revision to the third quarter’s US Gross Domestic Product (GDP), and the lower-than-expected Jobless claims have endorsed the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) hawkish stance for 2025.
This keeps the US Dollar index pinned near two-year highs ahead of the release of the Fed’s favorite inflation gauge. Investors are waiting to see whether the US central bank’s concerns about higher inflation are justified. A strong reading would cast further doubts on the Fed’s easing cycle and increase negative pressure on Gold.
Higher US yields, strong USD keep Gold recovery subdued
- XAU/USD is trading higher for the second consecutive day but lacks upside momentum, with traders reluctant to sell the US Dollar ahead of a key inflation report to be published at 13:30 GMT.
- US Treasury yields are steady above the 4.50% mark after having rallied 40 basis points over the last two weeks. This acts as a headwind for Gold as it is a non-interest-paying asset.
- US PCE inflation is expected to have increased at a steady 0.2% pace in November on month, with the yearly rate accelerating to 2.5% from 2.3% in October.
- The core PCE, considered more relevant for monetary policy purposes, is seen easing to 0.2% from 0.3% on month and accelerating to 2.9% on year from 2.8% in October.
- Data released on Thursday showed that the US economy grew at a 3.1% annualized pace in the third quarter, significantly improving from the already healthy 2.8% advance previously estimated.
- Likewise, weekly Jobless Claims declined to 220K on the week ending December 13 from the previous week's 242K reading, beating expectations of a slower decline to 230K.
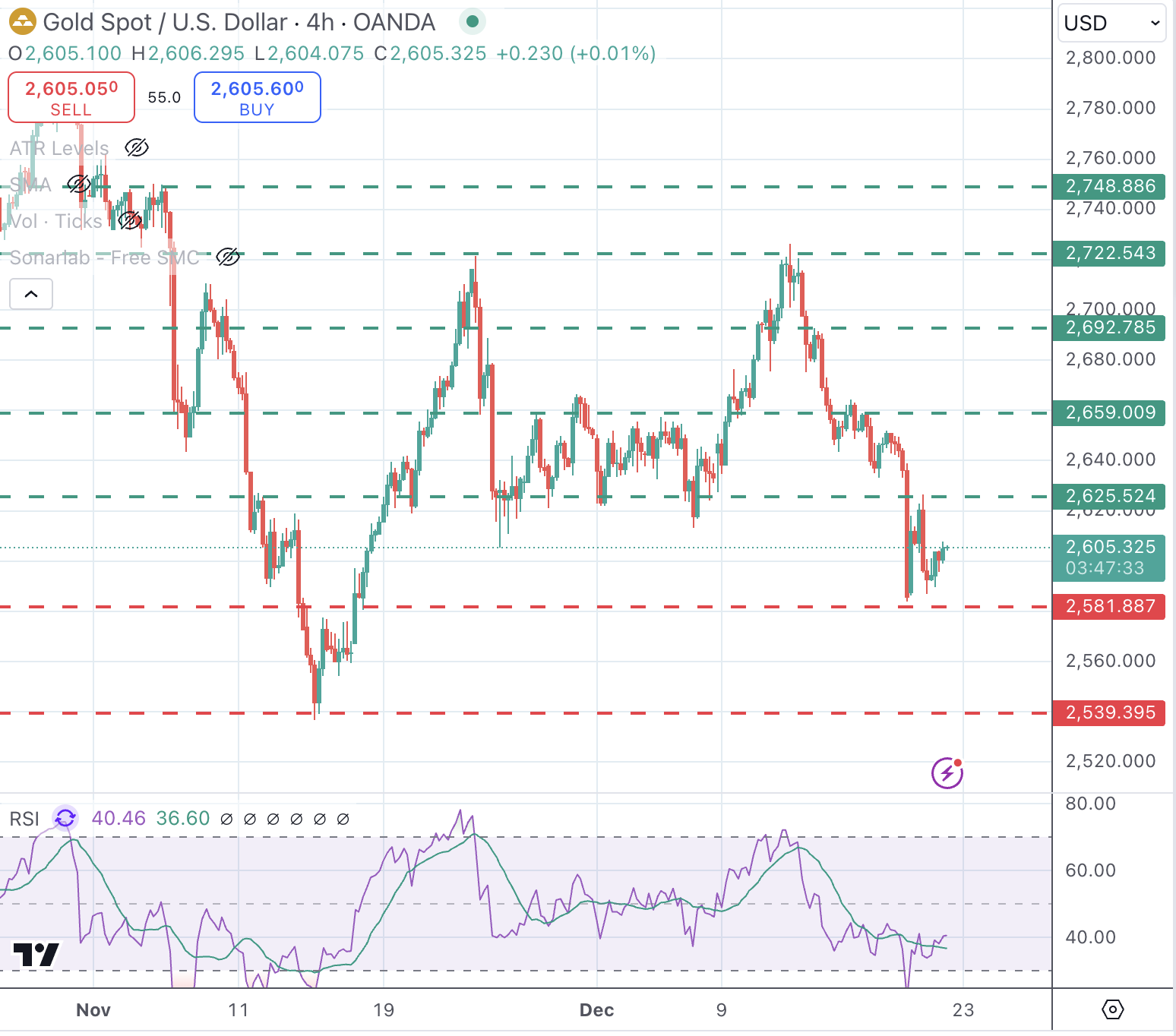
Technical analysis: XAU/USD maintains a negative trend below $2,625
Gold is going through a corrective recovery from heavily oversold levels. The broader trend, however, remains bearish. The pair is struggling to find acceptance above $2,600 and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) in the 4-hour chart remains flat at levels below the 50 threshold, highlighting the bearish momentum.
Immediate resistance is at the $2,605 intra-day high, with the key resistance area to challenge the bearish trend at the $2,625-$2,630 area (November 28, December 2 lows). On the downside, supports are at Wednesday’s low at around $2,580, ahead of November’s trough at $2,540.
XAU/USD 4-Hour Chart
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

