EUR/USD wobbles as Fed’s policy takes center stage
- EUR/USD consolidates around 1.0880 to start the week as investors await the Fed’s monetary policy decision on Wednesday.
- The Fed is widely anticipated to keep interest rates steady as the focus shifts to the dot plot and Powell’s comments.
- Greens’ signal to German debt restructuring deal and optimism over Russia-Ukraine peace have uplifted the Euro’s appeal.
EUR/USD trades in a tight range below the key level of 1.0900 in European trading hours on Monday. The major currency pair consolidates as investors await the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) interest rate decision, which will be announced on Wednesday.
The Fed is almost certain to keep interest rates steady in the current range of 4.25%-4.50%. Therefore, the US Dollar’s (USD) outlook will be guided by the Fed’s dot plot, which shows where officials see interest rates heading in the near and longer term, as well as the growth, employment, and inflation outlook in the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP). In the December meeting, Fed policymakers anticipated two interest rate cuts this year.
Investors will also focus on Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s remarks on the US economic outlook in the press conference following the monetary policy decision. A slew of US officials, including President Donald Trump, have stated that tariff policies could lead to some economic shocks in the near term. On Sunday, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said in an interview with NBC News, “I can predict that we are putting in robust policies that will be durable, and could there be an adjustment,” adding that the country needed to be weaned off of “massive government spending.” His comments came after the interviewer asked whether Trump’s agenda could lead the economy to a recession.
Last week, US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick said that policies by the President are the most important thing America has ever had, and “they worth it” after being asked whether it would be worth executing Trump’s policies even if they led to a recession.
Market participants worry that Trump’s tariff policies could be inflationary and batter households’ consumption. Such a scenario bodes poorly for the US Dollar.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD trades in tight range while Euro remains firm
- EUR/USD oscillates in a tight range as the US Dollar consolidates ahead of the Fed’s monetary policy meeting. The Euro (EUR) trades firmly as German leaders, including Franziska Brantner-led-Greens, agreed to set up a 500 billion Euro infrastructure fund and dramatic changes in the borrowing rules or stretch in the so-called ‘debt brake’, which would be approved in the lower house of Parliament on Tuesday.
- Market participants expect the decision of German leaders to boost defense spending through a historic change in the debt brake will prompt economic growth. Ahead of the German leaders meeting on the debt deal, a March 10-14 Reuters poll showed that economists had revised their economic projections for the Eurozone on the optimism over debt reforms to 1.3% for 2026 from 1.2% anticipated a month ago.
- A historic German debt restructuring plan has also increased Eurozone inflation expectations. This scenario is contrary to the European Central Bank’s (ECB) current monetary expansion stance. On Friday, ECB policymaker and Austrian Central Bank Governor Robert Holzmann supported keeping interest rates steady in the April policy meeting. Holzmann's endorsement for a pause in the policy-easing cycle was backed by the assumption that US President Trump’s tariffs and Germany’s defense spending have stemmed risks of a resurge in inflationary pressures.
- Meanwhile, increased hopes of a Russia-Ukraine truce have also improved the Euro’s appeal. Donald Trump is scheduled to meet Russian leader Vladimir Putin on Tuesday to discuss peace in Ukraine. Last week, Ukraine accepted a 30-day ceasefire deal after discussions with US leaders in Saudi Arabia.
- In the near term, the major risk for the Euro is a potential US-European Union (EU) tariff war. On Thursday, President Trump threatened to impose 200% tariffs on European alcohol after the EU proposed retaliatory tariffs on the US against a 25% blanket levy on steel and aluminum imported by the US.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD trades sideways around 1.0880
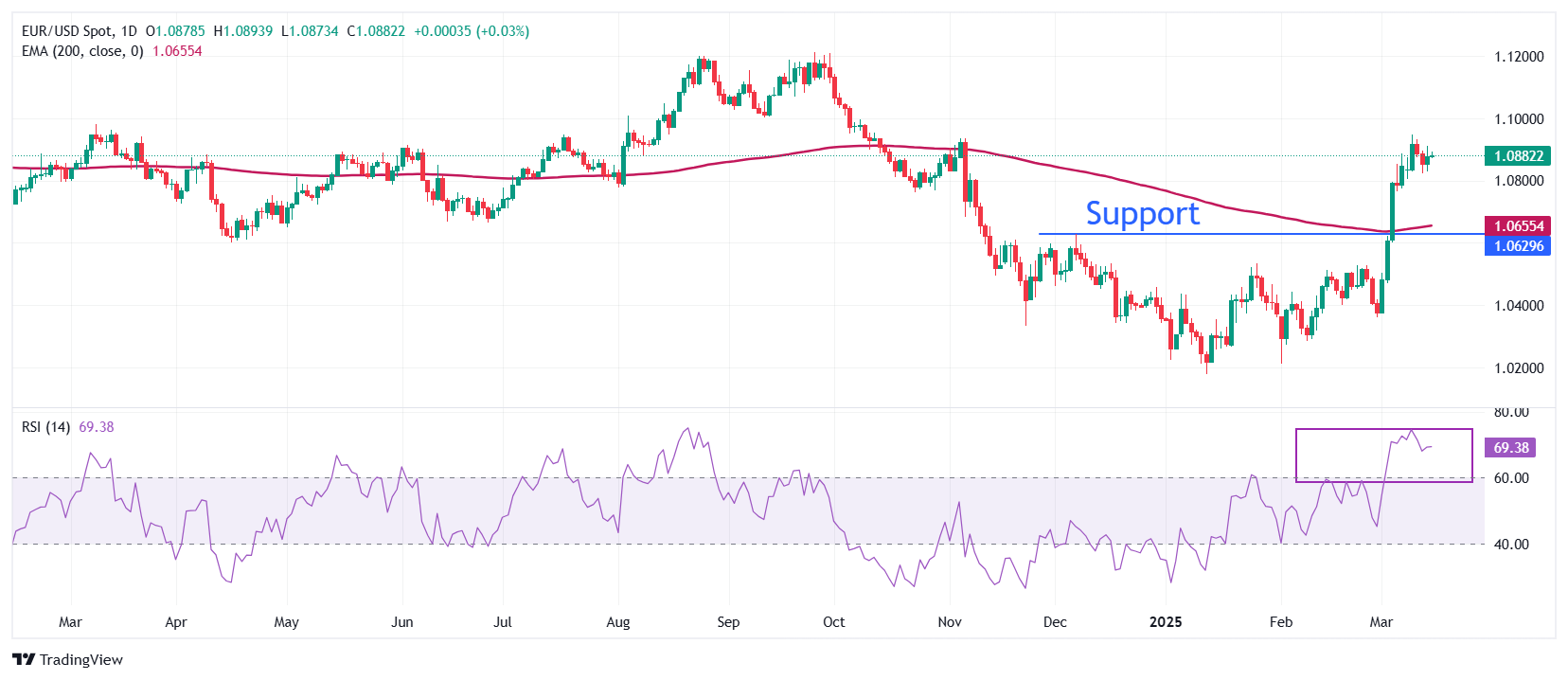
EUR/USD trades inside Friday’s trading range around 1.0880 on Monday. The long-term outlook of the major currency pair remains firm as it holds above the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.0655.
The pair strengthened after a decisive breakout above the December 6 high of 1.0630 last week.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) wobbles near 70.00, suggesting the strong bullish momentum is intact.
Looking down, the December 6 high of 1.0630 will act as the major support zone for the pair. Conversely, the psychological level of 1.1000 will be a key barrier for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.


