Pound Sterling rebounds against US Dollar amid optimism over Russia-Ukraine truce
- The Pound Sterling rises to near 1.2600 against the US Dollar due to positive developments in the Russia-Ukraine peace truce.
- Fears of US President Trump’s tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China loom large.
- The BoE is expected to follow a careful and gradual policy-easing approach.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) gains ground against the US Dollar (USD) after a two-day correction and rebounds to near 1.2610 in European trading hours on Monday. The GBP/USD pair bounces back as the risk premium of the US Dollar diminishes on optimism over a peace truce between Russia and Ukraine. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, falls to near 107.25 from an over two-week high of 107.65 posted on Friday.
Over the weekend, United Kingdom (UK) Prime Minister Keir Starmer said European leaders agreed to present a peace plan to Washington. The meeting between European leaders and Starmer was also attended by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, potentially a big positive step towards ending the three-year-long war in Ukraine. Technically, signs of easing geopolitical tensions diminish the safe-haven appeal of the US Dollar.
However, investors should avoid betting big against the US Dollar due to looming tariff fears. United States (US) President Donald Trump is poised to slap tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China for failing to restrict the flow of fentanyl into the US.
US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick confirmed over the weekend that the President’s plans of imposing tariffs on Canada and Mexico on Tuesday are on. However, his comments indicated that there is room for negotiation over the degree of tariffs.
US President Trump threatened to impose a 25% levy on Canada and Mexico and an additional 10% on China. Trump also slapped 10% tariffs on China in the first week of February.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling trades higher on multiple tailwinds
- At the start of the week, the Pound Sterling trades higher against its major peers, except the Euro, due to a potential Russia-Ukraine peace truce. Additionally, firm expectations that the Bank of England (BoE) will follow a moderate policy-easing cycle and a likely healthy trade deal between the US and the UK have kept the British currency on the frontfoot.
- On Friday, BoE Deputy Governor Dave Ramsden said that the central bank should keep a “careful and gradual” approach to the monetary policy expansion amid uncertainty over the labor market and global trade. Ramsden warned that inflationary pressures are still elevated due to persistent wage growth. “I no longer think that risks to hitting the 2% inflation target sustainably in the medium term are to the downside,” Ramsden said. Meanwhile, trades have fully priced in two interest rate cuts this year.
- The meeting between US President Trump and UK Prime Minister Starmer on Thursday didn’t end with a trade deal, but Trump was confident that an agreement could be made "pretty quickly" where tariffs “wouldn't be necessary".
- This week, investors will pay close attention to a slew of US economic data, notably on the Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data for February, which will be released on Friday. The labor market data will influence market expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook. The Fed is expected to keep interest rates steady in the March and May policy meetings, and there is a 77% chance that it will cut them in June, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
- In Monday’s session, investors will focus on the US ISM and revised S&P Global Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) data for February, which will be published during North American trading hours. The ISM Manufacturing PMI is estimated to have grown at a marginally slower pace of 50.8 from 50.9 in January.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling finds bids near 20-day EMA
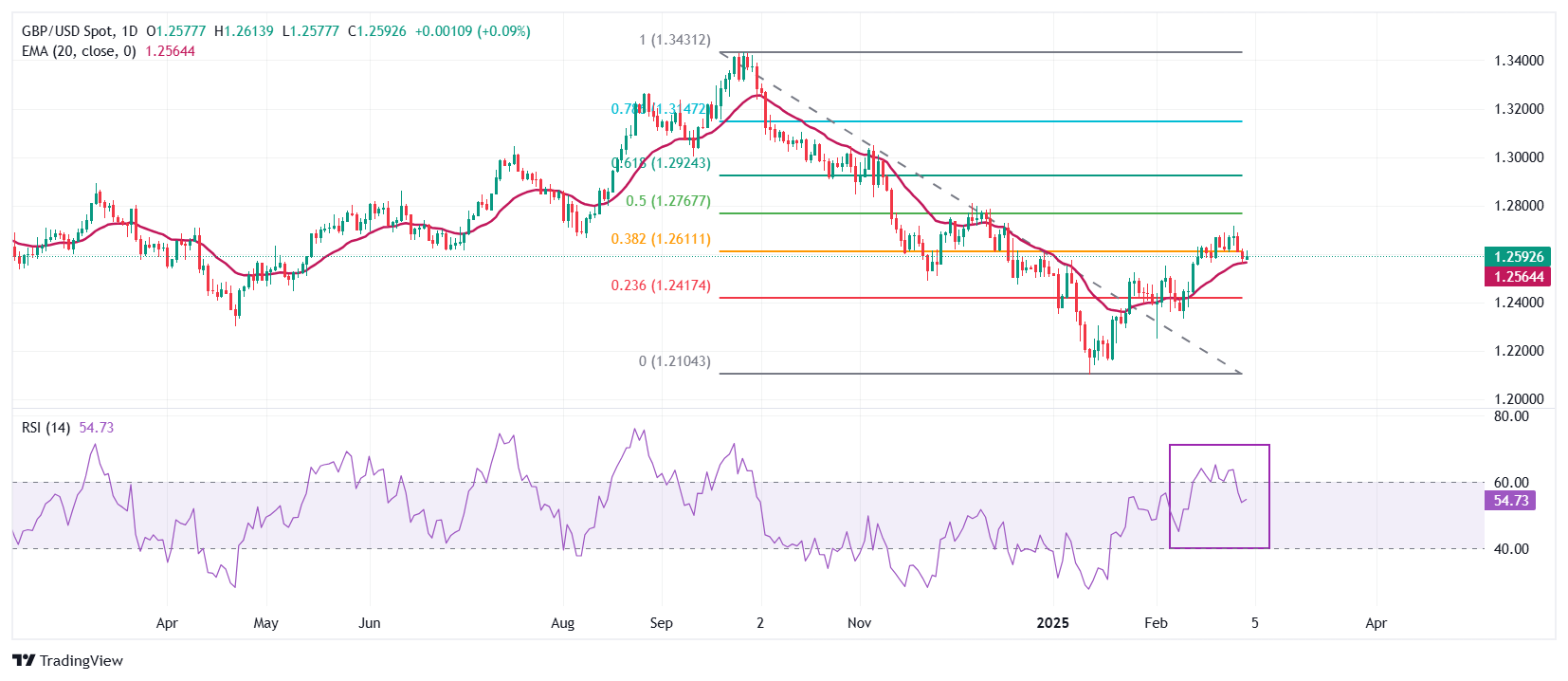
The Pound Sterling movers higher above 1.2600 against the US Dollar on Monday. The GBP/USD pair finds buying interest after a mean-reversion move to the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.2560.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls back within the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting that the bullish momentum has concluded for now. However, the positive bias remains intact.
Looking down, the February 11 low of 1.2333 will act as a key support zone for the pair. On the upside, the 50% Fibonacci retracement at 1.2765 will act as a key resistance zone.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

