Pound Sterling faces pressure as BoE Mann guides dovish monetary policy outlook
- The Pound Sterling is under pressure on Tuesday as BoE official Catherine Mann is concerned over weak demand and guides cracks in the labor market.
- US President Trump imposes 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum and is poised to announce reciprocal tariffs.
- Investors await BoE Bailey and Fed Powell’s speech on Tuesday.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) weakens against its major peers in European trading hours on Tuesday after a dovish commentary from Bank of England (BoE) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) member Catherine Mann in an interview with the Financial Times (FT) earlier in the day.
Investors were keenly awaiting Catherine Mann’s interview to know the reasons that forced her to favor a bigger interest rate reduction in the previous week’s policy decision after being an outspoken hawk for a long period.
Mann said that she changed her mind about the policy because “demand conditions are quite a bit weaker than has been the case”. So, a 50 basis points (bps) rate cut call from her was a way to communicate with traders about “what we think are the appropriate financial conditions for the United Kingdom (UK) economy”.
When asked about her outlook on inflation and demand, Mann was confident that inflation would remain consistent with the BoE’s target of 2% later this year and saw a “non-linear” fall in employment.
Last week, the BoE reduced its key borrowing rates by 25 bps to 4.5%, as expected, with a 9-0 vote split favoring a rate cut. Seven MPC members voted for a 25 bps interest rate reduction. Surprisingly, Catherine Mann joined MPC member Swati Dhingra and favored a larger-than-usual rate cut.
In Tuesday’s session, investors will focus on BoE Governor Andrew Bailey’s speech at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business in London for more interest rate guidance.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling drops against USD as Trump imposes 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum
- The Pound Sterling trades subduedly against the US Dollar (USD) around 1.2350 in Tuesday’s European session. The outlook of the GBP/USD pair remains bearish as the US Dollar performs strongly on the assumption that the impact of 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum imports by all nations into the United States (US) will be inflationary.
- On Monday, US President Donald Trump signed executive orders to impose 25% tariffs on all imports of steel and aluminum and confirmed that no country would be exempt from the duties, which will come into effect from March 4. Trump added that he will also announce reciprocal tariffs in the coming days.
- Market participants worry that US importers will bear the impact of higher metal prices. This scenario would be inflationary for the economy, as business owners would pass on the impact of higher input prices to end consumers. This would force Federal Reserve (Fed) officials to wait more months before resuming the policy-easing cycle, which the central bank paused in January.
- For meaningful cues on the interest rate outlook, investors will focus on Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s testimony before Congress at 15:00 GMT. Powell is also scheduled to testify before Congress on Wednesday.
- In the January policy meeting, Jerome Powell said that monetary policy adjustments would become appropriate only when the Fed will see “real progress in inflation or at least some weakness in the labor market”.
- This week, investors will also focus on the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for January, which will be released on Wednesday.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling extends losing spree
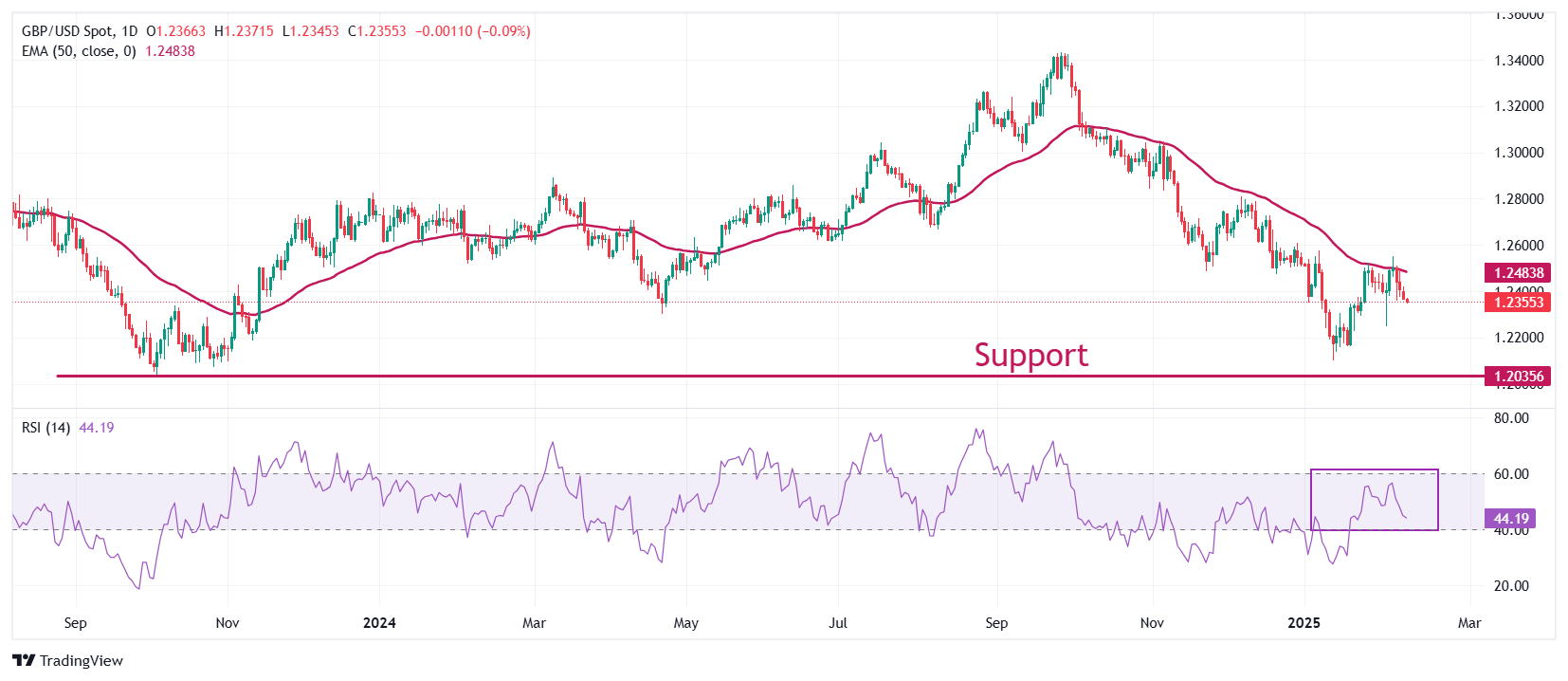
The Pound Sterling extends its losing streak for the fourth trading day against the US Dollar and posts a fresh weekly low near 1.2350 on Tuesday. The GBP/USD pair resumed its downside journey after recovering to near the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.2484.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) oscillates inside the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting a sideways trend.
Looking down, the January 13 low of 1.2100 and the October 2023 low of 1.2050 will act as key support zones for the pair. On the upside, the December 30 high of 1.2607 will act as key resistance.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.




