EUR/USD slips into a third straight loss as tariff concerns weigh
- EUR/USD lost another 0.3% on Monday, falling back into 1.0300.
- US President Trump signed off on sweeping tariffs late Monday.
- US inflation data to dominate market flows this week.
EUR/USD declined around one-third of one percent on Monday, falling back into the 1.0300 handle as market sentiment takes a knee. Investors are awaiting clearer signals from central bank policymakers, but a fresh batch of executive orders from US President Donald Trump regarding tariffs make the outlook murkier.
Read more: US President Donald Trump signs off on 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum
European data is broadly limited this week; an appearance from European Central Bank (ECB) President Christine Lagarde failed to move the needle in any meaningful way, a routine outing that has become the norm for talking points from ECB policymakers. Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell will be giving his latest testimony to the US Senate Banking Committee. Fed Chair Powell is expected to face questions about how the Fed will react to the ebb and flow of President Trump’s tariff threats.
German final Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices for the year ended January are due on Thursday, alongside pan-EU Gross Domestic Product figures for the fourth quarter slated for Friday. Neither datapoint is expected to move much.
The key datapoints this week will be US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation slated for Wednesday, and US Producer Price Index (PPI) due on Thursday.

EUR/USD price forecast
Three straight down days for EUR/USD has put the pair in pace to rediscover recent technical lows. Fiber flubbed a technical recovery above the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) in late January, and bids have been on a steady grind lower ever since. The 1.0200 handle is up next as the bears slowly crush bulls out of the picture.
EUR/USD daily chart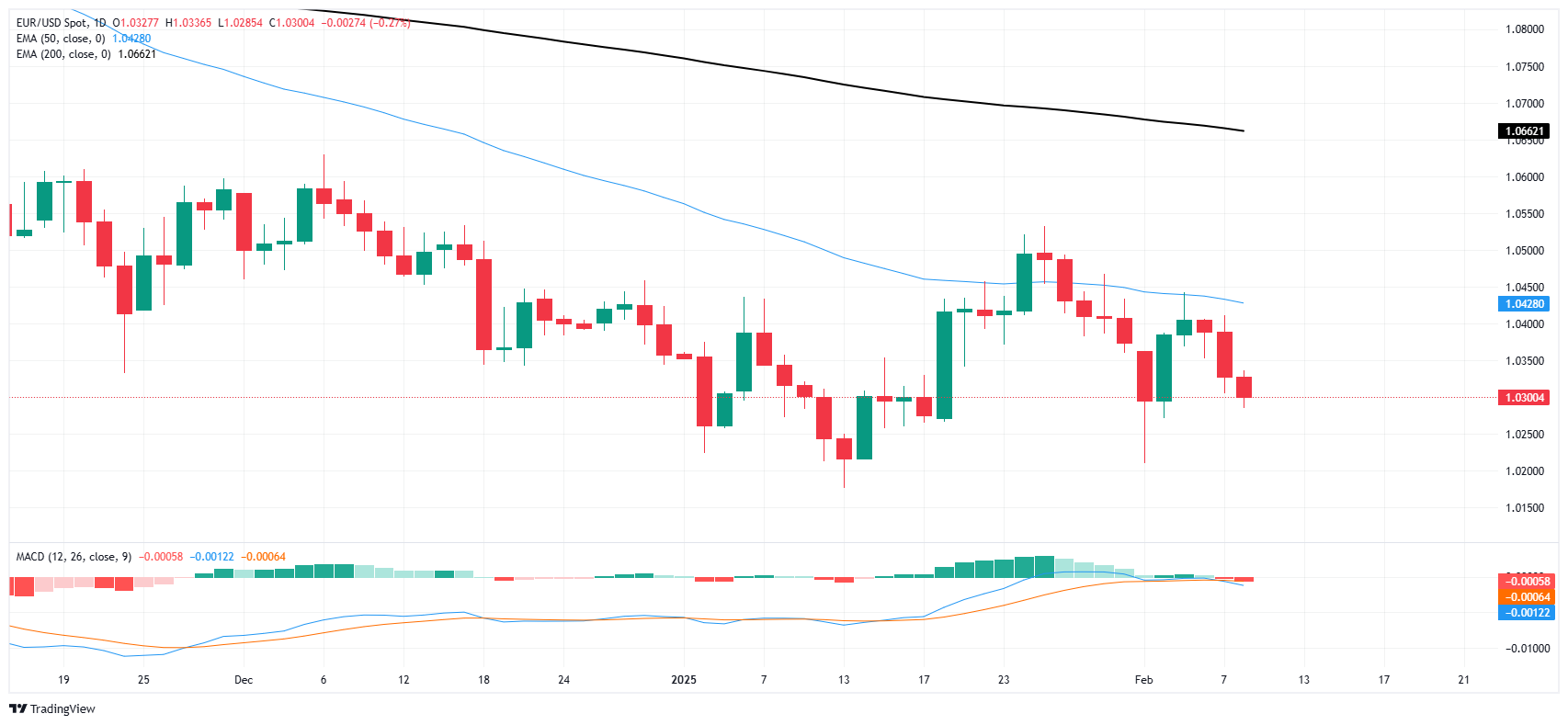
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

