EUR/USD slides on soft inflation in Germany’s six states, Trump’s tariff threats
- EUR/USD declines to near 1.0370 as inflation in six states of Germany decelerates in January.
- Donald Trump threatens to impose 100% tariffs on BRICS and 25% on Mexico and Canada.
- The Fed kept interest rates at their current levels on Wednesday.
EUR/USD faces selling pressure and declines to near 1.0370 in Friday’s European session. The major currency pair declines as the Euro (EUR) weakens amid a slowdown in inflationary pressures in six German states. Softer-than-expected Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for January boosts confidence that Eurozone price pressures are on track to return sustainably to the European Central Bank’s (ECB) desired rate of 2%, which will support the central bank in easing the monetary policy.
On Thursday, ECB President Christine Lagarde showed confidence in announcing a victory over inflation this year in the monetary policy statement after the central bank reduced its Deposit Facility Rate by 25 basis points (bps) to 2.75%
Christine Lagarde’s comments at the press conference indicated that the ECB has kept the door open for further policy easing. Lagarde said that we are still in “restrictive territory” and it is premature to “anticipate at what point where will stop”. She avoided providing a pre-defined interest rate cut path and reiterated that we decide meeting by meeting based on data.
Going forward, investors will focus on the flash Eurozone Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) data for January, which will be released on Monday.
But before that, the preliminary German HICP data for January will be published at 13:00 GMT. However, the impact is expected to be limited, as the inflation data in six German states have already indicated the current status of price pressures.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD weakens amid US Dollar’s strength
- EUR/USD remains under pressure as the broader outlook of the US Dollar (USD) remains firm, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) wobbling around 108.20. The safe-haven appeal of the Greenback strengthens as United States (US) President Donald Trump reiterated his intentions of imposing hefty tariffs on his North American peers and BRICS on Thursday.
- Donald Trump said on his social media platform, TruthSocial, that he requires a commitment from the BRICS that it will “neither create a new currency nor back any other currency” to replace the US Dollar. Trump threatened that any country tries should “face 100% tariffs”, and expect to say “goodbye to selling into the wonderful US economy.”
- Market experts believe that Donald Trump is using tariff measures as a tool to fulfill his economic agenda, and the imposition of hefty tariffs will be inflationary for the US economy. Such a scenario would support the Federal Reserve (Fed) in holding its stance of keeping interest rates unchanged in the range of 4.25%-4.50% for longer.
- On Wednesday, the Fed maintained the status quo and guided to remain in the waiting mode until the central bank sees any “real progress in inflation or some weakness in the labor market”.
- Meanwhile, the next move in the US Dollar will be guided by the US Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index (PCE) data for December, which will be published at 13:30 GMT. Economists expect monthly core PCE inflation to have grown at a faster pace of 0.2%, compared to a 0.1% increase in November. Year-on-year, core PCE is estimated to have grown steadily by 2.8%.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD slides below 20-day EMA
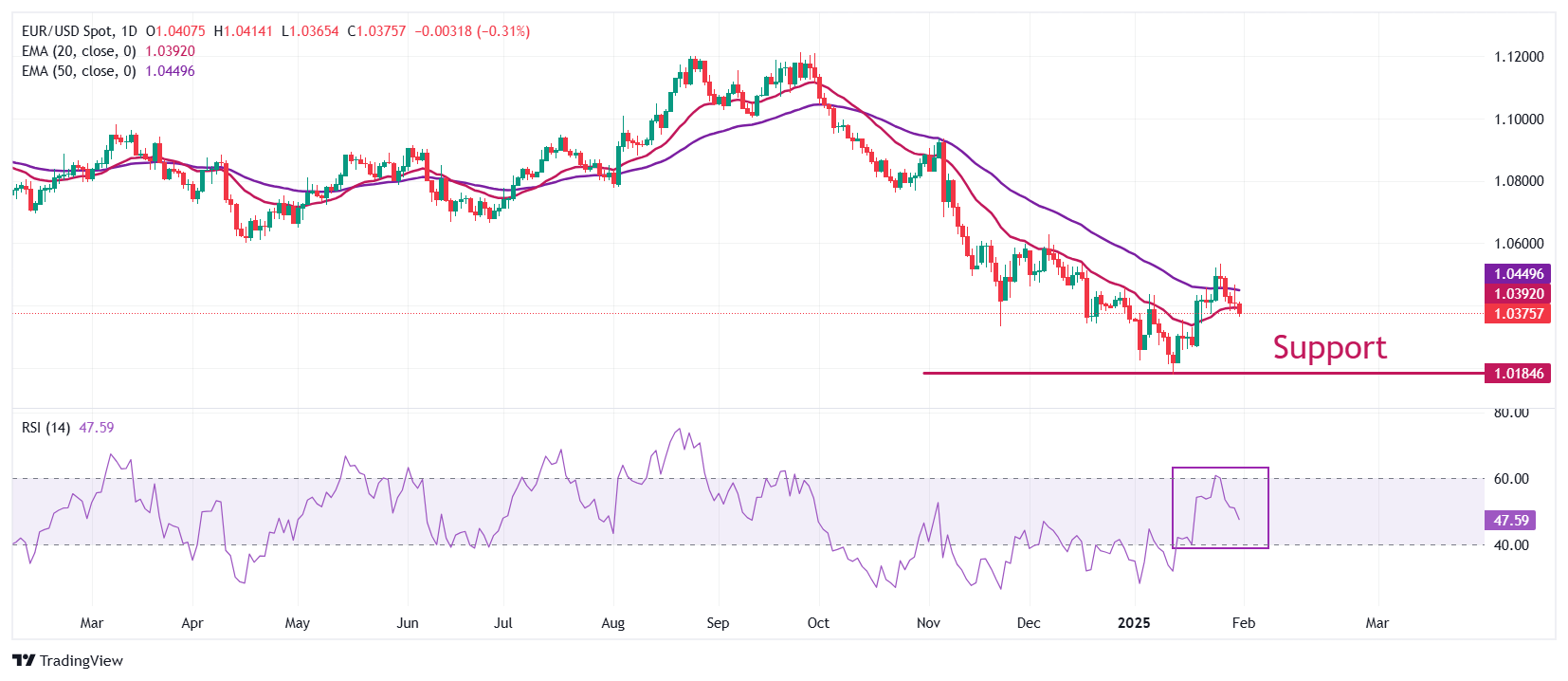
EUR/USD declines to near 1.0370 in Friday’s European session, below the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.0390. The major currency pair resumed its correction after failing to sustain above the 50-day EMA, which trades around 1.0449 at the press time.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) faces barricades near 60.00. Such a scenario indicates that the recovery move was short-lived.
Looking down, the January 20 low of 1.0266 and January 13 low of 1.0177 will act as major support for the pair. Conversely, the December 6 high of 1.0630 will be the key barrier for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

