Mexican Peso: up move halts at key level
- The Mexican Peso trades mixed after rising for four consecutive days.
- Gains came from a move by the Supreme Court to re-examine controversial reforms and a Banxico official’s comments.
- USD/MXN falls to critical support at the base of its rising channel and the 50-day SMA.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) fluctuates between minor gains and losses on Friday during the European session after clocking up four successive up days in all three of its most-traded pairs: USD/MXN, EUR/MXN, and GBP/MXN.
The Peso’s strength came initially from Deputy Governor of the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) Jonathan Heath, who commented on Tuesday that interest rates should remain higher for “more time”. Higher interest rates encourage more foreign capital inflows and strengthen the Peso. Later in the week, news of a Supreme Court decision to review and potentially revise controversial reforms to the judiciary encouraged a continuation of the rally.
It should be noted that the Peso is now at the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) level in all of three of its key pairs, a technical indicator institutional investors take into account during their decision-making.
Mexican Peso appreciates following Supreme Court motion
The Peso rallied on Thursday after the news that Mexico's 11 Supreme Court judges voted by a majority of eight to three to re-examine controversial constitutional reforms to the judiciary, passed by the government in September. The move could block the implementation of the reforms, which seek to have judges elected rather than appointed, according to El Financiero.
Mexican financial markets took a beating in June after the election of the Morena-led government amid investor concerns regarding these and other proposed reforms. They were a contributing factor in a 10% depreciation of the Mexican Peso. Critics argue that they threatened the independence of the judiciary, were anti-democratic, and endangered outside investment.
The new laws, which were voted in by the Mexican Parliament in September, remain a risk to Mexican assets including the Peso, as highlighted by advisory service Capital Economics in a recent note:
“At the moment, Mexico has an investment grade rating from all three major rating agencies and we doubt this will change in the near-term,” wrote Kimberley Sperrfechter, Emerging Markets Economist at Capital Economics, adding, “That said, if the judicial reform leads to a significant deterioration in the quality of institutions and weaker growth and fiscal policy isn’t tightened sufficiently, there is a risk that Mexico is downgraded in the medium-term.”
The decision to have the reforms re-examined has been spear-headed by Supreme Court Judge Juan Luis González Alcántara. It rests on the legal principle that the new laws risk undermining the independence of Mexico’s judiciary.
Whilst the Supreme Court does not have the power to annul the laws, it can decide whether they need to be revised. Morena’s Head of the Government of Mexico City, Marti Luis Batres, described the move as a “coup d’etat”.
Technical Analysis: USD/MXN falls to 50-day Moving Average
USD/MXN falls all the way down to the base of its rising channel and the level of the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) – a key line in the sand for traders.
USD/MXN Daily Chart
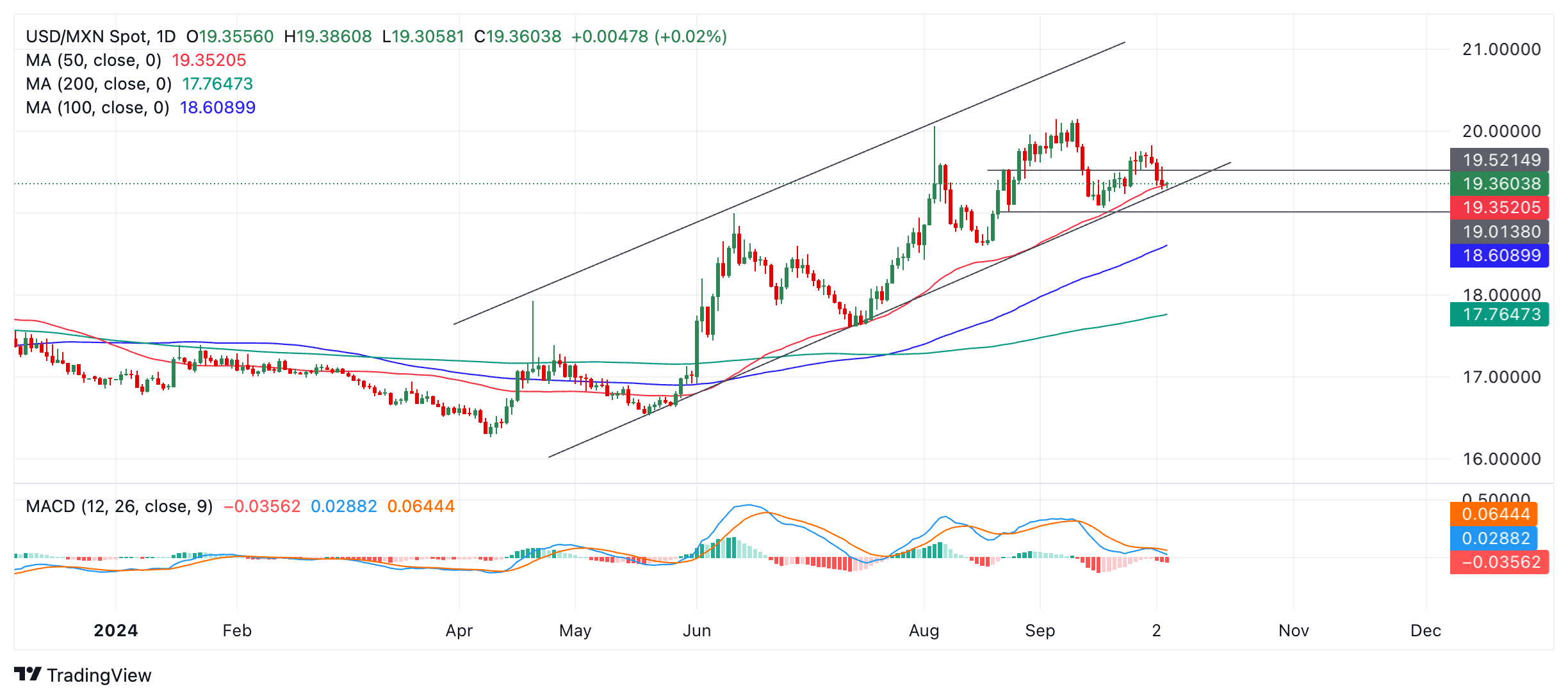
USD/MXN is expected to find support at this level, and there is a chance it will rebound and start moving higher within the range again. The medium and longer-term trends are now bullish, and given the technical analysis principle that “the trend is your friend,” the odds favor a recovery and continuation higher.
That said, the short-term trend is bearish, and the GBP/MXN cross has broken below its rising channel already, which can sometimes be a “canary in the coalmine” warning for other Peso pairs.
A decisive break below the channel and the 50-day SMA, therefore, risks threatening the medium-term uptrend in the USD/MXN. Such a move would be characterized by a longer-than-average bearish candlestick that pierced cleanly below both the channel line and the SMA, and closed near its low. Such a break would clear the way for losses, first down to 19.00 (August 23 low, round number) and then 18.60, the level of the 100-day SMA.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.

