GBP/USD rallies on Fed rate cut bets
- GBP/USD crossed back over 1.3200 on Wednesday amid risk-on sentiment.
- Fed rate call hopes are pinned to the ceiling as market anticipate 50 bps rate trim.
- UK CPI inflation and BoE rate call also on the table this week.
GBP/USD clipped into the high end on a quiet Monday, kicking off the new trading week with a fresh bullish bid back over the 1.3200 handle. Investor sentiment is holding steady on the high side as markets gear up for a hefty central bank showing this week, with a widely anticipated Fed rate cut and another showing from the Bank of England (BoE).
US Retail Sales are slated for an update on Tuesday, but the key datapoint that would normally drive some level of volatility is not expected to move the needle this week unless the print comes in wildly out of alignment with forecasts. MoM US Retail Sales growth in August is expected to ease back to 0.2% from July’s 1.0%, while core MoM Retail Sales (excluding automotive purchases) are expected to tick down to 0.3% from 0.4%.
Forex Today: US data takes centre stage pre-FOMC gathering
On the UK side, Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation figures are due early Wednesday, with the annualized figure through August expected to hold steady at 2.2% YoY. Like US Retail Sales, the standalone figure isn’t expected to drive much market reaction as long as the print comes in within a reasonable range of median market forecasts.
The Fed kicking off a new rate-cutting cycle on Wednesday is all but a given according to investors, and it now comes down to a debate of how much rather than when. According to the CME’s FedWatch Tool, rate traders are pricing in around 60% odds that the Fed’s first rate cut in over four years will be a 50 bps decline in the Fed funds rate, with the remaining 40% expecting a more demure 25 bps. Rate markets are also pricing in a total of 125-150 bps in cuts by the end of the year, with interest rate traders seeing a roughly 80% chance that the Fed funds rate will hit 400-425 total bps by December 18 versus the current interest rate of 525-550.
The BoE will also be delivering their own rate call on Thursday, but it is expected to be a much less noteworthy outing than the Fed’s rate call. The BoE is expected to hold its main reference rate at 5.0% this week, and the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is expected to vote seven-to-two in favor of holding, compared to the five-to-four quarter-point rate cut vote from the BoE’s last outing.
GBP/USD price forecast
Cable’s 0.6% surge on Monday has dragged the pair back over the 1.3200 handle, with daily candlesticks continuing to grind back into the high side with multi-year highs sitting just north of 1.3250.
Despite an overall bullish tilt, GBP/USD price action is running the risk of getting caught in a bull trap, with the pair having run hot in a 1.66% technical recovery from the last swing low into the 1.3000 handle.
GBP/USD daily chart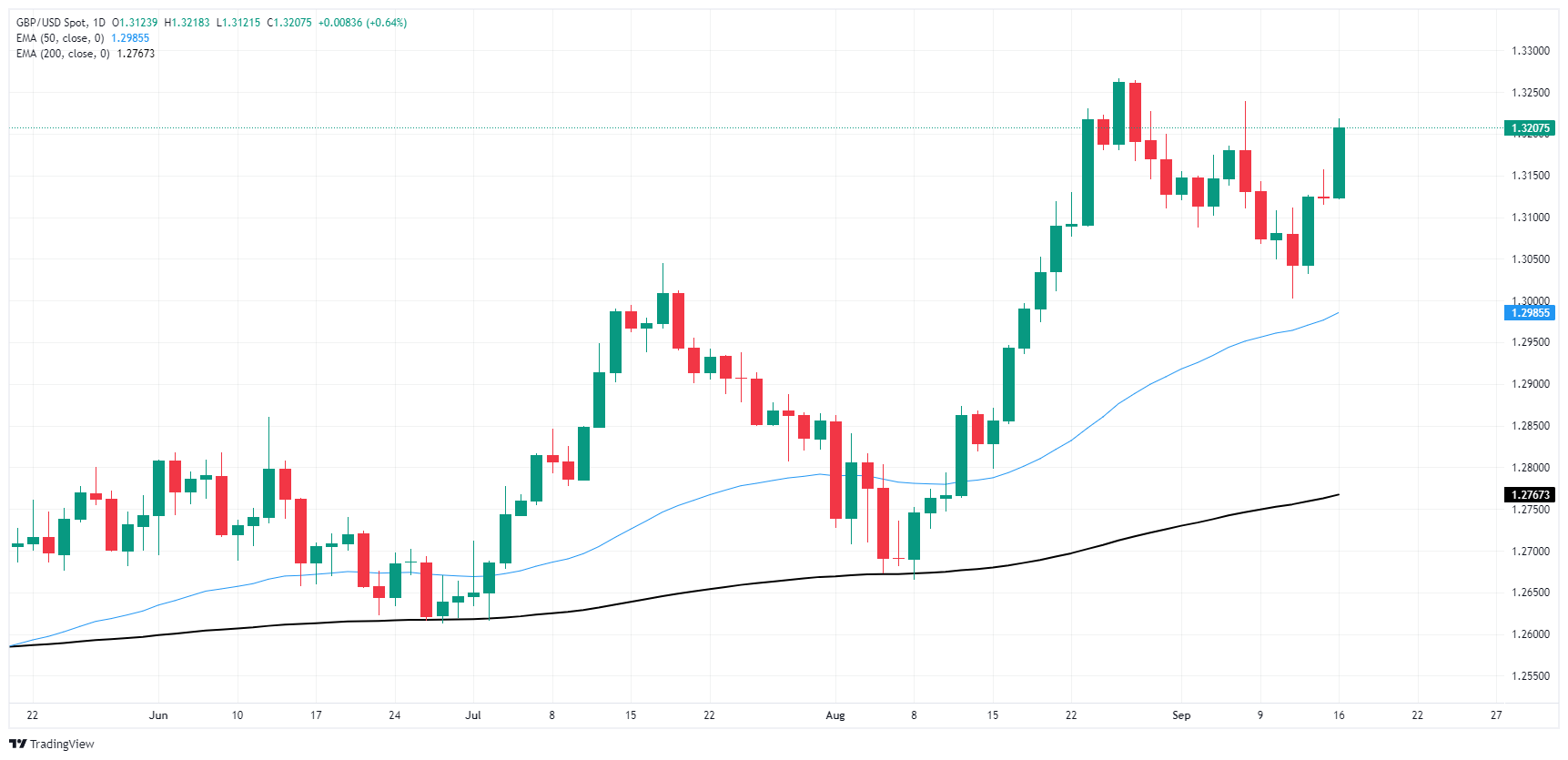
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, aka ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.




