
Day trading has become increasingly popular with the advent of online trading platforms and easy access to market data. While the allure of substantial profits draws many to day trading, the risks are equally significant, necessitating a disciplined approach and thorough preparation.
This article discusses day trading basics and how to use them. Furthermore, we will provide practical insights and strategies for those looking to practice and improve their day trading skills. Whether you're a novice intrigued by the fast-paced world of day trading or an experienced trader seeking to refine your techniques, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the complexities of day trading.
1. What is day trading?
Day trading is a style of trading where financial instruments such as stocks, currencies, commodities, or options are bought and sold within the same trading day. The key characteristic of day trading is that all positions are closed before the market closes for the day, preventing the trader from holding any overnight positions. This distinguishes day trading from other strategies like swing trading or long-term investing, where assets may be held for days, weeks, or even years.
Key features of day trading:
Short time frames: Day traders typically execute multiple trades throughout the day, aiming to capitalize on small price movements. The holding period for any given position can range from minutes to hours, but it never extends beyond the trading session.
High volume and frequency: Due to the brief holding periods, day trading often involves a high volume of trades. This frequent trading activity requires quick decision-making and the ability to respond rapidly to market changes.
Use of leverage: Many day traders use leverage, or borrowed capital, to increase their potential returns. While leverage can amplify gains, it also increases the potential for losses, making risk management a critical component of day trading.
Technical analysis: Day traders heavily rely on technical analysis to inform their trading decisions. This involves analyzing price charts, patterns, and various technical indicators to predict short-term price movements.
Market news and events: Day traders frequently react to economic reports, earnings announcements, and geopolitical developments, which can cause significant price volatility.
2. How to start day trading
Embarking on a day trading journey requires a solid foundation of knowledge, the right tools, and a disciplined approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you start day trading:
Educate yourself:
Understand the basics: Learn the fundamentals of how markets work, including the types of securities traded, market hours, and order types.
Study trading strategies: Familiarize yourself with different day trading strategies, such as scalping, momentum trading, and breakout trading. Understand the concepts of technical analysis, including chart patterns, indicators, and trend analysis.
Stay updated with financial news, economic indicators, and other factors that can affect market conditions.
Learning through books, online resources, and interacting with other traders can help you stay sharp and adapt to changes.
Choose a reliable broker:
Research and compare brokers: Look for brokers that offer robust trading platforms, low fees, and excellent customer service. Key features to consider include execution speed, order types, margin rates, and research tools.
Account types and minimums: Ensure the broker offers accounts suited to day trading, with reasonable minimum deposit requirements and access to leverage if needed.
Develop a trading plan:
Define goals and risk tolerance: Set clear, realistic goals for your trading activities, and understand how much capital you can afford to risk.
Strategy development: Based on your market knowledge and risk tolerance, develop a trading strategy that outlines entry and exit points, position sizes, and risk management rules.
Risk management: Implement strict risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and determining the maximum amount you're willing to lose per trade and per day.
Practice with a Demo account:
Simulate real trading: Use a demo account provided by your broker to practice trading with virtual money. This helps you become familiar with the trading platform and test your strategies without financial risk.
Analyze performance: Evaluate your trades regularly to understand what works and what doesn’t. This is crucial for refining your strategy and improving your skills.
 0 commission, low spreads
0 commission, low spreads Diverse risk management tools
Diverse risk management tools Flexible leverages and instant analysis
Flexible leverages and instant analysis Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money
Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money 
Start small and scale up:
Start small: Begin trading with a small amount of capital. This minimizes risk and allows you to gain experience without significant financial exposure.
Scale up: As you gain confidence and prove your strategy's effectiveness, you can gradually increase the size of your trades.
Discipline and emotional control:
Stick to your plan: Follow your trading plan strictly to avoid emotional decisions, which can lead to significant losses.
Avoid overtrading: It’s crucial to recognize when to trade and when to sit out. Overtrading reduces profits and elevates risk.
Starting day trading is a significant commitment that requires preparation, patience, and continuous improvement. By following these steps, new traders can build a strong foundation to potentially succeed in the fast-paced world of day trading.
3. How to practice day trading with real examples
Effective day trading practice entails using real market data and scenarios to gain experience and refine your strategies. Here’s a structured approach to practice day trading with real examples:
Open a Demo account:
Traders can choose a broker that offers a Demo account feature such as Mitrade (with 50,000 virtual USD).
Practicing day trading with a demo account is an excellent way to gain experience without financial risk. It allows traders to familiarize themselves with the trading platform, test and refine strategies, and understand market dynamics using real-time data.
Analyze price trend:
Traders can anticipate the price trend of a product using both technical and fundamental analysis. However, day traders typically prefer technical analysis, focusing on minute and hourly timeframes to make quick, data-driven decisions. This approach allows them to capitalize on short-term price movements and market trends.
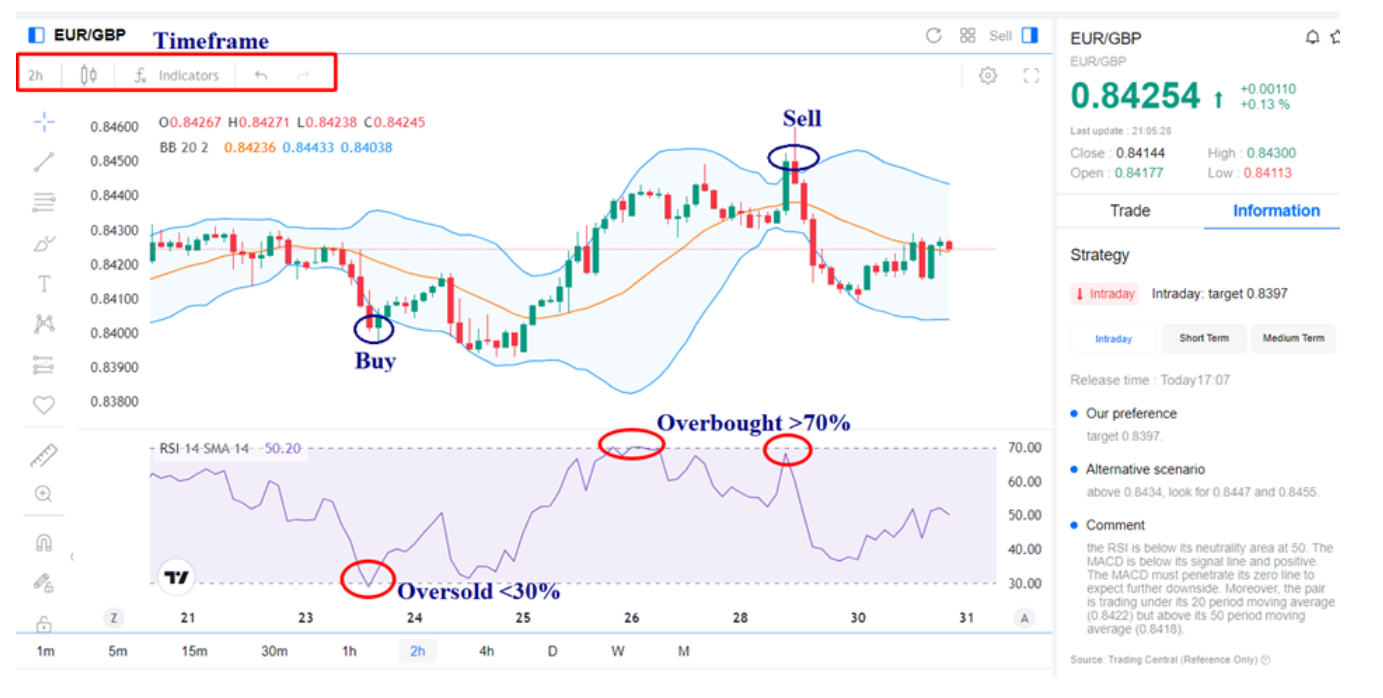 EUR/GBP price chart (Source: Mitrade)
EUR/GBP price chart (Source: Mitrade)
For example, in the EUR/GBP price chart, a trader might use a 2-hour timeframe in combination with the RSI and Bollinger Bands indicators to identify potential reversal points. When the RSI falls below 30%, it indicates an oversold condition, suggesting a potential buy signal. Conversely, when the RSI rises above 70%, it indicates an overbought condition, suggesting a potential sell signal. This strategy helps traders make informed decisions based on market momentum and volatility.
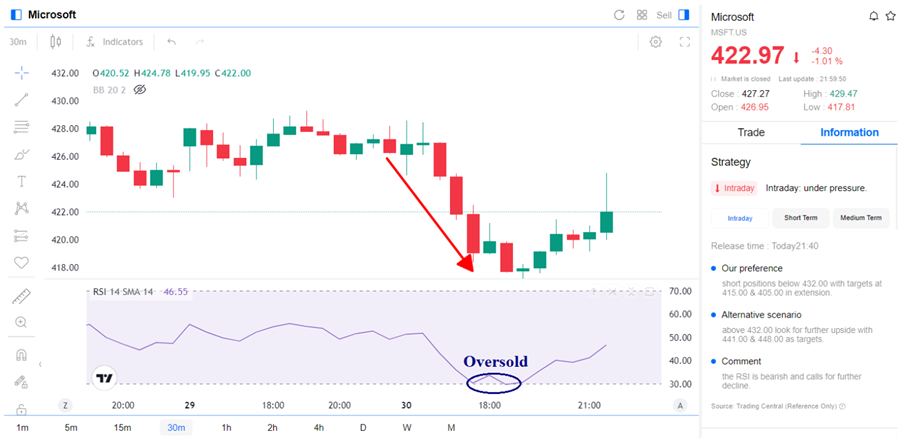
Microsoft price chart (Source: Mitrade)
For example: In the Microsoft price chart, a trader might use a 30-minute timeframe in combination with RSI indicators and market news to assess and identify the price trend of MSFT stock. On July 30, 2024 news was released that Microsoft's cloud growth missed estimates in Q4 (Yahoo Finance!). This could lead to a negative market reaction, potentially causing a decline in the stock price.
Trade:
you should consider opening a position—either selling or buying—depending on the direction indicated by your price trend analysis.
For example: If your analysis indicates a downward trend in MSFT stock but the RSI shows it as oversold, you might open a buy position, anticipating a short-term price recovery. However, with this strategy, always remember to use a stop-loss order to limit potential losses in case the stock continues to decline.
Track and analyze your trade:
Afterward, review your simulated trades to assess what strategies were effective and which ones were not. This analysis will help you refine your trading approach and improve your decision-making in future trades.
Day trading necessitates that traders spend a significant amount of time observing the markets during trading hours to understand price action, volume, and volatility.. This real-time monitoring helps traders respond quickly to market movements and identify trends. Regular practice and simulation of trades are essential for honing skills, refining strategies, and improving decision-making. The more a trader practices and analyzes their trades, the better they become at navigating market complexities and managing risk.
4. The best times to day trade
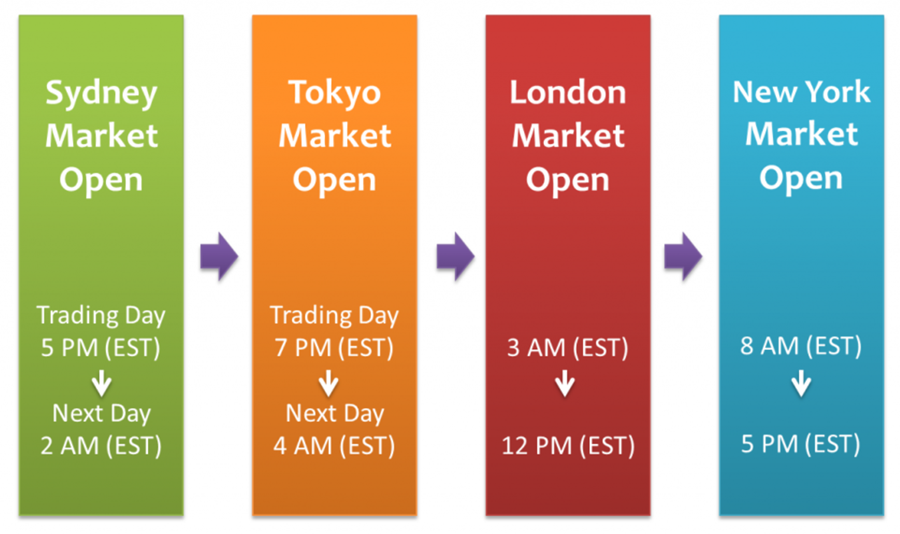
Source: amazonaws.com
Day trading involves capitalizing on short-term price movements, and certain times of the trading day are more conducive to this activity than others due to increased volatility and liquidity. Here are the best times to day trade, along with explanations of why these periods are advantageous:
Generally, the first hour following the market opening (9:30 AM to 10:30 AM Eastern Time in the U.S. stock market) is among the most volatile periods.The market opens with high trading volume as orders from the previous night and morning get executed. This leads to significant price movements. Additionally, overnight news, earnings reports, and economic data often drive volatility during this period, creating opportunities for traders to profit from rapid price changes. The opening hour often sets the tone for the day, with prices adjusting to new information, making it a prime time for trading breakouts and reversals.
Late Morning (Around 10:30 AM - 12:00 PM): This period follows the initial burst of volatility and volume, but still offers good trading opportunities. By this time, the market often settles into trends established during the first hour, providing opportunities for trend-following strategies.
Afternoon Session (1:30 PM - 3:30 PM): This period sees an uptick in activity as traders return from lunch and position themselves for the market close. As the market nears its close, there is often an increase in trading activity, especially as traders adjust positions or react to news.
Last hour of trading (3:00 PM - 4:00 PM):The final hour of the trading day is often referred to as the "power hour”. Similar to the market opening, the final hour often experiences a surge in trading volume as traders finalize their positions for the day. Moreover, institutional investors and funds often make significant trades during this time, leading to sharp price movements.
5. Risk management in day trading
Risk management is a crucial aspect of day trading, as it helps protect your capital from significant losses and ensures long-term sustainability in trading. Given the inherent volatility and fast-paced nature of day trading, effective risk management strategies are essential for minimizing potential losses and maximizing profitability.
Here are the tips that can help day traders manage risks:
Determine risk tolerance: Assess your comfort level with risk, which will influence how much capital you allocate to each trade and the strategies you employ.
Set risk limits per trade: Fixed Dollar Amount or Percentage: Establish a maximum amount you're willing to risk on a single trade, typically expressed as a percentage of your total trading capital (e.g., 1-2%). Example: If you have a $5,000 trading account and set a 1.5% risk limit, you would risk $75 per trade.
Use Stop-loss orders: Always implement a stop-loss order when opening a position to help manage risk and protect your capital from excessive losses. Example: Place stop-loss orders based on technical analysis, such as below key support levels for long positions or above resistance levels for short positions.
Avoid overleveraging: Use leverage cautiously and ensure that leveraged positions align with your risk tolerance and risk management plan. Be aware of margin requirements and the risk of margin calls, which can force the liquidation of positions at unfavorable prices.
Position sizing: Determine the appropriate position size based on your risk per trade and the distance to the stop-loss level.
Formula: Position Size = Risk per Trade / (Entry Price - Stop-Loss Price)
Example: If your risk per trade is $100, the entry price is $50, and the stop-loss price is $49, then Position Size = $100 / ($50 - $49) = 100 shares.
Emotional discipline: Emotional decisions often lead to excessive risk-taking. Adhere strictly to your trading plan and risk management rules, especially during periods of market volatility or personal stress.
Implementing these risk management strategies can help you navigate the challenges of day trading and protect your trading capital. Remember, successful day trading is not just about making profitable trades but also about managing losses effectively to ensure long-term success.
6. Summary
Day trading is an exciting but challenging endeavor that offers the potential for significant profits within short time frames. However, it requires a thorough understanding of the market, disciplined risk management, and continuous learning. Successful day traders rely on well-developed strategies, including the use of stop-loss orders, appropriate position size, and trading during optimal market hours.
By consistently practicing, managing risks carefully, and staying informed, traders can navigate the fast-paced world of day trading and aim for consistent profitability. Ultimately, day trading success comes from a blend of knowledge, discipline, and adaptability.
Before making any trading decisions, it is important to equip yourself with sufficient fundamental knowledge, have a comprehensive understanding of market trends, be aware of risks and hidden costs, carefully consider investment targets, level of experience, risk appetite, and seek professional advice if necessary.
Furthermore, the content of this article is solely the author's personal opinion and does not necessarily constitute investment advice. The content of this article is for reference purposes only, and readers should not use this article as a basis for any investment decisions.
Investors should not rely on this information as a substitute for independent judgment or make decisions solely based on this information. It does not constitute any trading activity and does not guarantee any profits in trading.
If you have any inquiries regarding the data, information, or content related to Mitrade in this article, please contact us via email: insights@mitrade.com. The Mitrade team will carefully review the content to continue improving the quality of the article.












