
Traders leverage various strategies to try and squeeze optimum profits as prices fluctuate in the financial markets. While some strategies are aggressive, trying to take advantage of the slightest price movements, others are more conservative, trying to balance risk and reward. Position trading is one of the popular strategies leveraged by long-term investors or traders.
1. What is Position Trading?
Position trading is a trading strategy akin to investing, whereby traders hold positions for weeks or months. Instead of focusing on taking advantage of short-term price movements, traders focus on long-term price movements while shunning short-term swings or fluctuations.
It is an ideal trading strategy for people less disturbed by short-term price fluctuations or the day's news. Consequently, traders time their trades to benefit from a lucrative trend when the price is moving toward the long-term trend.
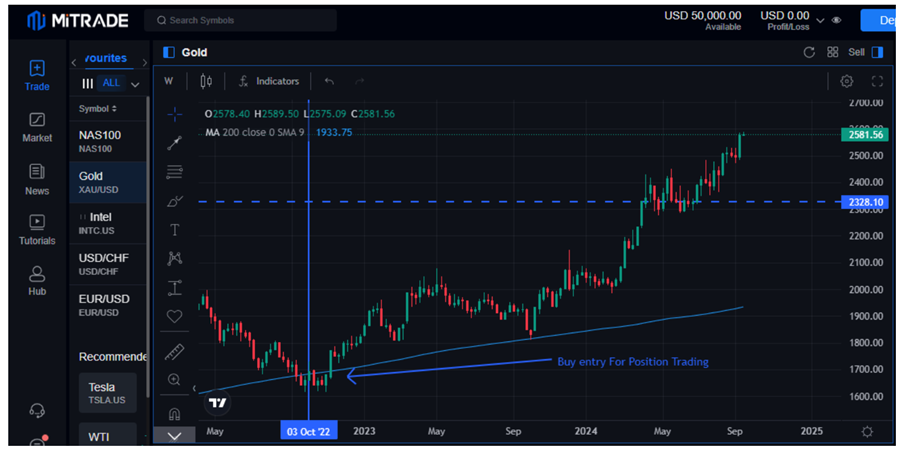
Image Source: Mitrade
The chart above clearly shows gold has been in an uptrend since October 2022. Position traders have accumulated significant profits on buying the precious metal
When traders hold positions for extended periods, they consider technical and fundamental analysis. Technical analysis focuses on the price fluctuations on the chart, which different indicators can enhance. Fundamental analysis examines the impact of broader economic factors such as gross domestic product, inflation, employment, and so on affect the value of a specific security.
Characteristics of Position Trading
Some of the key traits of position trading include:
Long-term trading positions: Traders only open positions to hold for weeks or even months to squeeze optimum profits before a given trend reverses.
Time-saving: It's often considered a time-saving strategy as it does not require frequent chart checks. While a good amount of time is spent on analysis to try and identify long-term trends, once a trade is opened, a stop loss and take profit levels are opened, and the trade is left to run.
Prone to trend reversals: One of the biggest risks with position trading is that positions are always exposed to potential trend reversals. Since traders ignore slight fluctuations, there is always the risk of the trend reversing, resulting in losses.
Patience and Discipline: The trading strategy is ideal for traders with extreme discipline and patience. It's the only way to let a trade run its course while ignoring short-term swings that can result in losses.
Financially Demanding: The trading strategy is financially demanding as traders require significant capital amounts to shrug off the effects of short-term price swings that can result in losses.
Lost Opportunity: Position trading can lead to missed profits because it ties a specific amount of capital to a position for an extended period of time.
2. The pros and cons of position trading
Advantages:
It is a less risky trading strategy compared to scalping swing or day trading, given the long-term element involved.
It is a time-saving trading strategy whereby traders conduct technical and fundamental analyses to identify long-term trends. After initiating a trade, there is no further action required for weeks or months.
Position trending allows traders to think through every entry, reducing the risk of making trades out of pressure or fear of missing out.
Position trading works best in the stock market, where traders hold positions for weeks or even months and can, therefore, receive dividend payments whenever the company makes them available. Consequently, it provides a way of generating passive income in addition to price increases.
The fact that traders enter and exit positions less often translates to reduced trading costs and optimum returns
Disadvantages:
It is a financially demanding strategy as one must have significant capital in an account to support trade through various market swings.
Position trading can also lead to missed opportunities because it focuses on long-term trades and needs to take advantage of new opportunities that arise over time.
Positional trading can also result in significant losses if a trader does not use proper risk management strategies to cut losses whenever a vital trend is reversed.
3. Strategies of Position Trading
Position trading involves earning profits over an extended period. Establishing a set plan for buying and selling and a target price is essential to break even.
# Strategy 1: Technical Analysis
It is arguably the most popular position trading strategy, and it is based on the belief that the history of asset volume and price fluctuations provides valuable insights into future price movements. Therefore, traders utilize trading indicators to examine previous price movements and predict their future direction.
Additionally, technical analysis entails the analysis of chart patterns to have a firmer understanding of what the market is doing and is likely to do in the future. In technical analysis, the focus is usually on determining key support and resistance levels and demand and supply zones.
Once traders identify a demand zone, it serves as a crucial support level, prompting positional traders to initiate buy or long positions, anticipating a price increase as part of an emerging uptrend. Similarly, traders can identify a supply zone that serves as a crucial resistance level, initiating short or sell positions in anticipation of price declines.
Example:
The chart below shows the gold XAUUSD chart, showing the price was trading near the demand zone between April and July.
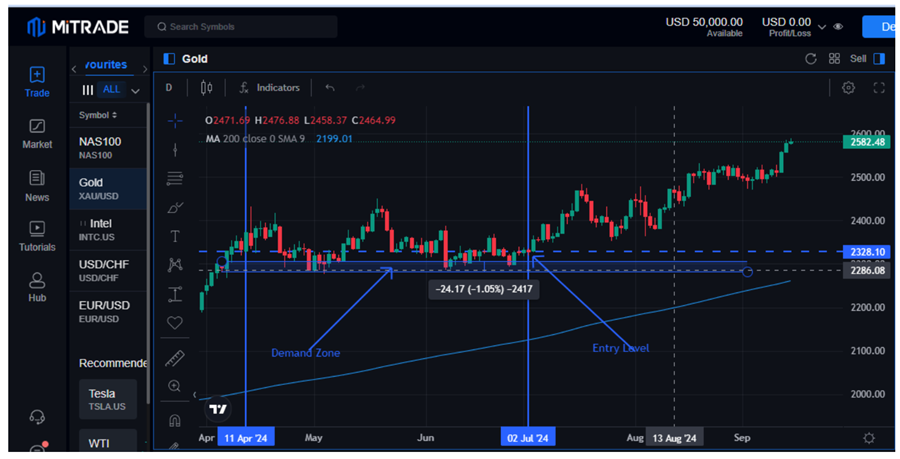
Image Source: Mitrade
Given that gold was trading in an uptrend above the 200-day moving average, it was clearly in an uptrend. Therefore, any pullback to the demand zone provided an opportunity for position traders to enter long or buy positions in anticipation of price edging higher. That is evident as gold broke out in July from the $2328 level and has since been trending up.
# Strategy 2: Fundamental Analysis
While technical analysis focuses on price action in charts to predict the direction in which price is likely to move, fundamental analysis focuses on underlying fundamentals, both internal and external, that are likely to affect an asset's performance.
Consequently, the fundamental analysis for position trading focuses on macroeconomic data. For instance, positional traders in the currency market can focus on economic reports such as gross domestic product, employment data such as son farm payroll, Retail sales data, and manufacturing data.
By analyzing the economic data, traders can try to predict the direction in which a given currency pair is likely to move over an extended period.
Position traders focused on the stock markets can look at companies' leadership, business artery financial reports, and core business performance to determine how a given stock is likely to perform.
Example:
Since 2023, EURUSD has been trading in a range, its upward momentum limited to a strengthened US dollar. The USD strengthened as the US Federal Reserve hiked interest rates to tame inflation, leading to euro weakness.
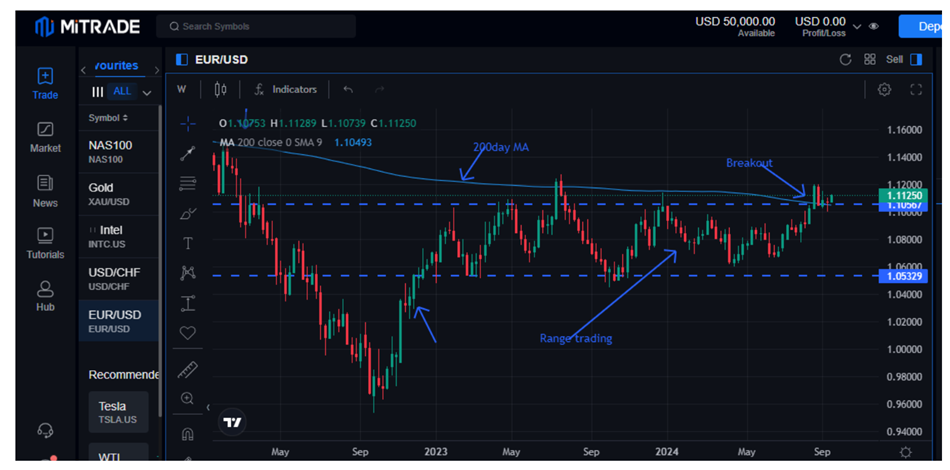
Image Source: Mitrade
Fast forward, the euro is showing signs of strengthening as the US central banks start cutting interest rates, which should lead to weakness in the USD. Consequently, the EURUSD shows signs of breaking out, allowing position traders to enter long positions.
# Strategy 3 Support and Resistance Strategy / Pull Back Strategy
It is a trading strategy whereby position traders base their trading ideas on how a given asset behaves at a given support or resistance level.
For instance, if there are more buyers at a given support level, a positional trader would look to open a buy position in anticipation of higher prices in the long run. Likewise, if there are more sellers in a given resistance level, a positional trader can look to open a sell or short position in anticipation of price dropping.
Remember, when you breach a certain level of support or resistance, its role changes.. For instance, should the price drop below a support level and continue moving lower, the support level becomes the resistance level. Likewise, should price power through a resistance level, it becomes an essential support level form where positional traders can look to enter long or buy positions.
It's thought that a shift in the balance of supply and demand happens when the price exceeds a support or resistance level, causing the previously breached level to switch back to being supportive or resistant.
Example:
The USDCHF chart showed a critical support level below 0.92230, which supported the USDCHF to the upside.
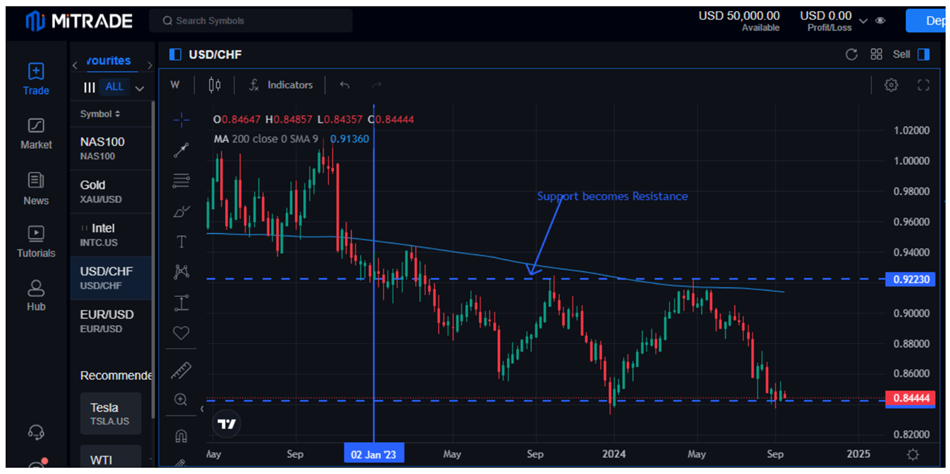
Image Source: Mitrade
Nevertheless, once it was breached in January, it became a key resistance level whereby any bounce back in price to the level attracted sellers who pushed the price lower. Consequently, position traders entered short or sell positions at 0.92230 throughout the year.
4. How to practice position trading
When practicing position trading, the idea is to identify the long-term trend to determine the direction in which the market is likely to move. In this case, technical analysis should commence on higher time frames regardless of the asset one is trading.
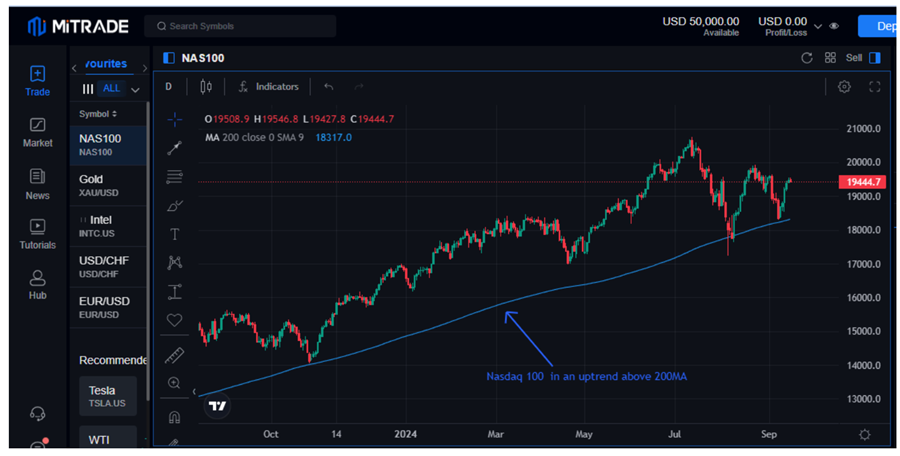
Image Source: Mitrade
Mitrade offers one of the best platforms for practicing position trading. Regardless of the asset one trades, one can access monthly and weekly charts of any asset to identify the long-term charts.
Once we determine whether an asset is in an uptrend or downtrend, we can shift our focus to the lower time frames to identify the ideal entry-level.Hourly or daily charts can provide valuable insights into the perfect entry levels.
5. Summary
Position trading is a popular strategy for traders looking to hold trades for weeks or even months. Therefore, it is a long-term thinking strategy akin to investing, as traders don't focus on short-term price fluctuation but on the broader picture or trend.
The plan works best when conducting an in-depth technical analysis to identify the long-term trend. Additionally, one should be able to perform a fundamental study to understand whether an asset is a buy or a sell depending on the underlying fundamentals.
6. FAQs
#What are the risks associated with position trading?
The risks include exposure to potential trend reversals, the need for significant capital to withstand short-term price swings, and the possibility of losing opportunities as capital is tied up in long-term positions. Proper risk management is crucial to mitigate these risks.
#How can I manage risk in position trading?
Risk management in position trading can be achieved through techniques such as setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and regularly reviewing your positions. It's also important to assess your risk tolerance and adjust your position sizes accordingly.
#How long should I hold a position in position trading?
The holding period in position trading can vary widely, typically ranging from several weeks to several years. The duration depends on the trader's strategy, market conditions, and the specific asset's performance. Traders should regularly evaluate their positions and adjust based on changing market dynamics.
Before making any trading decisions, it is important to equip yourself with sufficient fundamental knowledge, have a comprehensive understanding of market trends, be aware of risks and hidden costs, carefully consider investment targets, level of experience, risk appetite, and seek professional advice if necessary.
Furthermore, the content of this article is solely the author's personal opinion and does not necessarily constitute investment advice. The content of this article is for reference purposes only, and readers should not use this article as a basis for any investment decisions.
Investors should not rely on this information as a substitute for independent judgment or make decisions solely based on this information. It does not constitute any trading activity and does not guarantee any profits in trading.
If you have any inquiries regarding the data, information, or content related to Mitrade in this article, please contact us via email: insights@mitrade.com. The Mitrade team will carefully review the content to continue improving the quality of the article.





