Trading is an online global business practiced in more than 185 countries worldwide, where all transactions are executed as orders. Orders are the authoritative commands or instructions traders give to their broker to buy or sell a financial instrument under specific arrangements and conditions.
Among these order types, limit orders are particularly noteworthy. Limit orders instruct the broker to execute a trade only at a specified price or better.
1. What are limit orders?
A limit order is a type of trading instruction that allows you to buy or sell a financial asset (like a stock or currency) at a specific price or better. This is different from a market order, which executes the trade at the current market price.
With a limit order, you are telling your broker the exact price at which you want to enter or exit a trade. For example, you could place a limit order to buy a stock at $50 per share, or to sell it at $60 per share. The order will only execute if the market price reaches that limit price or becomes more favorable to you.
The main benefits of using limit orders are:
Price Control: Limit orders let you control the exact price you pay or receive, rather than accepting the current market price.
Preventing Losses: You can use a sell limit order to automatically close a position if the price moves against you, limiting your potential losses.
Capturing Profits: A buy or sell limit order allows you to lock in your target price to take profits when a trade goes your way.
Limit orders are very useful for traders and investors who want to be more strategic about their entry and exit points in the market. They provide more control compared to just relying on market orders alone.
2. All the types of limit orders
The types of limit orders practiced under the mentioned categories are presented below:
2.1. Buy Limit and Sell Limit Order:
#Buy limit
Buy limit order is also known as a Purchase Limit Order, where an order is placed to buy a security at a set price or lower than the set price. A buy limit order is mostly used in markets that are trending upwards.
Therefore one can wait for the price to pull back after moving higher significantly. In this case a buy limit order is placed a few pips below the prevailing price in anticipation of a pull back that would allow one to buy low therefore accrue more profits once price pulls back hits the limit orders and continues moving up in continuation of the uptrend.
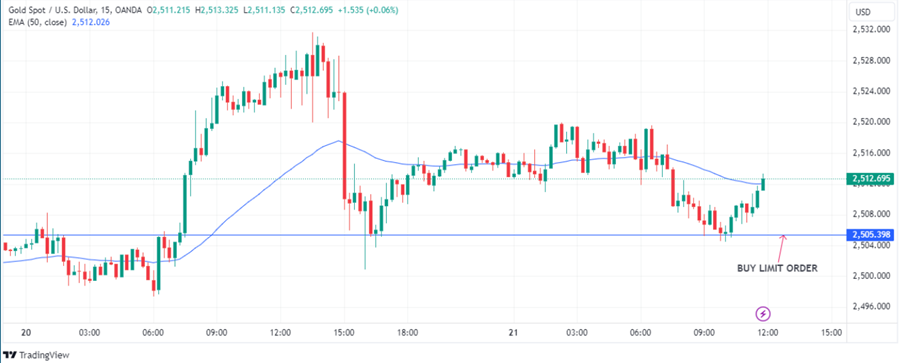
Source: Tradingview
Example: The current price of XAUUSD is 2512.69 and says one is willing to buy this commodity at 2505.39 in anticipation of price pulling back before moving higher, they can do so with a buy limit order.
#Sell limit
Sell limit order is an order to sell a security at a set price or higher than the set price.The limit order is mostly used whenever a trader believes a given price will bounce back and afterwards move lower in continuation of a long term sell off. Therefore a sell limit order allows people to sell higher for higher returns when the market moves lower.
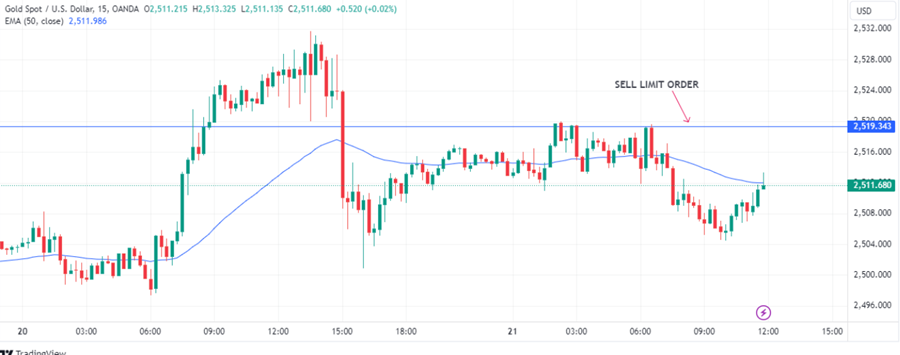
Source: Tradingview
Example: The current price of XAUUSD is 2511.68, and one is willing to sell this commodity at a price higher, so a sell limit order is set at 2519.34.
2.2. Buy Stop Limit Order & Sell Stop Limit Order:
#Buy Stop Limit Order
Buy Stop Limit Order is a tailor-made purchase strategy that unites limit and stop orders. At the stop order price, it executes a purchase limit order.
Example: The current price of XAUUSD is 2507.23 and says one is willing to buy this commodity under a specific condition only if the market reaches 2508.23 and one is willing to buy the commodity at or under 2509.23. The stop limit order is placed where the stop order is at 2508.23, and the limit order is at 2509.23.
#Sell Stop-Limit Order
Sell Stop-Limit Order is a tailor-made selling instruction to the broker that unites limit and stop orders. At the stop order price, it executes a selling limit order.
Example: The current price of XAUUSD is 2507.23 and says one is willing to sell this commodity under a specific condition only if the market falls to 2506.23 and one is willing to sell at or above 2505.23. The sell stop limit order is placed where the stop order is 2506.23, and the limit order is 2505.23.
2.3. Good -Til - Canceled (GTC) Limit Order:
A Good Till Canceled limit order is a special type of limit order that remains valid until a trader cancels it or it is executed. The order is mainly used whenever people wish to buy or sell securities at a specific price but are unsure when the price will reach that level.
Consequently, the limit order allows traders to place an order and wait for the market to move in their favor. The order can remain valid for up to 365 days.
Example: If a stock is trading at $50 a share and a trader opens a GTC buy order at $30, the order will remain open until the day the stock price pulls to the $30 level. If the price drops to $30, the order will trigger automatically, opening a buy position.
The order remains valid until the trader cancels it. For example, in the Forex Market, all limit orders are, by default, GTC Limit orders.
2.4. Day Limit Order:
A day limit order is a type of limit order that must be executed on a given day. The order will execute automatically if the price pulls to the specified level. In this case, the day order can be a limit for buying or selling a security.
On the other hand, if the price does not pull back or bounce back to the specified level before the end of the day, the day limit order expires at the end of the trading session. Consequently, it expires if the order is not executed when a trader places it.
Example: Intraday orders are present in many markets like Indian Markets where intraday orders are placed; brokers remove them once the trading day is over in case of non-execution.
2.5. Fill or Kill (FOK) Limit Order:
A fill or kill limit order is commonly used in the stock market to ensure a given amount of shares of a given stock are purchased at a specific price and at a specified time. Therefore, it is a conditional order that requires a transaction to be executed immediately and to its full amount at a specific price point.
Any slight change in the amount of stock price or time can impact the execution of the fill or kill limit order.
Example: Assume an investor wishes to buy 40,000 shares of Company XYZ stock at a maximum price of $20 per share. They can submit a fill or kill order to meet their needs. After submission, the order will attempt to be executed right away. Should the fill or kill order fail to obtain the desired quantity of shares, at $50/share, or the transaction not be finalized promptly, the FOK order would automatically cancel the order.
2.6. Limit Order: Immediate or Cancel (IOC):
It is one of the many duration order types that investors use to specify how long an order can remain active in the market and under what conditions it should be closed. The Immediate or Cancel limit order, when used, instructs the broker to execute a buy or sell order in part or in full immediately and then cancel any unfulfilled portion of the order.
Example: Consider a trader placing an IOC order to purchase 10,000 shares of company ABC at $30 per share. Any portion of the 10,000 shares that will not be purchased immediately at the defined price point will automatically cancel.
 0 commission, low spreads
0 commission, low spreads Diverse risk management tools (limit orders)
Diverse risk management tools (limit orders) Flexible leverages and instant analysis
Flexible leverages and instant analysis Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money
Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money 
3. How Limit Orders Work
Limit orders are predetermined levels where demand and supply zones are taken out using technical analysis, and advance orders are placed at research levels.
Detailed Explanation of Buy Limit Orders:
Buy Limit orders control traders' expenses and risk by outlining the maximum or highest price one is willing to pay for the security. First, let us understand how buy-limit orders work.
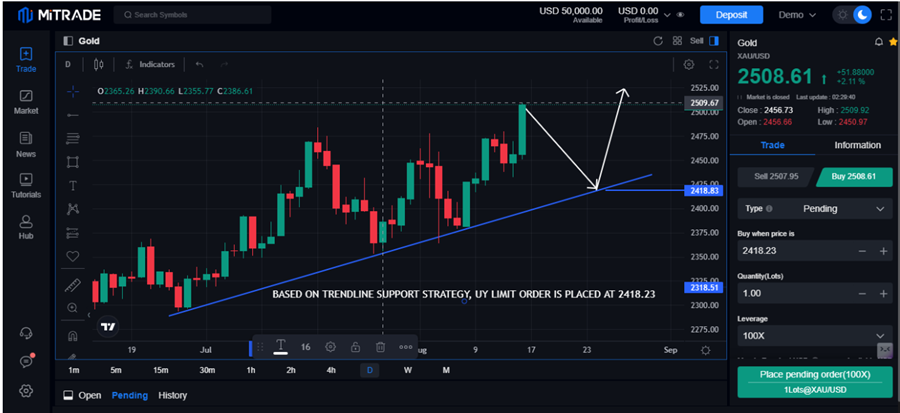
Source: Mitrade
Example: The current price of XAUUSD is 2508.61, and the trader is willing to buy this commodity at a support, so a buy limit order is set at 2418.23 using a trendline support strategy.
Detailed Explanation of Sell Limit Orders
A Sell limit order controls the trader's expense and risk by outlining the lowest price one is willing to accept for the security. A sell limit order is used to book profit or to initiate a short position. First, let us understand how to sell limit order works:
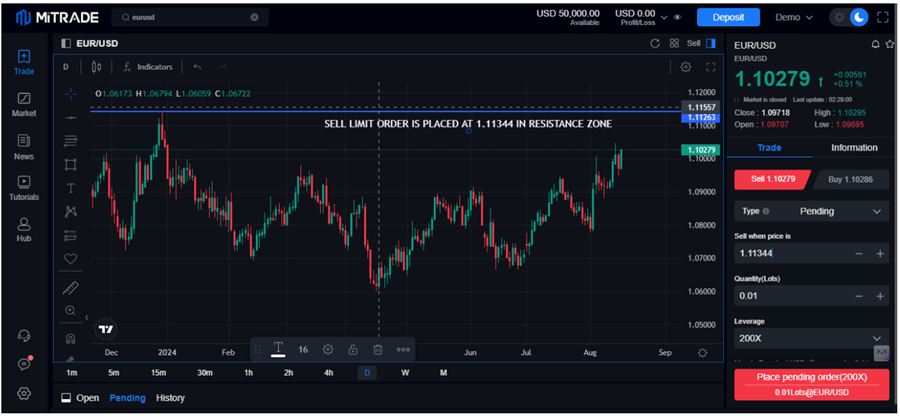
Source: Mitrade
Example: The current price of EURUSD is 1.10279, and the trader is willing to sell this currency pair at a price at resistance either to book profit to initiate a short position, so a sell limit order is set at 1.11344
Difference between Market Orders and Limit Orders
Limit Orders: Focus on managing prices with limited assurance of immediate execution. Traders can set their desired trade price, but transactions may not occur if the prices don't match an existing offer.
Market orders: They have no control over the precise price but concentrate on quick execution. They guarantee the deal is filled quickly, although they might cause price changes.
4. Scenarios For Using Buy Limit And Sell Limit Orders
The scenarios for using a Buy Limit Order are purchasing security at a discounted price and managing pullbacks or limited liquidity.
The scenarios for using a Sell Limit Order are selling a security at a high price, automating the selling strategy based on market expectations, taking profits at target levels, and exiting at resistance points.
By lining up transactions with particular price points and investment methods, both varieties of limit orders provide traders with more control over their trading decisions.
• Determining exact locations for entry and departure.
• Using technical analysis in conjunction.
• Controlling slippage and volatility.
• Automating transactions for ease of use.
• Complying with risk-reduction techniques.
• Selecting the appropriate order duration.
• Consistently keeping an eye on and modifying orders.
These tactics help to enter the intelligent money category, for they always prefer limit orders, as these orders provide trading accuracy and effective risk management.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages Of Limit Orders
Advantages:
Price control guarantees that an agreed-upon price is met or exceeded.
Prevents Slippage: Stops money from being spent or received differently than planned.
Strategic Execution: Enables accurate places of entry and departure.
Automated trading lessens the need for continual market observation.
Cost Efficiency: Prevents unfavorable pricing swings, aiding cost management.
Disadvantages:
Execution Risk: If the market price falls short of the limit, orders might not be filled.
Potential Expense: Trades lost if the market exceeds your limit price.
Orders may be partially filled if there is not enough liquidity.
Order management calls for tracking and making adjustments to orders.
Possible Delays: In erratic or low-liquidity markets, execution could take longer.
6. Limit Order Strategies
Buying the Dip: Use purchase limit orders at support levels when prices decline.
Selling the Rally: During a price uptrend, place sell limit orders at resistance levels.
Scaling In and Out: Use numerous limit orders to increase or decrease the number of places gradually.
Trading Breakouts: Place buy limit orders above necessary technical levels to enter trades when a breakout occurs.
Trade price reversions to the mean using limit orders predicated on circumstances where the market is overbought or oversold.
Trade price gaps by limiting orders at gap-fill levels or probable reversal points. This strategy is known as gapping.
Trend Following: At crucial price points, match limit orders to the current trend.
Combining market and limit orders for particular entry or exit criteria results in market orders with limit conditions.
7. FAQs
# How do limit orders help market makers in bulk buying and bulk selling?
Market makers are smart money whose buying and selling volumes make a huge difference in the market, and their orders are enormous compared to retail investors. They are range traders, and unlike retail investors, they do not chase prices. They do bulk trading in a range, and their buying results are in the accumulation phase, and their selling results are in the distribution phase. These phases are the results of their limit orders.
#How do I find out the right limit price?
A market is a history that repeats itself in the future; hence, history repeats itself in the market. Market history helps you find the potential demand and supply zone. Using technical analysis tools like support and resistance, candlesticks, trends, patterns, and indicators on past market data, you can predetermine potential demand and supply zones and place your limit orders according to your research.
#Is a Stop Limit Order associated with breakout trading?
Yes, stop limit orders can be used in breakout trading where a stop order is placed at a breakout level in the market, and a stop order is executed only when the breakout happens following limit order execution.
Before making any trading decisions, it is important to equip yourself with sufficient fundamental knowledge, have a comprehensive understanding of market trends, be aware of risks and hidden costs, carefully consider investment targets, level of experience, risk appetite, and seek professional advice if necessary.
Furthermore, the content of this article is solely the author's personal opinion and does not necessarily constitute investment advice. The content of this article is for reference purposes only, and readers should not use this article as a basis for any investment decisions.
Investors should not rely on this information as a substitute for independent judgment or make decisions solely based on this information. It does not constitute any trading activity and does not guarantee any profits in trading.
If you have any inquiries regarding the data, information, or content related to Mitrade in this article, please contact us via email: insights@mitrade.com. The Mitrade team will carefully review the content to continue improving the quality of the article.