BoE set for a second interest rate cut this year on Thursday
- Investors expect the Bank of England to cut its policy rate by 25 bps.
- UK disinflationary pressure gathered further steam in September.
- The 200-day SMA near 1.2810 holds the downside in GBP/USD.
Market consensus points to further easing by the Bank of England's (BoE) upcoming interest rate decision on Thursday. The BoE has held rates steady at 5.00% in the previous gathering, but shifting investor sentiment now suggests a possible 25-basis-point cut this week.
No surprises are expected at the BoE meeting
At the bank’s September 19 meeting, policymakers stuck to quarterly rate cuts for now, with a November cut the most likely outcome. Regarding quantitative tightening, the committee voted unanimously to maintain the pace of reducing bond holdings by GBP 100 billion over the next 12 months, which again was in line with expectations.
The only dovish elements were the slight downgrades to Q3 GDP and Q4 CPI, though this is more a case of marking to market, which of course is subject to change depending on incoming data.
Looking ahead, indicators of inflation persistence—labour market tightness, private pay growth, and services CPI—should continue to guide policy.
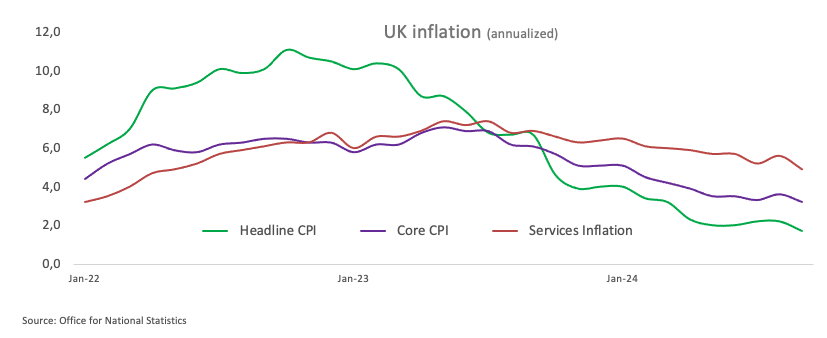
Back to inflation, the headline Consumer Price Index (CPI) receded to 1.7% YoY in September, while the core CPI (which excludes food and energy costs) eased to 3.2% over the last twelve months, and Service inflation remained elevated at 4.9% from a year earlier.
Following the September BoE event, policymaker Catherine Mann expressed a cautious stance on the likelihood of multiple interest rate cuts in the coming months, emphasizing the importance of keeping policy restrictive.
However, early in October, Governor Andrew Bailey indicated that the Bank of England could take a "more activist" approach to rate cuts if there is continued positive news on inflation. Aligning behind Mann’s approach, Chief Economist Huw Pill stated that the British central bank should adopt a gradual approach when reducing interest rates.
Ahead of the BoE’s meeting, TD Securities analysts noted: “We anticipate a 7-2 majority to cut Bank Rate by 25bps and little change from September's guidance. Incoming growth and inflation data has been softer than the MPC expected in their August projection, but the budget will force some tweaks to the projection (but these will be less positive than markets expect). We do not expect any signal about December's policy decision.”
How will the BoE interest rate decision impact GBP/USD?
Even though the inflation pressure slowed its pace in September, market participants still appear to favour a rate cut at the BoE's monetary policy meeting on November 7 at 12 GMT.
FXStreet’s Senior Analyst, Pablo Piovano, notes that a rate cut could put further pressure on the British Pound, which could see additional downside if GBP/USD falls below its November low of 1.2833 (November 6). In that case, the next contention should emerge at the key 200-day SMA at 1.2811, prior to the July low of 1.2615.
“On the upside, bulls will be initially eyeing the provisional 55-day SMA at 1.3119. The breakout of that region could put a potential visit to the 2024 peak at 1.3434 (September 26) back into focus”, Pablo concludes.
Economic Indicator
BoE Interest Rate Decision
The Bank of England (BoE) announces its interest rate decision at the end of its eight scheduled meetings per year. If the BoE is hawkish about the inflationary outlook of the economy and raises interest rates it is usually bullish for the Pound Sterling (GBP). Likewise, if the BoE adopts a dovish view on the UK economy and keeps interest rates unchanged, or cuts them, it is seen as bearish for GBP.
Read more.Next release: Thu Nov 07, 2024 12:00
Frequency: Irregular
Consensus: 4.75%
Previous: 5%
Source: Bank of England
BoE FAQs
The Bank of England (BoE) decides monetary policy for the United Kingdom. Its primary goal is to achieve ‘price stability’, or a steady inflation rate of 2%. Its tool for achieving this is via the adjustment of base lending rates. The BoE sets the rate at which it lends to commercial banks and banks lend to each other, determining the level of interest rates in the economy overall. This also impacts the value of the Pound Sterling (GBP).
When inflation is above the Bank of England’s target it responds by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is positive for the Pound Sterling because higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls below target, it is a sign economic growth is slowing, and the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit in the hope businesses will borrow to invest in growth-generating projects – a negative for the Pound Sterling.
In extreme situations, the Bank of England can enact a policy called Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the BoE substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. QE is a last resort policy when lowering interest rates will not achieve the necessary result. The process of QE involves the BoE printing money to buy assets – usually government or AAA-rated corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Pound Sterling.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE, enacted when the economy is strengthening and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Bank of England (BoE) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to encourage them to lend; in QT, the BoE stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive for the Pound Sterling.




