Dow Jones Industrial Average rebounds after Fed holds the line
- Equity markets rallied after the Fed stuck to its guns on 2025 rate cuts.
- Despite growing risks and concerns, especially around tariffs, Fed still sees rate cut hope.
- Dow climbed over 500 points, while the S&P 500 added 90 points.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) gained ground on Wednesday, adding around 540 points at its peaks with equities climbing higher after the Federal Reserve (Fed) gave a nod to still expecting around two rate cuts through the remainder of the year. Despite growing headwinds from ham-handed policy from the Trump administration, Fed policymakers continue to lean on signs of still-strong growth and strength within the US labor market, even as growth forecasts get another haircut.
The Dow Jones climbed back over the 42,000 major price handle and the Standard and Poor’s 500 (S&P 500) rose around 1.5% as equities tilted back into the bullish side following the latest rate call from the Fed. Fed Chair Jerome Powell noted that growth projections for 2025 have been significantly hindered by the Trump administration's erratic policy of announcing trade tariffs on social media only to later retract them. As a result, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) revised its end-2025 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) forecast to 1.7%, a sharp decline from the 2.1% estimate shared in December.
Fed's Powell: We are not going to be in any hurry to move on rate cuts
Additionally, the median dot plot suggests that the end-2025 interest rate will remain at 3.9%, indicating little change since the last policy meeting. The FOMC plans to begin slowing down its balance sheet runoff starting in April. Rate markets continue to signal a greater than 50% chance of a quarter-point rate cut in June, with most rate traders assigning a 65% probability of a quarter-point or larger cut on June 18.
Despite rising risks to the US economy from lagging growth metrics and increasing concerns that the US's erratic tariff policy could trigger both new inflation and an economic recession simultaneously, Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated on Wednesday that the current economic outlook remains generally healthy, and the Fed is not in a hurry to alter its expectations of at least two more rate cuts later in the year.
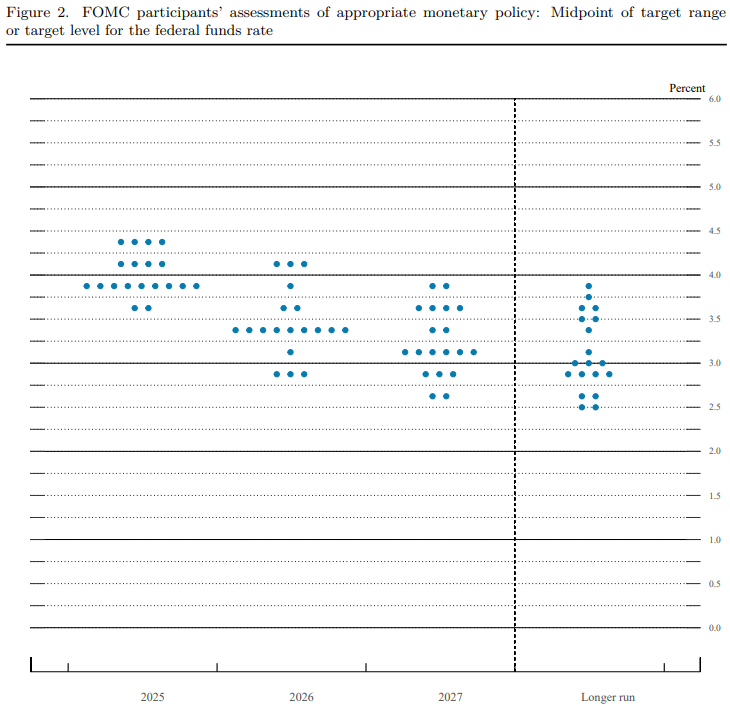
This policy outlook aligns with the aggregate score of Fed policymaker speeches, evaluated by FXStreet's internal Fed Sentiment Index, which indicates that Fed speakers have been vocal about the increasing risks and concerns facing the US economy. However, the overall sentiment remains slightly toward the dovish side, though close to neutral, as the Fed awaits clearer data direction.
In other stock news, Boeing is back on the rise as order filling for 737 jets take off.
Dow Jones price forecast
Despite Wednesday’s bullish print, the Dow remains hindered by the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near the 42,000 key handle. Price action has gathered its feet back under it following a near-term plunge that saw major equity indexes test into correction territory, but bids remain on the hopeful side as technical barriers weigh.
Dow Jones daily chart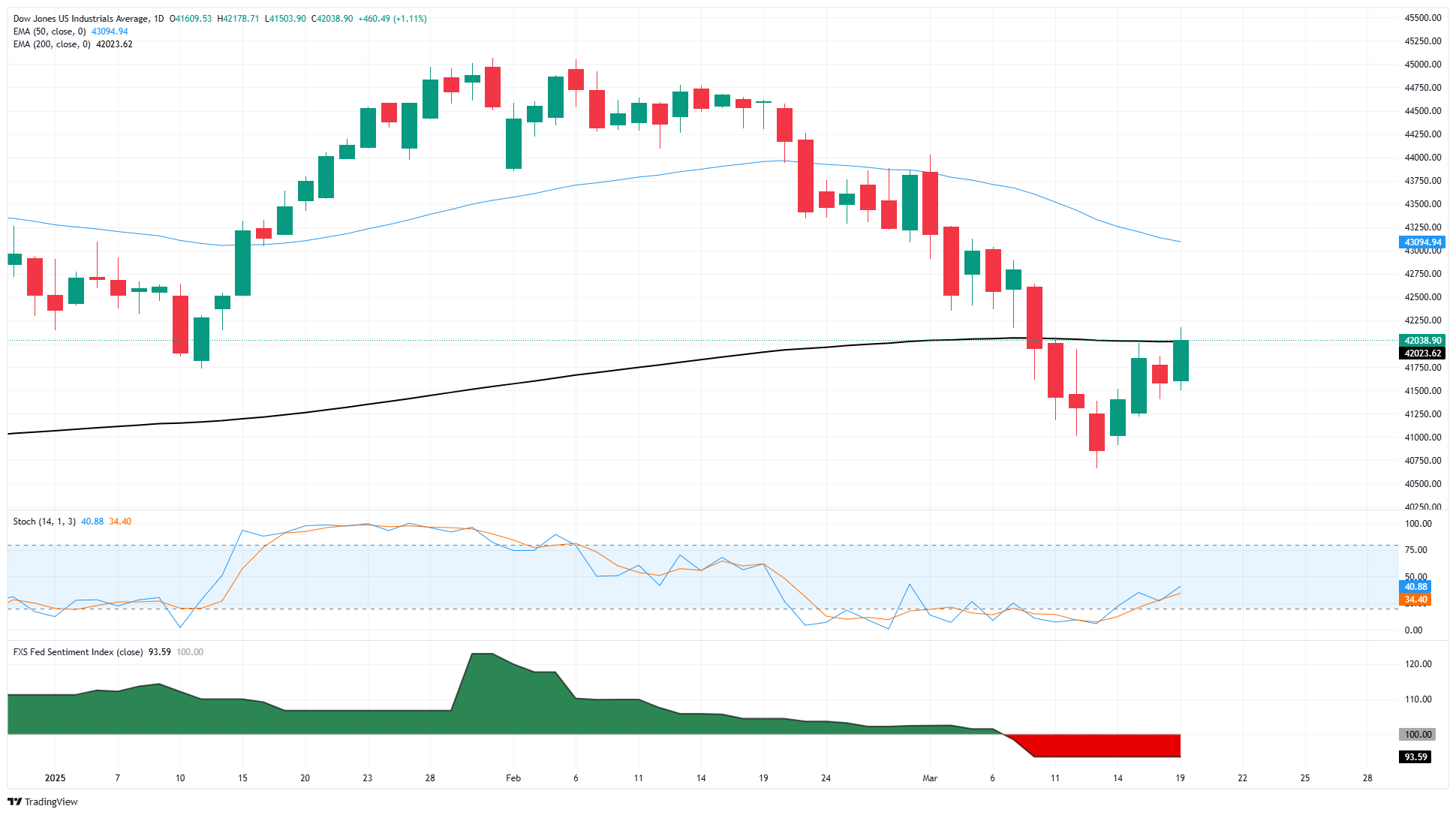
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.


