US Dollar flat as geopolitical takes centre stage
- The Greenback steadies and trades sideways on Monday after a soft start in Asia.
- All eyes shift back to geopolitics, with the Biden Administration delivering the green light for Ukraine to use long-range US missiles for targets in Russia.
- The US Dollar index holds ground above 106.50 while looking for direction.
The US Dollar (USD) consolidates on Monday after a very calm start of the week in the Asian session, with the US Dollar Index (DXY), which gauges the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, slightly in the red near a fresh year-to-date high reached last Thursday above 106.50. The main driver for the currency on Monday is the green light from the Biden Administration on Sunday for Ukraine to use long-range US missiles to target Russian infrastructures within Russian borders, just ahead of the G20 meeting in Rio De Janeiro this Monday.
The US response comes after Moscow deployed nearly 50,000 troops to Kursk, the southern Russian region. Reporting on that, “the change comes largely in response to Russia's deployment of North Korean ground troops to supplement its own forces, a development that has caused alarm in Washington and Kyiv,” Reuters said.,.
The US economic calendar is very light this Monday. Besides a speech by Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago President Austan Goolsbee, nothing really market moving on the docket. Markets will instead look out for the G20 meeting and comments around Ukraine.
Daily digest market movers: The storm has passed
- It is a very calm start to the week, and all eyes will shift to Rio de Janeiro in Brazil for the G20 summit, where Ukraine will be high on the calendar. Headlines around Ukraine started to pick up again last Friday when German Chancellor Olaf Schultz had a phone call with Russian President Vladimir Putin after nearly two years of radio silence. Over the weekend, Russia launched its biggest missile and drone attack thus far in this conflict. In response, the US Biden administration provided a green light for Ukraine to use long-range US missiles to target tactical infrastructure within Russia.
- At 15:00 GMT, Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago President Austan Goolsbee delivers welcome remarks at the Financial Markets Group annual conference in Chicago.
- The National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) will release its monthly Housing Market Index for November at 15:00 GMT. The expectation is for a slight increase to 44 compared to 43 previously.
- Equities are very mixed at their start this Monday, with some minor losses and gains dispersed across the quote board. All eyes are on after the US closing bell on Wednesday when Nvidia will release its earnings.
- The CME FedWatch Tool is pricing in another 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the Fed at the December 18 meeting by 61.9%. A 38.1% chance is for rates to remain unchanged. While the rate-cut scenario is the most probable, traders have significantly pared back some of the rate-cut bets compared with a week ago.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 4.42%, just off the high printed on Friday at 4.50%
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Settle down boy!
The US Dollar Index (DXY) has undergone market repricing on President-elect Donald Trump having secured his presidential victory and gaining control of the House of Representatives and the Senate. For now, it looks like the past weeks’ moves have topped out and will start to ease a touch. levels seen before heading into the US Presidential Elections two weeks ago.
After a brief test and a firm rejection last Thursday, the 107.00 round level remains in play. A fresh yearly high has already been reached at 107.07, which is the static level to beat. Further up, a fresh two-year high could be reached if 107.35 gets taken out.
On the downside, a fresh set of support is coming live. The first support is 105.93, the closing level on November 12. A touch lower, the pivotal 105.53 (April 11 high) should avoid any downturns towards 104.00.
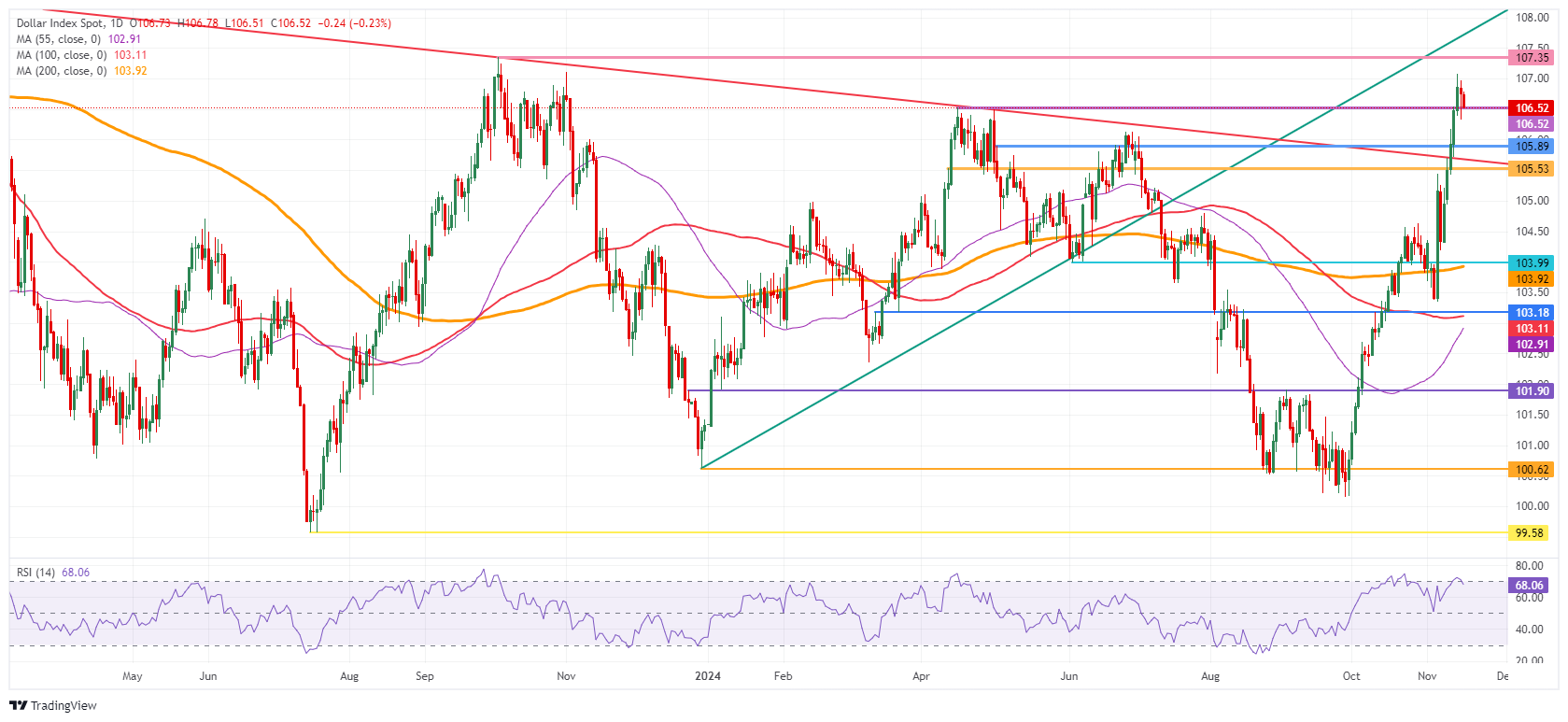
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.




