Gold price nears $3,000 as US economy shows signs of cooling
- Gold trades at $2,999, rising 0.40% as traders brace for the Federal Reserve’s policy decision on Wednesday.
- US Retail Sales disappoint, while manufacturing activity plummets, fueling recession fears and boosting rate cut expectations.
- Weaker US Dollar and lower Treasury yields support bullion with the 10-year T-note yield slipping to 4.308%.
Gold price rises on Monday late in the North American session, hoover near the $3,000 mark for the second straight day, after data from the United States (US) shows the economy is cooling. The XAU/USD trades at $2,999, up over 0.40%.
Risk appetite improved as reflected by US equities with traders shrugging off a weak US Retail Sales report for February. In addition, the New York Fed Empire State Manufacturing Index plunged, sparking fears that the economy might be tipped into a recession.
Therefore, money market futures are pricing in 64 basis points (bps) of easing by the Federal Reserve (Fed) toward the end of the year.
The main event during the week is the Fed’s monetary policy decision on Wednesday, followed by Fed Chair Jerome Powell's press conference and the release of the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP).
In the meantime, Bullion continued to climb, sponsored by falling US Treasury yields and a weaker US Dollar. The US 10-year T-note yield dropped one basis point to 4.308%. At the same time, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s performance against a basket of six currencies, fell 0.35% to 103.37.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price is unfazed by high US real yields, extends rally
- US real yields, as measured by the US 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) yield, which correlates inversely to Gold prices, rose four bps to 2.00% via Reuters.
- February US Retail Sales improved, increasing by 0.2% MoM, missing forecasts of 0.6%, up from January’s -1.2% plunge.
- The New York Fed showed that manufacturing activity dipped from 5.7 to -20, with input prices increasing to their highest level in over two years.
- Despite recent cooler-than-expected inflation data, economists caution that tariffs on US imports could lead to a renewed inflationary uptick in the coming months.
- UBS projects Gold to reach $3,200 in 2025. “With the price now reaching our long-held target of $3,000/oz, the main question is whether the rally will continue. We think so, as long as policy risks and an intensifying trade conflict continue to spur safe-haven demand,” UBS said.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price struggles to hold above $3,000
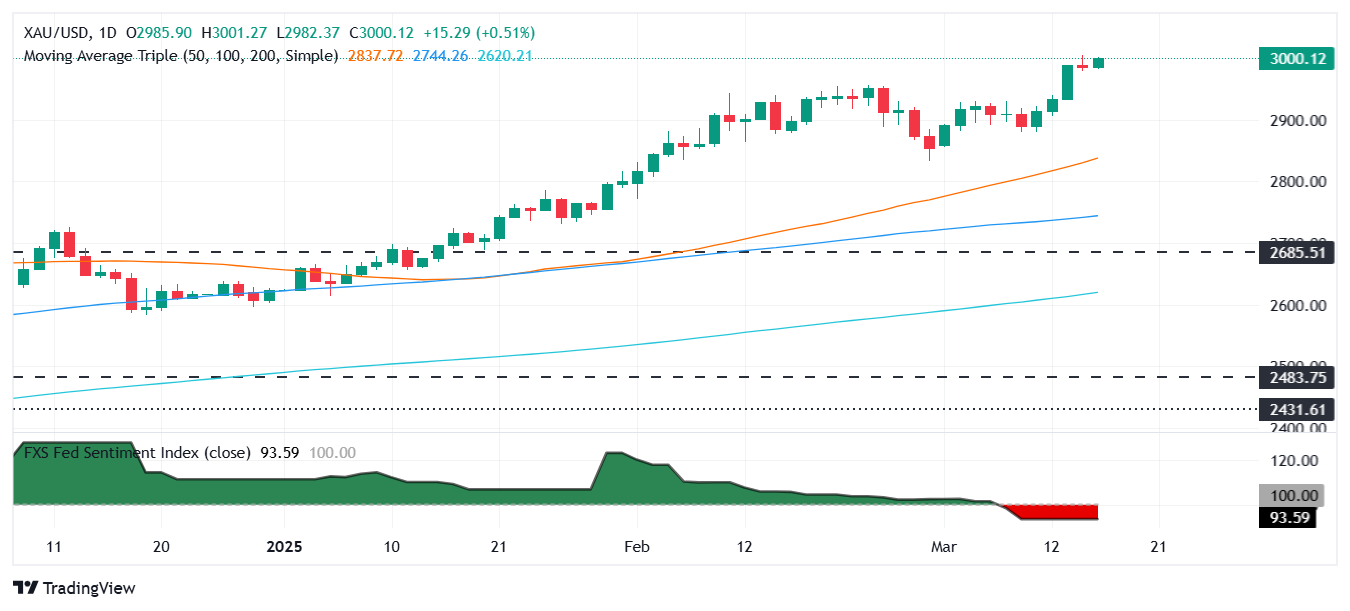
Gold prices remain near record highs yet fail to advance sharply as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) has exited overbought territory, opening the door for a pullback. It should be said there is a negative divergence with XAU/USD reaching higher prices, while the RSI failed to print new peaks.
Nevertheless, if XAU/USD clears the previous record high of $3,004, the next resistance would be $3,050 and $3,100. Conversely, a daily close below $3,000 could sponsor a retracement toward the February 20 daily high at $2,954, followed by the $2,900 mark.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.




