Gold plunges 3% weekly as trade policies, recession fears fuel USD rally
- Gold drops over 1% Friday as USD strengthens, hitting 10-day high at 107.66.
- XAU/USD falls to $2,845 as Fed rate-cut bets rise
- Trump confirms 25% tariffs on Mexico and Canada, fueling market uncertainty.
- Fed expected to cut rates by 70 bps in 2025 with first cut projected for June.
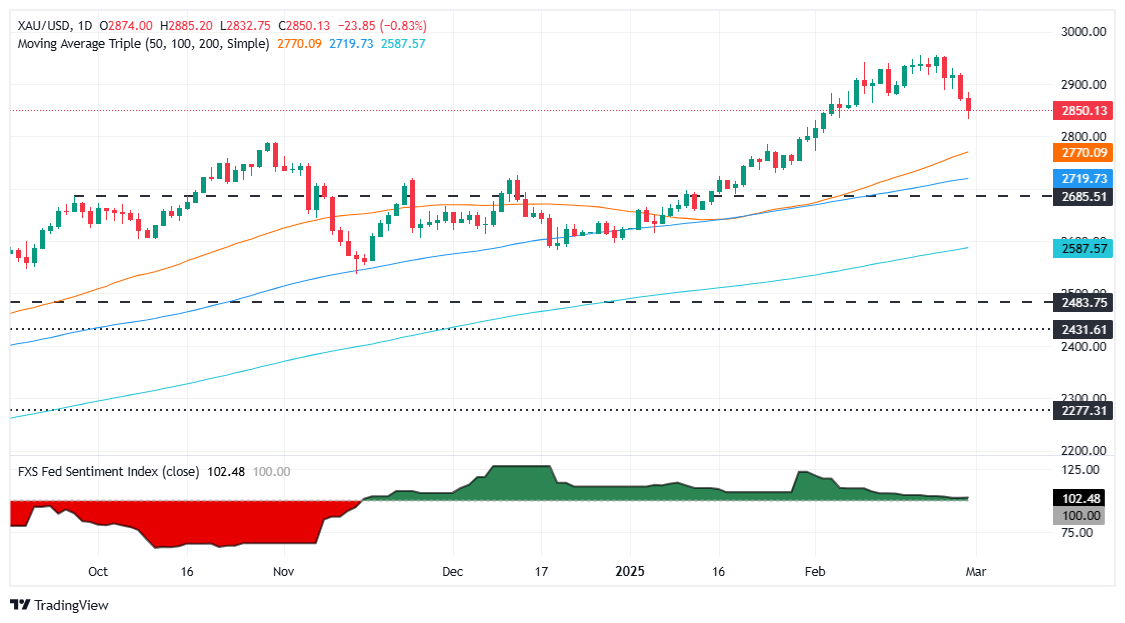
Gold extended its losses on Friday, down more than 1% and over 3% in the week. The US Dollar rose to a ten-day peak of 107.66 amid fears of trade policies in the United States (US) and data that has sparked recessionary worries. The XAU/USD trades at $2,845 after reaching a daily peak of $2,885.
According to US President Donald Trump, 25% tariffs on Mexican and Canadian products will be applied next week on March 4. The release of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) preferred inflation gauge, the Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, hinted that inflation continued progressing toward the 2% Fed goal.
Expectations that the Fed would continue to ease policy rose after the data. According to Prime Market Terminal, the Fed will lower interest rates by 70 basis points this year with investors projecting the first rate cut in June.
The Atlanta Fed GDPNow estimate has also been updated for Q1 2025. The model shows the economy will contract from a 2.3% expansion to -1.5 %. After the data, the 10-year US Treasury note yield dropped three basis points, and the US Dollar (USD) advanced on recession woes.
In the meantime, some Fed speakers crossed the wires. The Cleveland Fed’s Beth Hammack said that a rate hike is not in the cards, and the impact of trade policies on monetary policy and the economy remains uncertain.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price treads water as US recession looms
- The core PCE in the US rose 0.3% MoM from December and increased 2.6% YoY, as estimated, down from December's 2.8% increase.
- The headline PCE jumped by 2.5% YoY as expected, dipping from 2.6%, and remained unchanged every month at 0.3%, as projected.
- Meanwhile, traders continued to digest US President Donald Trump's tariff rhetoric. He said 25% tariffs on Mexico and Canada would start next week, alongside an additional 10% on China.
- The US 10-year Treasury note yield is at 4.229%, capping the Bullion price decline. US real yields, as measured by the yield in the US 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), edge lower five bps to 1.853%.
- Last week, Goldman Sachs revised Gold price projections to $3,100 by the end of 2025.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold extends losses beneath $2,850
Gold price registers back-to-back bearish candles, a sign that traders are booking profits ahead of the weekend and squaring their portfolios at the end of the month. Once XAU/USD dropped below $2,900, it extended its fall toward $2,832, but a daily close above 2,850 would keep buyers hopeful for higher prices.
In that outcome, XAU/USD first resistance would be the $2,900 mark, ahead of the year-to-date (YTD) high of $2,956. Otherwise, Gold’s first support would be $2,800, followed by the October 31 daily peak at $2,790 and by the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $2,770.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

