Gold price ticks higher in a familiar range; holds steady above $2,900 mark
- Gold attracts buyers for the second straight day amid concerns about a global trade war.
- Bets that the Fed would cut rates further lend support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
- A modest USD uptick might cap gains, though the bias remains tilted in favor of bulls.
Gold price (XAU/USD) trades with a mild positive bias above the $2,900 mark during the Asian session on Tuesday, though it lacks bullish conviction and remains confined in a familiar range that has held over the past week or so. Investors remain worried that US President Donald Trump's threat of reciprocal tariffs would trigger a global trade war. This turns out to be a key factor that continues to underpin demand for the safe-haven bullion.
Adding to this, expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) might cut interest rates further this year, bolstered by the unforeseen drop in US Retail Sales, offers support to the non-yielding Gold price. That said, a goodish bounce in the US Treasury bond yields and a modest US Dollar (USD) uptick hold back the XAU/USD bulls from placing fresh bets. Nevertheless, the uncertainty over Trump's trade policies should act as a tailwind for the commodity.
Gold price continues to attract haven flows amid worries about Trump’s trade policies
- US President Donald Trump threatened on Friday, saying that levies on automobiles would be coming as soon as April 2. This comes on top of Trump's reciprocal tariff plans on countries that charge duties on US imports and continues to underpin the safe-haven Gold price.
- The disappointing release of US Retail Sales figures on Friday, along with mixed signals on inflation, suggests that the Federal Reserve could possibly cut rates at the September or October policy meeting. Fed Funds Futures see the possibility of a 40 basis point rate cut in 2025.
- Philadelphia Fed President Patrick Harker said on Monday that the labor market is largely in balance and the current economy argues for a steady policy as inflation has been sticky over recent months. Future Fed rate policy choices will be data-driven, Harker added further.
- Fed Board of Governors member Michelle Bowman noted that high asset prices may have impeded progress on inflation and more certainty is needed on declining inflation before reducing rates. Bowman added that wage growth above level is consistent with the Fed inflation target.
- Fed Board of Governors member Christopher Waller said that inflation progress last year has been excruciatingly slow and that rate cuts would be appropriate in 2025 if inflation repeats the 2024 pattern. Waller expects disinflation and interest rate cuts to resume year on year.
- The US Dollar attracts some buyers and for now, seems to have snapped a three-day losing streak to its lowest level since December 17. This might hold back traders from placing aggressive bullish bets around the XAU/USD and keep a lid on any further appreciating move.
- Traders look to the release of the Empire State Manufacturing Index from the US for some impetus later during the North American session. Apart from this, speeches by influential FOMC members would drive the USD demand and produce short-term trading opportunities.
Gold price might confront some resistance near $2,925 before testing all-time peak
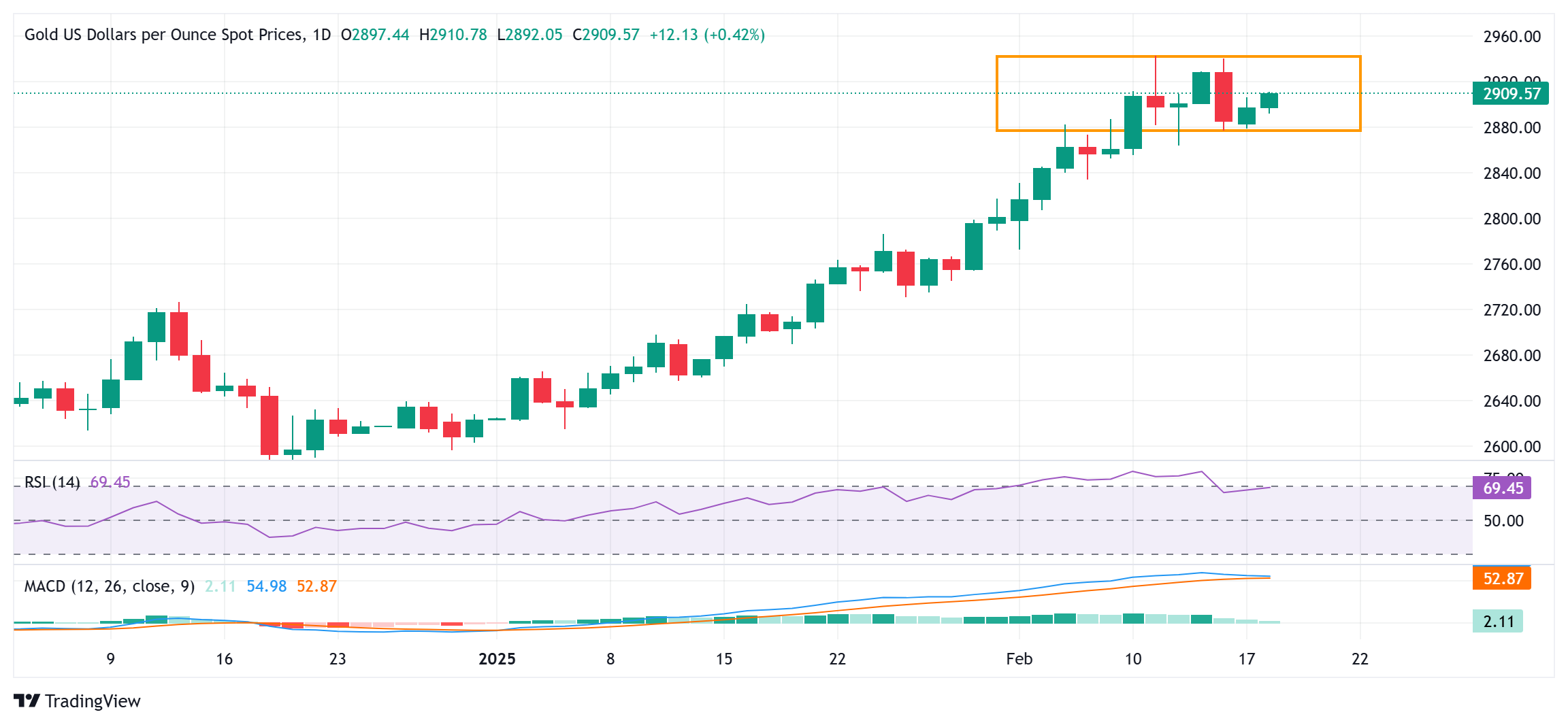
From a technical perspective, the range-bound price action witnessed over the past week or so could be categorized as a bullish consolidation phase against the backdrop of the recent rally to a record high. Moreover, oscillators on the daily chart are holding comfortably in the positive territory and suggest that the path of least resistance for the Gold price remains to the upside. That said, the daily Relative Strength Index (RSI) remains close to overbought territory. Hence, any subsequent move up is more likely to confront stiff resistance near the $2,925 horizontal zone. This is followed by the $2,942-2,943 area, or the all-time peak, which if cleared decisively will mark a fresh breakout and pave the way for an extension of a two-month-old uptrend.
On the flip side, weakness below the $2,900 mark now seems to find decent support near the $2,878-2,876 region. Any further decline towards the $2,860-2,855 area could be seen as a buying opportunity, which should help limit the downside for the Gold price near the $2,834 zone. A convincing break below the latter, however, might prompt some technical selling and drag the XAU/USD towards the $2,815 region en route to the $2,800 mark and the $2,785-2,784 support.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.

