Gold price dips amid buoyant US Dollar and easing geopolitical tensions
- Gold price drops pressured by Trump's tariff threats against BRICS nations, rising US bond yields.
- US ISM Manufacturing PMI hits a six-month high, contributing to a stronger Dollar, limits Gold's gains.
- Mixed signals from Fed officials on rate cuts keep markets cautious; December FOMC meeting closely watched.
Gold prices slump as the last month of the year begins. They edge lower, weighed down by a strong US Dollar sponsored by Trump’s harsh rhetoric on BRICS countries and some easing of geopolitical tensions. The XAU/USD trades at $2,635, down 0.58%.
The golden metal extended its losses after Trump warned BRICS countries that moving away from the Greenback could make them face 100% tariffs “and should expect to say goodbye to selling into the wonderful U.S. Economy,” he added.
Once Monday’s Asian session got underway, XAU/USD plunged to a daily low of $2621 before recovering some ground, but the jump in US Treasury bond yields and the US Dollar Index (DXY) capped Gold’s advance.
Data-wise, the US economic docket featured the release of the ISM Manufacturing PMI for November, which rose to its highest reading since June. Earlier, S&P Global announced that manufacturing activity in the United States (US) improved, indicating that the economy remains robust.
After the data, the Atlanta Fed GDP Now for Q4 2024 rose from 2.69% to 3.16% after the ISM data release.
Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic crossed the wires. Bostic stated he’s undecided on whether a cut this month is needed, but he believes that interest rates should continue to be lowered over the following months. He said that rates should be at a reasonable level that “neither stimulates nor restrains economic activity,” adding that he’s keeping his options open.
In the meantime, the CME FedWatch Tool shows that the odds for a 25-basis point rate cut stand at 63%, down from 66% last Friday. This suggests the December 17-18 meeting would be live.
Regarding geopolitics, US officials are concerned the Lebanon ceasefire could unravel, according to Axios. The White House is concerned that the fragile ceasefire in Lebanon could unravel after Israel and Hezbollah exchanged fire in recent days.
This week, the US economic docket will feature Fed speakers, including Chairman Jerome Powell, the JOLTs Job Openings for October, S&P and ISM Services PMI surveys, and Nonfarm Payroll figures.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price undermined by higher US real yields
- Gold prices dive as US real yields climbed one and a half basis points to 1.936%.
- The US 10-year Treasury bond yield rose almost two basis points to 4.196%.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck's performance against six currencies, edged up 0.63% at 106.44 on the day.
- The ISM Manufacturing PMI in November rose from 46.5 to 48.4, exceeding forecasts of 47.5. The S&P Global Manufacturing PMI for the same period increased from 48.5 to 49.7, above the 48.8 expected by the consensus.
- Fed officials seemed convinced that further easing is needed and may cut rates at the December meeting. However, they adopted a more cautious stance, opening the door for a pause in the easing cycle.
- Data from the Chicago Board of Trade, via the December fed funds rate futures contract, shows investors estimate 24 bps of Fed easing by the end of 2024.
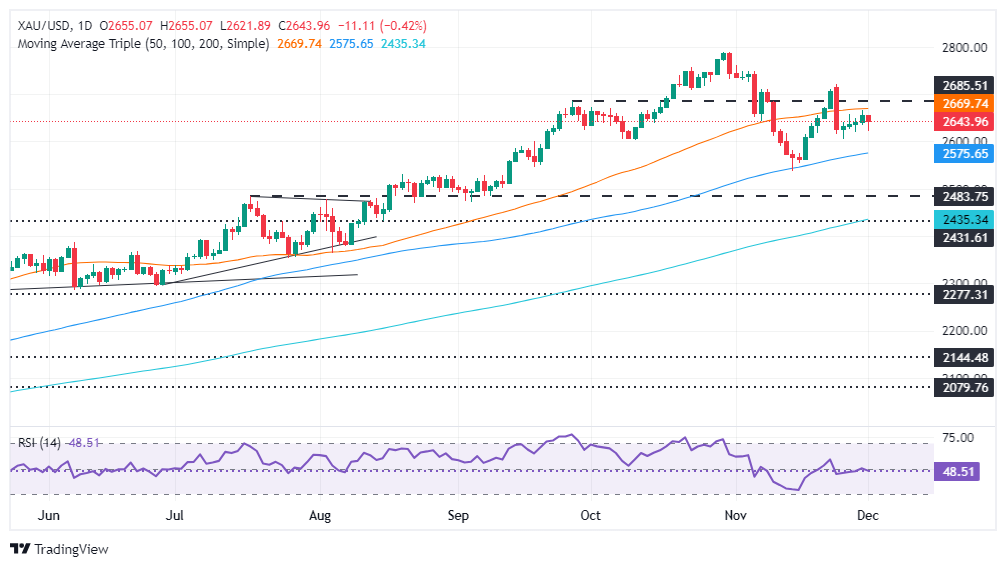
Technical outlook: Gold price retreats deeper below 50-day SMA
Gold’s uptrend remains intact, though buyers could not decisively clear the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) of $2,669. Further consolidation lies ahead, as depicted by the Relative Strength Index (RSI) hovering around the 50 neutral line.
That said, if XAU/USD cleared the 50-day SMA, key resistance levels would be exposed, like $2,700, the $2,750 figure, and the all-time high at $2,790. On the other hand, if sellers drag the non-yielding metal below $2,600, they could target the 100-day SMA ahead of the November 14 swing low of $2,536.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

