Gold price finds decent support near $2,600 and rebounds from one-week low
- Gold price attracts some haven flows near $2,600 after Trump’s tariff threats.
- Rebounding US bond yields revive USD demand and might cap gains in XAU/USD.
- Traders now look to FOMC meeting minutes for some meaningful impetuses.
Gold price (XAU/USD) plunged over 3% on Monday and eroded a major part of last week's strong gains, which marked the best weekly performance since March 2023. Scott Bessent's nomination as the US Treasury Secretary, coupled with reports that Israel was close to reaching a ceasefire with military group Hezbollah in Lebanon, triggered a fresh wave of global risk-on trade. This overshadowed a modest US Dollar (USD) weakness and weighed heavily on the precious metal.
The subsequent fall, however, stalls ahead of the $2,600 mark during the Asian session on Tuesday amid reviving safe-haven demand in the wake of US President-elect Donald Trump's tariff threat. That said, expectations for a less dovish Federal Reserve (Fed), a fresh leg up in the US Treasury bond yields, and renewed US Dollar (USD) buying should cap the non-yielding yellow metal. Traders now look to the release of the FOMC meeting minutes for some meaningful impetuses.
Gold price benefits from reviving safe-haven demand amid trade war fears
- The optimism over Scott Bessent's nomination as the US Treasury secretary and the Israel-Hezbollah ceasefire deal weighed heavily on the safe-haven Gold price at the start of a new week.
- Hopes that Bessent will take a more phased approach on tariffs in an attempt to rein in the budget deficit triggered a sharp fall in the US Treasury bond yields and undermined the US Dollar.
- The yield on the benchmark 10-year US government bond dropped by the most since early August, though the downfall remains limited amid bets for a less dovish Federal Reserve.
- Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee said on Monday that barring some convincing evidence of overheating, he foresees the central bank continuing to lower rates.
- Separately, Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari said that it is still appropriate to consider another interest-rate reduction at the December FOMC policy meeting.
- Traders, however, continue scaling back their bets for another 25-basis-points Fed rate cut in December amid expectations that Trump's policies will boost inflation.
- This acts as a tailwind for the US bond yields and assists the USD to fill the weekly bearish gap, which might cap any meaningful upside on the non-yielding yellow metal.
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatened to impose a 25% tariff on all products coming into the US from Mexico and Canada and an additional 10% tariff on all Chinese imports.
- Meanwhile, Israeli forces have intensified operations in north Gaza in recent weeks and continue to hammer Lebanon, raising the risk of a further escalation of conflict.
- Adding to this, worries about the economic impact of increased duties temper investors' appetite for riskier assets and drive some haven flows towards the XAU/USD.
- Market players now look to the FOMC minutes for cues about the future rate-cut path, which will drive the USD demand and provide a fresh impetus to the commodity.
- This week's US economic docket also features the first revision of the US Q3 GDP print and the release of the US Personal Consumption and Expenditure (PCE) Price Index.
Gold price might struggle to build on intraday bounce; $2,600 holds the key for bears
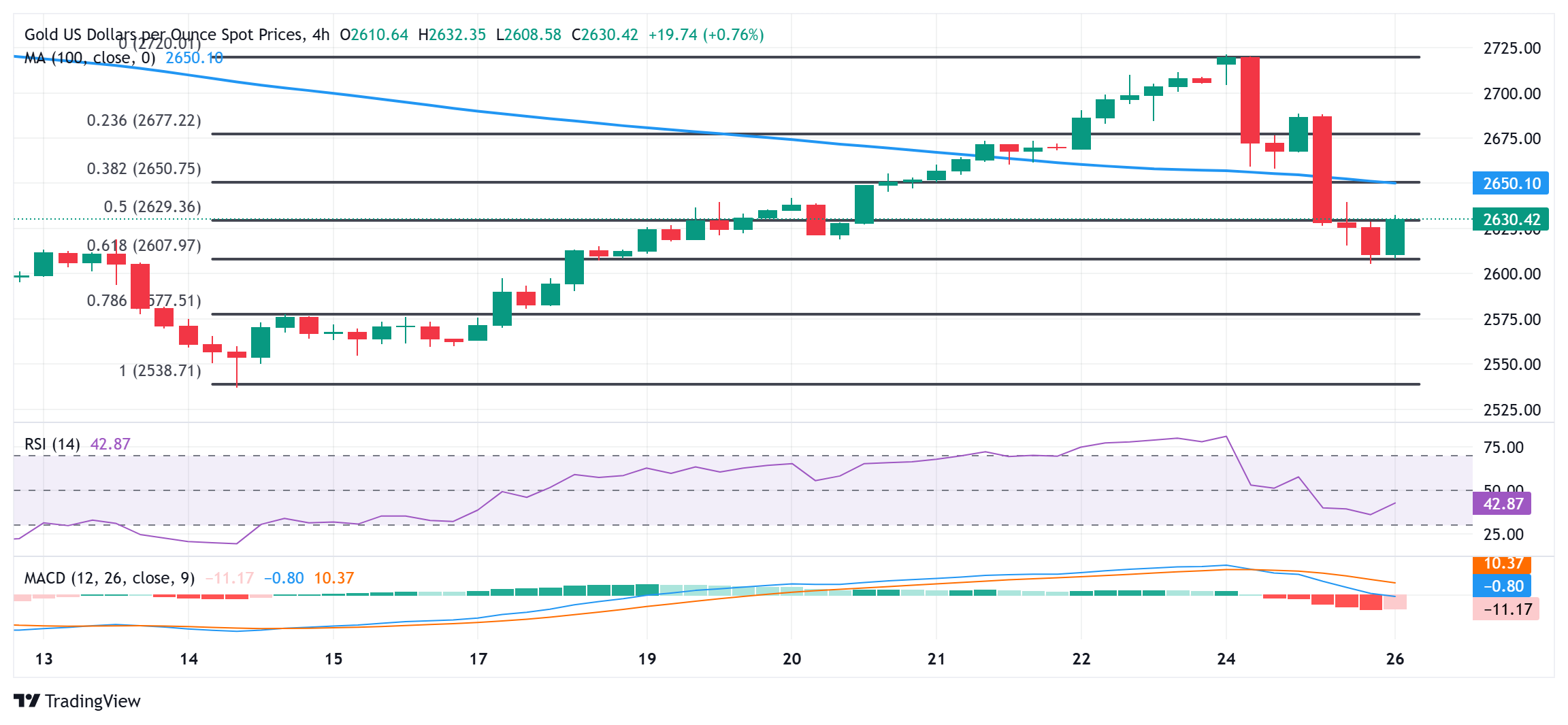
From a technical perspective, the intraday bounce from the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level of the recent recovery from a two-month low is likely to face stiff resistance near the $2,650 confluence. The said area comprises the 100-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) on the 4-hour chart and the 38.2% Fibo. level, which, in turn, should act as a key pivotal point. A sustained strength beyond could trigger a short-covering rally towards the $2,700 mark en route to the overnight swing high, around the $2,721-2,722 zone.
On the flip side, the $2,600 round figure (61.8% Fibo. level) might continue to protect the immediate downside. Some follow-through selling will expose the 100-day SMA, currently pegged near the $2,565 region. The subsequent decline has the potential to drag the Gold price towards the monthly swing low, around the $2,537-2,536 area. A convincing break below the latter will be seen as a fresh trigger for bearish traders and set the stage for an extension of the recent sharp retracement slide from the $2,800 neighborhood, or the all-time peak touched in October.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

