Pound Sterling gains as UK Retail Sales surprisingly grew in February
- The Pound Sterling rises against its peers on Friday after surprisingly upbeat UK Retail Sales data for February.
- The UK economy expanded at a robust pace of 1.5% in the last quarter of 2024.
- Investors brace for US PCE inflation and impending tariffs from US President Trump.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) advances against its major peers on Friday, except the Japanese Yen (JPY), after the release of the United Kingdom (UK) Retail Sales data for February and revised Q4 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that Retail Sales, a key measure of consumer spending, surprisingly rose by 1% month-on-month. Economists expected the data to have declined by 0.3%. In January, retail sales grew at a robust pace of 1.4%, revised lower from 1.7%.
In the 12 months to February, the consumer spending measure grew strongly by 2.2% compared to estimates of 0.5% and the former release of 0.6%, revised lower from 1%. Upbeat Retail Sales data is expected to support Bank of England (BoE) officials, who guided a "gradual and cautious" monetary easing outlook in last week's policy meeting after leaving interest rates unchanged at 4.5%.
Meanwhile, revised GDP figures show that the economy expanded at a faster pace of 1.5% against the preliminary estimate of 1.4%.
This week, UK Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves delivered a budget update in which she announced a significant cut in welfare benefits and halved its GDP forecasts for the current year to 1%. Reeves added that amendments in welfare spending would save £4.8 billion, and she would rebuild a nearly £10 billion fiscal buffer.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling ticks higher against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling edges higher to near 1.2960 against the US Dollar (USD) in Friday’s European session. The GBP/USD pair gains slightly ahead of the United States (US) Personal Consumption Expenditures Price (PCE) Index for February, which will be published at 12:30 GMT.
- The US core PCE inflation, which is the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) preferred inflation gauge, is estimated to have grown at a faster pace of 2.7% year-over-year, compared to the 2.6% increase seen in January. Month-on-month core PCE inflation is expected to have grown steadily by 0.3%. In this month's policy meeting, the Fed revised their forecast for the core PCE Index for this year to 2.8%, up from the 2.5% projected in the December meeting.
- Historically, the underlying inflation significantly influences market expectations for the Fed’s monetary policy outlook. This time, the impact is expected to be limited as investors brace for impending reciprocal tariffs by US President Donald Trump, which are expected to force market experts to revise their consumer inflation expectations. However, Fed officials and financial market participants had already anticipated that tariffs would be inflationary for the economy in the near term. Still, they need clarity on tariff rates to know the degree of acceleration in price pressures.
- US President Trump is set to announce reciprocal tariffs on April 2, the same day his recently announced 25% levy on autos will be implemented. Meanwhile, UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer seeks to secure a deal with the US before Trump unveils reciprocal tariffs. “Trade wars are no good for anyone," Chancellor Rachel Reeves said in an interview with Bloomberg Television on Thursday and added that they are working intensely these next few days to try and secure “a good deal for Britain”.
- Market participants also expect that the impact of Trump’s tariffs will be very limited on the UK. In late February, Trump commented that he is not sure about imposing tariffs on the UK and sounded confident that a deal could be made as Keir Starmer was "very nice".
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling aims to hold 1.2930
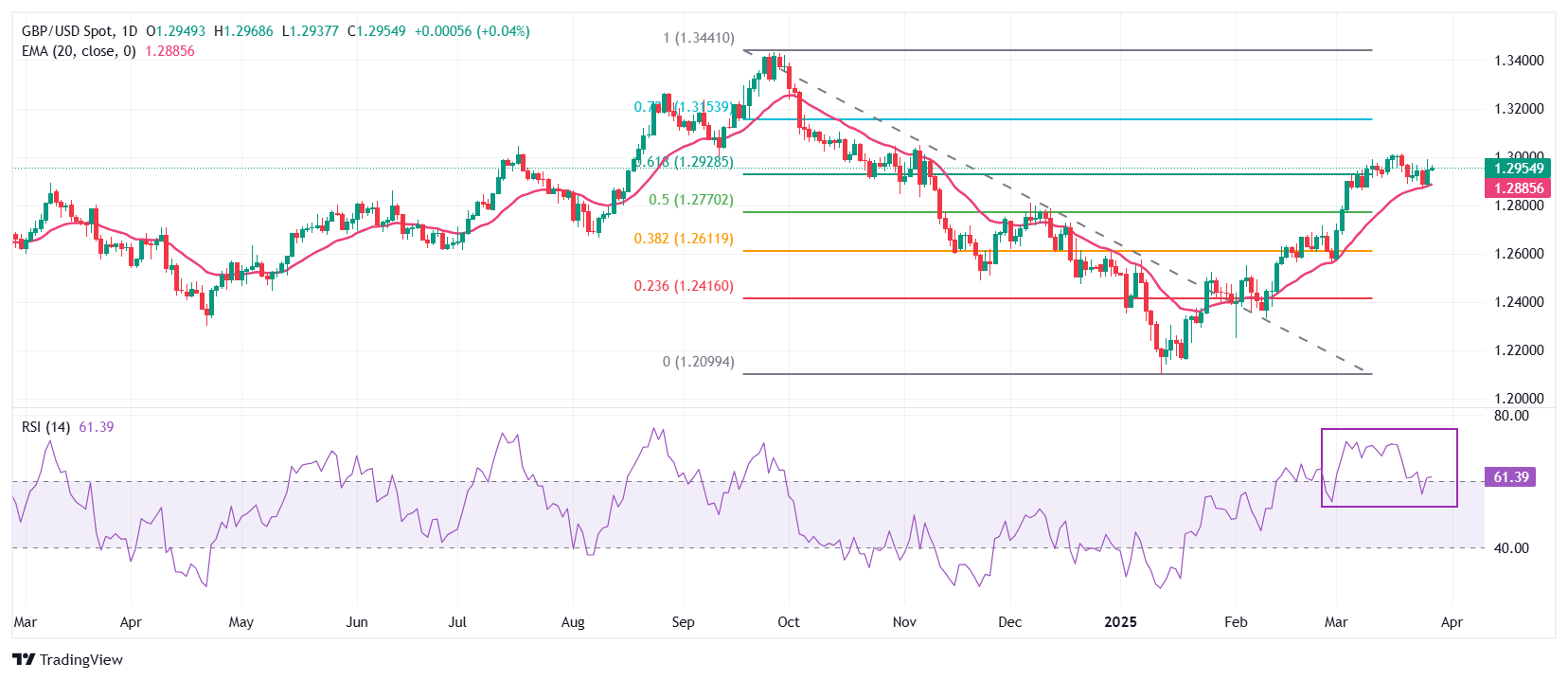
On Friday, the Pound Sterling strives to hold the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement, plotted from late-September high to mid-January low, near 1.2930 against the US Dollar. The 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) continues to provide support to the pair around 1.2885.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) cools down to near 60.00 after turning overbought above 70.00. Should a fresh bullish momentum come into action if the RSI resumes the upside journey after holding above the 60.00 level
Looking down, the 50% Fibonacci retracement at 1.2770 and the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement at 1.2615 will act as key support zones for the pair. On the upside, the October 15 high of 1.3100 will act as a key resistance zone.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

