Mexican Peso slips amid Trump’s tariffs and Banxico policy divergence
- Mexican Peso depreciates as market sentiment remains bearish on trade risks.
- Trump confirms tariffs on Mexico are moving forward, pressuring the Peso.
- Banxico signals further 50 bps rate cuts as inflation nears the 3% target.
- US-Mexico trade talks continue, with a potential breakthrough expected Friday.
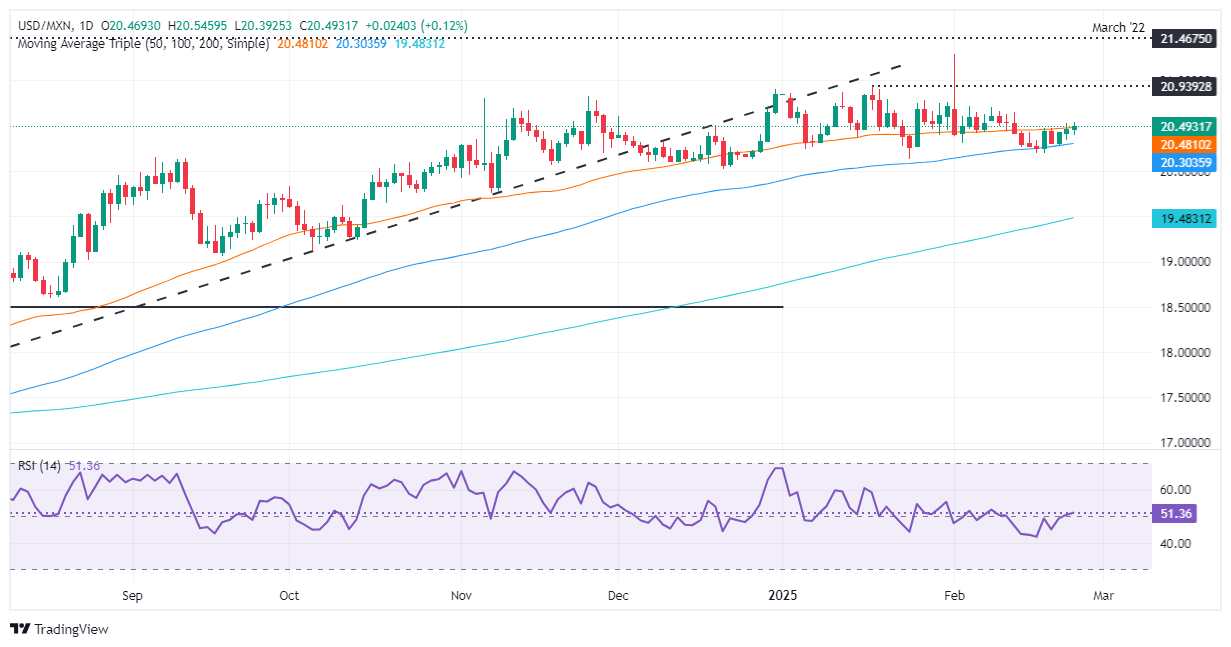
The Mexican Peso (MXN) extends its losses for the third straight day against the Greenback as market sentiment shifts sour due to United States (US) President Donald Trump's reiterating that tariffs on Mexico are on schedule. At the time of writing, USD/MXN trades at 20.49, up a modest 0.11%.
Geopolitics are hurting the prospects of the Peso, which began Tuesday’s session positively but has lost ground. Late on Monday, US President Trump said that duties on Mexico are moving forward, at a time when US and Mexican officials talks continued.
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum said that ongoing negotiations between the US and Mexico could bear fruit this Friday, when she may hold a phone call with President Trump.
Although this could be positive for the Mexican currency, divergence in monetary policy between both countries could weigh on the Peso.
The latest inflation report showed that prices converge towards Banco de Mexico's (Banxico) 3% goal. This, along with Banxico’s last meeting minutes hinting at subsequent 50 bps rate cuts, gives the US Dollar the upper hand.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) has adopted a “slightly hawkish” stance, as officials are in wait-and-see mode, assessing US trade policies proposed by Trump. Therefore, further USD/MXN upside is seen unless the Fed shifts dovish amid renewed fears of a stagflationary scenario.
In the meantime, Mexico’s Current Account in Q4 printed a surplus of 12,601 million US Dollars, up from 11,745 million, revealed Banxico.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso depreciates on US trade policies, Banxico’s dovish stance
- Mexico’s February mid-month core inflation increased from 3.61% to 3.63% YoY. Headline prices rose by 3.74% YoY, as expected by analysts.
- Washington is pushing the Mexican government to levy tariffs on Chinese imports to the country.
- The swaps markets hint that the Federal Reserve might ease policy by 58 basis points, up from last week's 40 bps in 2025, via data from the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT).
- Trade disputes between the US and Mexico remain front and center. Although the countries found common ground previously, USD/MXN traders should know that the 30-day pause is about to end, and tensions could trigger volatility in the pair during the rest of the week.
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso drops as USD/MXN hurdles 50-day SMA
The USD/MXN pair extended its gains above the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 20.45, with the exotic pair pushing above 20.50. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) above 50 keeps bulls hopeful of higher prices, though they must clear the January 17 high of 20.93, followed by 21.00 and the year-to-date (YTD) high of 21.28.
Conversely, if USD/MXN struggles at the 50-day SMA, it could drop to the 100-day SMA at 20.24. On further weakness, the pair might surpass that dynamic support and head towards the 20.00 figure.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.

