Mexican Peso falls as Trump announces new tariffs
- Mexican Peso weighed down by steek and aluminum tariffs enacted by The White House.
- Mexican automobile production and exports declined, creating a headwind for the emerging market currency.
- USD/MXN traders eye testimony from Fed Chair Jerome Powell on Tuesday.
The Mexican Peso depreciated against the US Dollar on Monday after US President Donald Trump decided to apply 25% tariffs on aluminum and steel imports into the United States (US), including Mexico and Canada. At the time of writing, the USD/MXN trades at 20.67, a gain of 0.66%.
On Sunday, Trump stated that he would apply tariffs on base metals. He added that reciprocal tariffs could be enacted as soon as Tuesday or Wednesday and that the tariffs would address the deficit.
The USD/MXN jumped on those remarks, extending its gains during the North American session. Meanwhile, the market mood remained upbeat, as depicted by US equities trading with gains.
Mexican data revealed that auto production dipped and exports plummeted for the third consecutive month in January, according to the Instituto Nacional de Estadistica Geografia e Informatica (INEGI).
Earlier, Banxico Governor Victoria Rodriguez Ceja was dovish, revealing that the Central Bank could cut rates of the same magnitude as in February, adding that the job of bringing inflation to the 3% goal has not concluded.
Mexican Industrial Production for December is expected to remain unchanged at 0.1% MoM. US Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell will cross the wires in the US for his semi-annual testimony at the US Congress. US inflation data on the consumer and producer side and retail sales will also update the status of the US economy.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican data failed to cap Peso’s fall spurred by Trump’s rhetoric
- Mexico’s Auto Exports plunged from -5.8% YoY to -13.7% in January. Production dipped from 4.2% to 1.7% YoY.
- Banxico’s Rodriguez added that Mexico’s role in US production chains allowed American consumers access to products at competitive prices. She said the central bank remains attentive to what might happen in March after the 30-day grace period provided by Trump.
- She added that despite being volatile, the Mexican Peso market has operated in an orderly way.
- The New York Fed Survey of Consumer Expectations revealed that US consumers expect inflation to remain at 3%. For five years, prices are expected to edge up from 2.7% to 3% in December.
- Trade disputes between the US and Mexico remain in the boiler room. Although the countries found common ground previously, USD/MXN traders should know that there is a 30-day pause and that tensions could arise toward the end of February.
- Money market fed funds rate futures are pricing in 39 basis points (bps) of easing by the Fed in 2025.
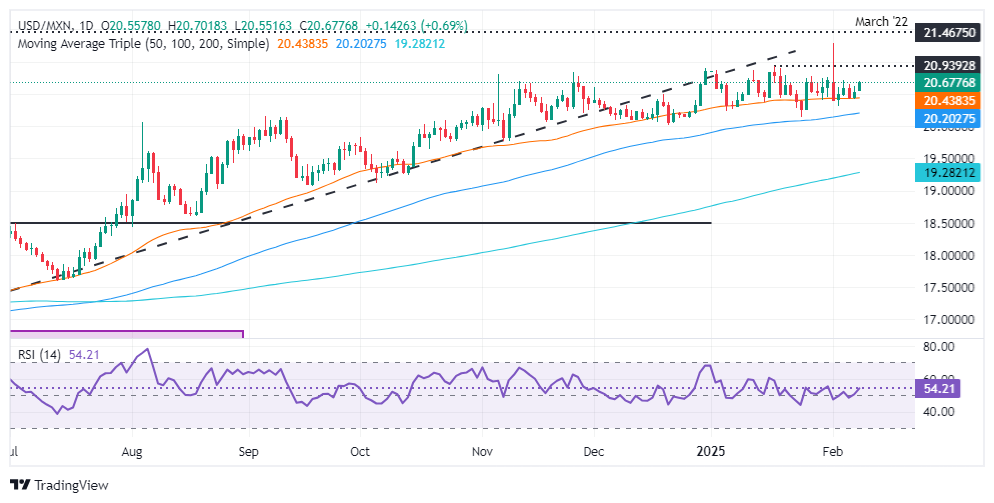
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso poised for further losses
The USD/MXN uptrend remains in place, but the exotic pair could remain sideways in the short term, trading within the 20.30 – 20.70 area. Momentum remains bullish, as depicted by the Relative Strength Index (RSI), but buyers need to push prices above 20.70, so they could target higher prices.
The next resistance would be the January 17 daily peak at 20.90 before testing the 21.00 figure and the year-to-date (YTD) high at 21.29. Conversely, a drop below the 50-day Simple Moving average (SMA) at 20.57 could clear the path toward the 100-day SMA at 20.22. On further weakness, look for a test of 20.00.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.

