Pound Sterling retraces on slower than projected UK GDP growth, weak factory data
- The Pound Sterling drops as the UK GDP rose at a slower-than-expected pace, and factory activity contracted in November.
- Traders have raised BoE dovish bets for February’s policy meeting.
- Investors await the US weekly jobless claims and Retail Sales data for December on Thursday.
The Pound Sterling faces selling pressure in Thursday’s European session after the release of the United Kingdom's (UK) monthly Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and factory data for November. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that the economy returned to growth after contracting in October. However, the growth rate was slower than projected. The economy rose by 0.1% after declining at a similar pace in October. Economists expected the economy to have expanded by 0.2%.
Both Manufacturing and Industrial Production data contracted in November on a monthly as well as annual basis. Month-on-month, Industrial and Manufacturing Production contracted by 0.4% and 0.3%, respectively. The pace of decline was slower than that seen in October. Economists expected Industrial Production to have grown by 0.1%, while Manufacturing Production was estimated to have remained flat.
Signs of continuous weakness in the UK factory activity suggest that producers are not fully utilizing their operating capacity on the assumption that the already weak demand environment will worsen further after United States (US) President-elect Donald Trump slaps hefty import tariffs globally once he takes office.
However, growing expectations that the Bank of England’s (BoE) monetary policy easing will be less gradual this year would offer some relief for factory owners. Traders have raised BoE dovish bets after the release of the UK Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for December on Wednesday, which showed signs of cooling price pressures.
Traders see a roughly 84% chance that the BoE will reduce interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 4.5% at its policy meeting in February.
Cooling price pressures have offered some relief to Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves as they led to a pause in the rally in yields on UK gilts. 30-year UK gilt yields have corrected to 5.28% from their more-than-26-year high of 5.47%. The British currency has faced a significant decline in the last few trading days as soaring UK gilt yields due to uncertainty over the economic outlook.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling struggles against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling drops to near 1.2200 against the US Dollar (USD) in European trading hours. The GBP/USD pair falls due to weak UK data. However, the US Dollar consolidates, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) wobbling around 109.00. The USD Index turns sideways as traders reassess expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) likely interest rate action for the entire year.
- Market participants expect the Fed’s policy-easing path to be less gradual than anticipated earlier. Expectations for the Fed policy outlook were impacted after the release of the United States (US) inflation data for December on Wednesday, which showed that the progress in the disinflation trend has not stalled yet.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders expect the Fed to deliver more than one interest rate cut this year and anticipate the first reduction in June. Before December’s inflation data, traders were anticipating only one interest rate reduction in September.
- For more cues on the interest rate outlook, investors will focus on the US Initial Jobless Claims data for the week ending January 10 and the Retail Sales data for December, which will be published at 13:30 GMT.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling remains weak as 20-day EMA slops downwards
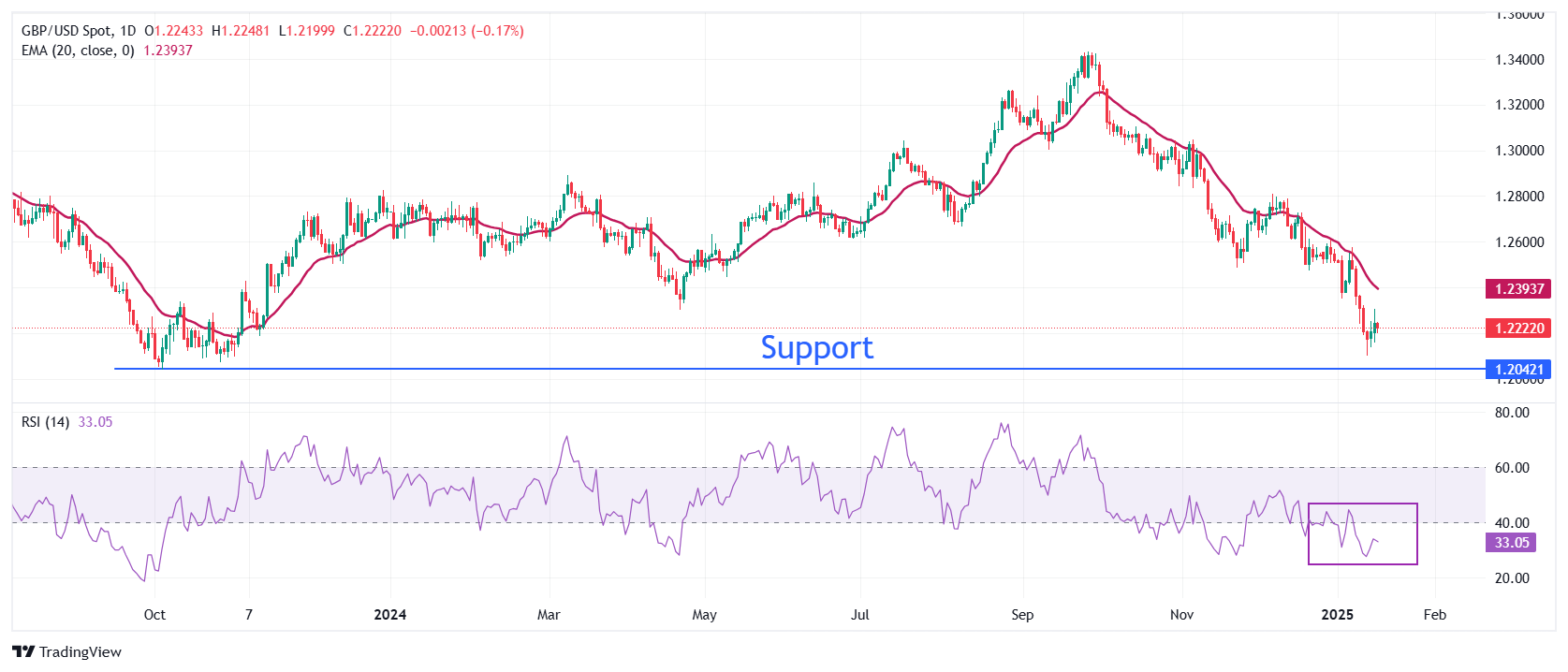
The Pound Sterling trades near the key level of 1.2200 against the US Dollar on Thursday. The outlook for the Cable remains weak as the vertically declining 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.2394 suggests that the near-term trend is extremely bearish.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) rebounds slightly after diving below 30.00 as the momentum oscillator turned oversold. However, the broader scenario remains bearish until it recovers inside the 20.00-40.00 range.
Looking down, the pair is expected to find support near the October 2023 low of 1.2050. On the upside, the 20-day EMA will act as key resistance.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

