Pound Sterling gains as UK wages grow by more than expected
- The Pound Sterling moves higher after the UK labor market data for the three months ending October showed a strong wage growth.
- UK’s jobless rate steadied at 4.3% as expected, and 173K fresh workers were added to the labor force.
- Investors expect the BoE to leave interest rates unchanged, while the Fed is expected to cut them this week.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) rises sharply against its major peers on Tuesday after the release of the United Kingdom (UK) labor market data for three months ending October. The British currency strengthens as Average Earnings Excluding bonuses, a key measure of wage growth, rose at a robust pace of 5.2%, faster than estimates of 5% and accelerating from the former 4.9% advance.
Bank of England (BoE) officials closely track wage growth data when deciding on interest rates as it is a major driving force to inflationary pressures in the UK service sector.
Meanwhile, Average Earnings Including bonuses also rose by 5.2%, faster than expectations of 4.6% and the former reading of 4.4%.
Robust wage growth data has strengthened the British currency, offsetting other components of the labor data release that weren't that GBP-positive. For example, in the three months ending October, the economy added 173K new workers, lower than the former release of 253K, upwardly revised from 219K. The ILO Unemployment Rate came in line with estimates and the prior release of 4.3%.
Higher wage growth suggests that UK service inflation could remain high, with fresh inflation data to be released on Wednesday. The core Consumer Price Index (CPI) – which excludes volatile items – is estimated to have grown by 3.6%, faster than the 3.3% advance in October.
Such an outcome would cement market expectations that the BoE will leave interest rates unchanged at 4.75% in the monetary policy announcement on Thursday.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling to be influenced by Fed-BoE policy meetings
- The Pound Sterling rises to near the psychological resistance of 1.2700 against the US Dollar (USD) in Tuesday’s London session. The GBP/USD pair moves higher as the USD wobbles, with the US Dollar Index (DXY) hovering near an almost three-week high around 107.00 ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) policy announcement on Wednesday.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders are almost certain that the Fed will reduce interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 4.25%-4.50%. As the Fed is widely anticipated to cut its key borrowing rates, investors will pay close attention to Chair Jerome Powell’s comments at a press conference and the dot plot for fresh interest rate guidance.
- Market participants expect the Fed to shift its policy stance from “dovish” to “slightly hawkish” on the assumption that upside risks to inflation have accelerated while downside risks to employment have diminished, according to the latest Bloomberg survey.
- The Flash US S&P Global PMI report for December also showed that employment edged higher in December, up for the first time in five months, reflecting a second successive monthly rise in manufacturing jobs and the first increase in service sector employment since July.
- In Tuesday’s session, investors will focus on the monthly US Retail Sales data for November, which will be published at 13:30 GMT. The Retail Sales data, a key measure of consumer spending, is estimated to have grown by 0.5%, faster than the former release of 0.4%.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling rises to near 20-day EMA
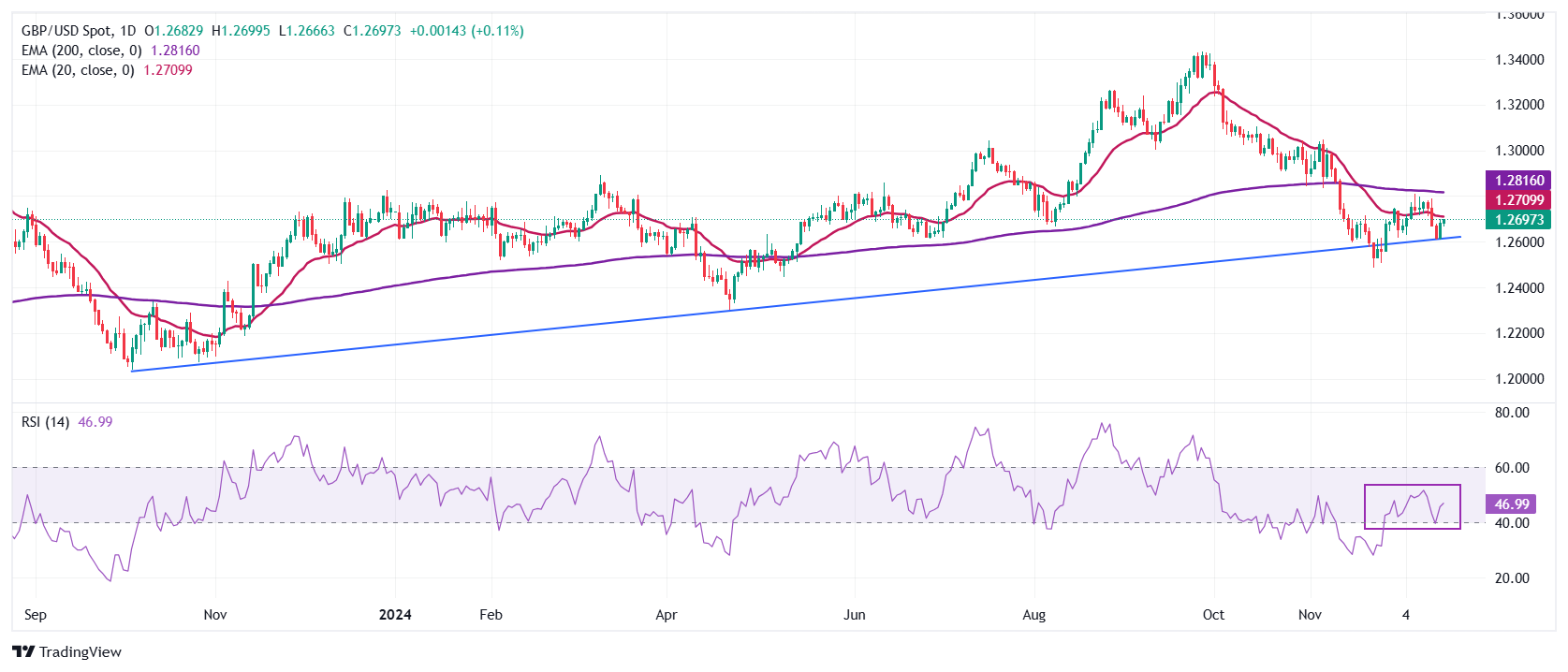
The Pound Sterling moves higher to near the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.2815 against the US Dollar (USD). The GBP/USD pair rebounded after gaining ground near the upward-sloping trendline around 1.2600, which is plotted from the October 2023 low of around 1.2035.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) oscillates in the 40.00-60.00 range, suggesting a sideways trend.
Looking down, the pair is expected to find a cushion near the psychological support of 1.2500. On the upside, the 200-day EMA near 1.2710 will act as key resistance.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

