Australian Dollar depreciates due to risk aversion following Trump’s tariff decision
- The Australian Dollar extends its losses as market sentiment takes a hit following Donald Trump’s announcement of increase in tariffs.
- Australia’s Monthly Consumer Price Index for October is the focus on Wednesday.
- The latest US PMI has reinforced the likelihood of the Fed slowing the pace of rate cuts.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) continues to weaken against the US Dollar (USD) on Tuesday, driven by dampened market sentiment following President-elect Donald Trump's announcement of a 10% increase in tariffs on all Chinese goods entering the United States (US), along with a 25% tariff on imports from Mexico and Canada.
The downside for the AUD/USD pair may be limited, as the Australian Dollar could find support from the Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) hawkish outlook on future interest rate decisions. Traders are now turning their attention to Australia’s Monthly Consumer Price Index (CPI) for October due on Wednesday, a key indicator that could influence expectations regarding domestic monetary policy.
The RBA’s November Meeting Minutes indicated that the board remains cautious about the risk of further inflationary pressures, underscoring the need to maintain a restrictive monetary policy stance. While the board noted there was no "immediate need" to adjust the cash rate, it stressed the importance of keeping all options open for future policy changes, highlighting a flexible and data-driven approach.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar weakens amid dampened market sentiment
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the USD's performance against six major currencies, remains subdued near 107.30 due to bond market optimism. This follows President-elect Donald Trump's selection of fund manager Scott Bessent as the US Treasury secretary, a seasoned Wall Street figure and fiscal conservative.
- The downside risks for the USD remain contained, bolstered by robust preliminary S&P Global US Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data, which have reinforced expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) may slow the pace of rate cuts.
- Futures traders are now assigning a 52.3% probability to the Federal Reserve cutting rates by a quarter point, down from 58.7% a week earlier, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
- In November, S&P Global US Composite PMI climbed to 55.3, indicating the strongest growth in private sector activity since April 2022. The US Services PMI rose to 57.0, up from 55.0 in October and significantly surpassing market expectations of 55.2, marking the sharpest expansion in the services sector since March 2022. Meanwhile, the US Manufacturing PMI increased to 48.8 from 48.5 in October, aligning with market forecasts.
- The Judo Bank Australia PMI Composite Output Index dropped to 49.4 in November from 50.2 in October, indicating a modest contraction in private sector output for the second time in three months. Manufacturing PMI rose to 49.4 in November from 47.3 in October, marking its 10th consecutive month of contraction. Meanwhile, the Services PMI fell to 49.6 from 51.0, signaling the first contraction in services activity in ten months.
- Australia's four largest banks are predicting the Reserve Bank of Australia's first rate cut. Westpac has revised its forecast for the first cut to May, up from February. National Australia Bank (NAB) also expects the cut in May. Meanwhile, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA) and ANZ are cautiously forecasting a rate cut in February.
- Fed Chair Jerome Powell downplayed the likelihood of imminent rate cuts, highlighting the economy's resilience, robust labor market, and persistent inflationary pressures. Powell remarked, "The economy is not sending any signals that we need to hurry to lower rates."
Australian Dollar extends losses to near 0.6450 due to persistent bearish bias
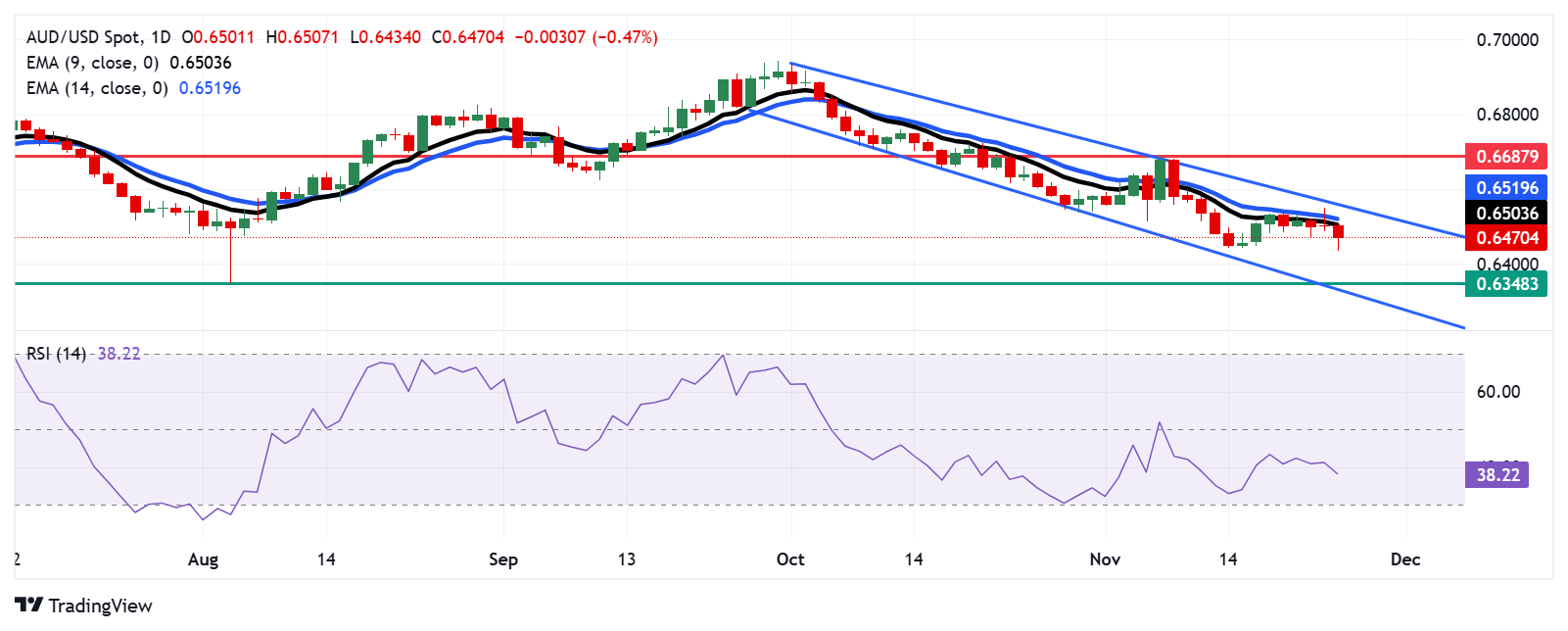
The AUD/USD pair hovers near 0.6470 on Tuesday, with technical analysis of the daily chart suggesting strengthening short-term bearish momentum. The pair remains confined within a descending channel, while the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) stays below 50, signaling persistent negative sentiment.
On the downside, the AUD/USD pair could test its yearly low of 0.6348, last reached on August 5, with additional support found near the descending channel's lower boundary at 0.6330.
The resistance lies at the nine-day EMA of 0.6503 and the 14-day EMA of 0.6512. A decisive break above these levels could weaken the bearish outlook and open the door for a potential rally toward the four-week high of 0.6687.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. Australian Dollar was the weakest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.31% | 0.28% | -0.08% | 0.99% | 0.40% | 0.38% | 0.19% | |
| EUR | -0.31% | -0.03% | -0.39% | 0.68% | 0.09% | 0.07% | -0.12% | |
| GBP | -0.28% | 0.03% | -0.33% | 0.71% | 0.13% | 0.11% | -0.09% | |
| JPY | 0.08% | 0.39% | 0.33% | 1.07% | 0.47% | 0.44% | 0.26% | |
| CAD | -0.99% | -0.68% | -0.71% | -1.07% | -0.58% | -0.61% | -0.79% | |
| AUD | -0.40% | -0.09% | -0.13% | -0.47% | 0.58% | -0.02% | -0.21% | |
| NZD | -0.38% | -0.07% | -0.11% | -0.44% | 0.61% | 0.02% | -0.19% | |
| CHF | -0.19% | 0.12% | 0.09% | -0.26% | 0.79% | 0.21% | 0.19% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Australian Dollar from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent AUD (base)/USD (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.




