EUR/USD plummets as Trump announces victory in US presidential election
- EUR/USD is hit badly with Trump’s victory in the US presidential election in sight.
- The Fed is expected to cut interest rates again on Thursday but by a lower size of 25 bps.
- The Euro underperforms across the board as concerns over Eurozone economic growth have deepened.
EUR/USD slightly recovers to 1.0750 after nosediving to near 1.0700 in Wednesday’s European session, the lowest level in over four months. The major currency pair hits badly as Republican candidate Donald Trump appears to take the Senate from Democrats, with Grand Old Party (GOP) gaining an unconquered lead in key battleground states, according to The Associated Press. The agency shows that Trump is inches away from winning 270 seats, a level the party needs to cross to form the government.
Meanwhile, Trump has declared victory over Democratic rival Kamala Harris, according to Sky News.
A clear victory of Trump in sight keeps the US Dollar (USD) on the front foot. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which gauges Greenback’s value against six major currencies, rallies to near 105.30. Market action clearly shows that Trump’s victory is favorable for the US Dollar, which was already anticipated as the Republican candidate vowed to hike tariffs on imports and lower corporate taxes. A scenario that will boost overall business activity and labor demand and escalate inflationary pressures.
However, the plot is unfavorable for currencies of economies like the Eurozone, the United Kingdom (UK), China, and Canada, which are major trading partners of the United States (US). Trump’s protectionist policies will directly impact the export sector of the above-mentioned economies, which will boost the risks of an economic downturn.
Going forward, investors will also focus on the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy decision, which will be announced on Thursday. According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders have priced in a 25-basis point (bps) interest rate cut, pushing rates lower to the 4.50%-4.75% range. This would be the second interest rate cut by the Fed in a row. However, the rate cut size will be lower than the 50 bps announced in the September meeting.
Investors will also focus on Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference to get cues about the impact of Trump’s victory on the interest rate path and the inflation outlook.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD is punished by upbeat US Dollar and weak Euro
- EUR/USD faces severe selling pressure due to the US Dollar’s outperformance and the Euro’s (EUR) sharp depreciation against other major currencies. The outlook of the Euro has weakened as market participants expect that the implementation of Trump’s protectionist policies will significantly damage European economic growth.
- According to the Dutch bank, Trump's tariffs would shave approximately 1.5 percentage points off European growth, translating to a potential €260 billion economic loss based on Europe's estimated 2024 GDP of €17.4 trillion.
- Should Europe's growth falter under Trump's tariffs, the European Central Bank (ECB) may be compelled to respond aggressively, slashing rates to near zero by 2025, according to Euronews.
- Trump’s victory would likely force the ECB to cut its Deposit Facility Rate by a larger-than-usual size of 50 bps in its next monetary policy meeting in December. This would be the fourth interest rate cut by the ECB this year.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD posts fresh four-month low near 1.0700
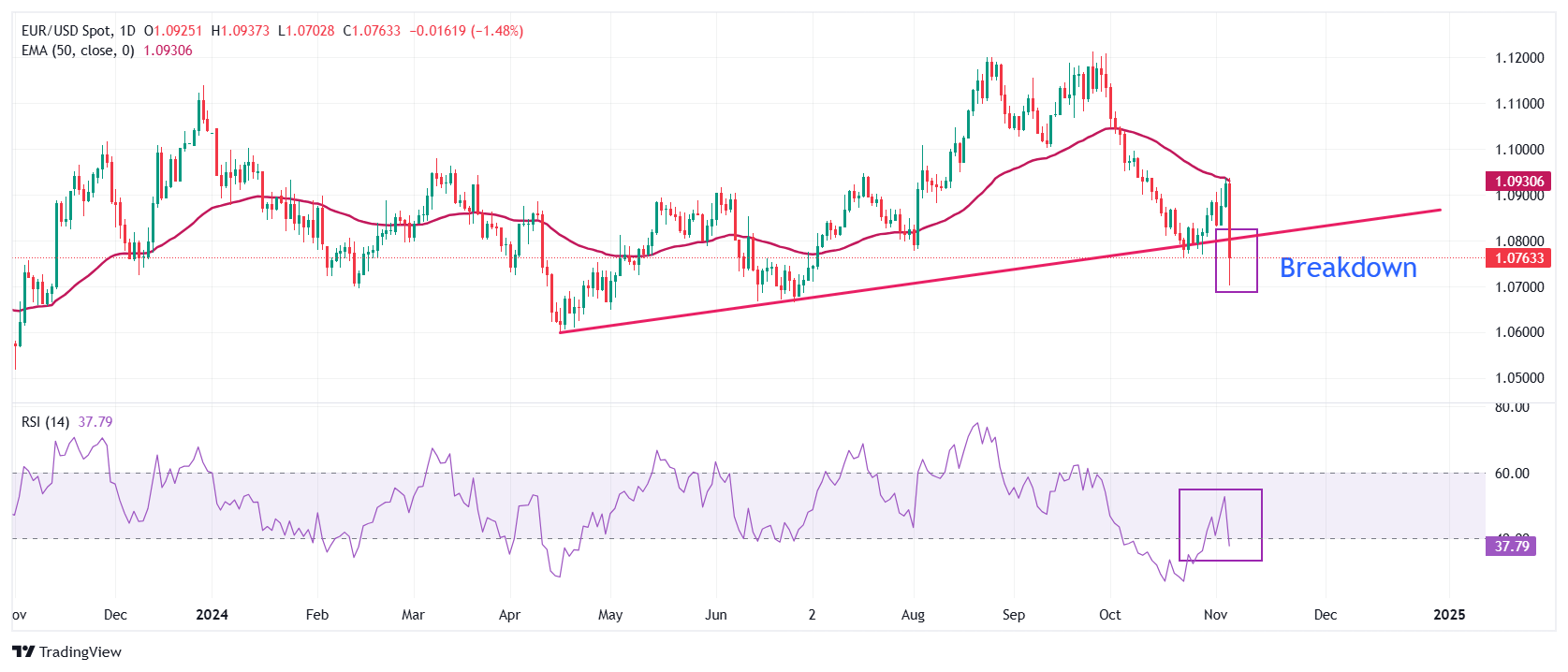
EUR/USD slides swiftly to near the key support of 1.0700. The outlook of the major currency pair weakens as it breaks below an upward-sloping trendline around 1.0750, which is plotted from the April 16 low at around 1.0600
The declining 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.0930 suggests a firm bearish trend.
Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) retreats below 40.00, suggesting a resumption of the bearish momentum.
Looking down, the shared currency pair could decline to the year-to-date (YTD) low of 1.0600. On the upside, the round-level resistance of 1.0800 will act as a key barrier for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

