Mexican Peso edges higher, supported by resilient Q3 growth
- The Mexican Peso continues its recovery supported by resilient Q3 GDP growth data.
- Multiple risk factors weigh, however, including the risk of Trump tariffs, Banxico interest-rate cuts and domestic political jitter.
- USD/MXN faces tough resistance just above the key 20.00 handle as bulls try to push higher.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) edges higher across its key pairs on Friday, continuing the recovery of the previous day, in part supported by the release of higher-than-expected Mexican Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth data, which showed a 1.5% rise in the third quarter.
Mexican Peso strength could be capped by political risk factors
The Mexican Peso upside may be limited, however, as fears persist that a victory for former president Donald Trump in the US presidential election will lead to increased tariffs on imported Mexican goods.
Concerns are easing, however, with the realization that Trump’s threats may be more rhetorical than realistic given how intertwined the two countries' supply chains are after three decades of free trade. Goods made in Mexico generally contain a substantial quantity of US or Canadian components and involve multiple border crossings to be manufactured, suggesting a trade war with Mexico would cause a self-inflicted wound on the US economy.
Mexico’s lawmakers tighten grip on power
A further potentially negative risk factor for the Peso comes in the form of moves by the Mexican legislature to limit the power of the Supreme Court to suspend or block its reforms, according to El Financiero. This risks reviving market concerns about the rule of law and balance of power in the country, impacting its ability to attract foreign investment. The move recently led to eight of Mexico’s eleven Supreme Court judges handing in their resignations, effective from August 2025.
Banxico expected to still cut in November – Capital Economics
Mexico’s surprise growth in Q3 does not “preclude another rate cut in November” from the Bank of Mexico (Banxico), according to Kimberley Sperrfechter, Emerging Markets Economist at London-based advisory service Capital Economics.
If the Banxico was to go ahead with a 25 basis point (bps) (0.25%) cut to Mexico’s relatively high 10.50% key interest rate, it might put pressure on the Peso since lower interest rates attract less capital inflows.
“We still think the conditions are currently in place for Banxico to press ahead with another interest rate cut at its November meeting. But a lot will depend on the outcome of the US election. A Trump victory – and higher US Treasury yields and a stronger Dollar – would probably prompt Banxico to halt,” added Sperrfechter in the note.
According to Christian Borjon Valencia, an analyst at FXStreet, “Money market futures hint that the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) is expected to cut rates between 175 to 200 basis points over the next 12 months.”
Data out on Friday includes Mexican Business Confidence for October, the Unemployment Rate for September, and the S&P Manufacturing PMI for October.
Technical Analysis: USD/MXN faces tough resistance in the 20.00 zone
USD/MXN seems to have stalled after stretching a foreshortened “c wave” higher of a bullish “abc” pattern, which began at the October 14 swing low.
Whilst it is still possible wave c could reach its minimum upside target at 20.29 – the Fibonacci 61.8% extension of the length of wave “a” – resistance in the 20.00 region is making lives difficult for bulls.
USD/MXN 4-hour Chart
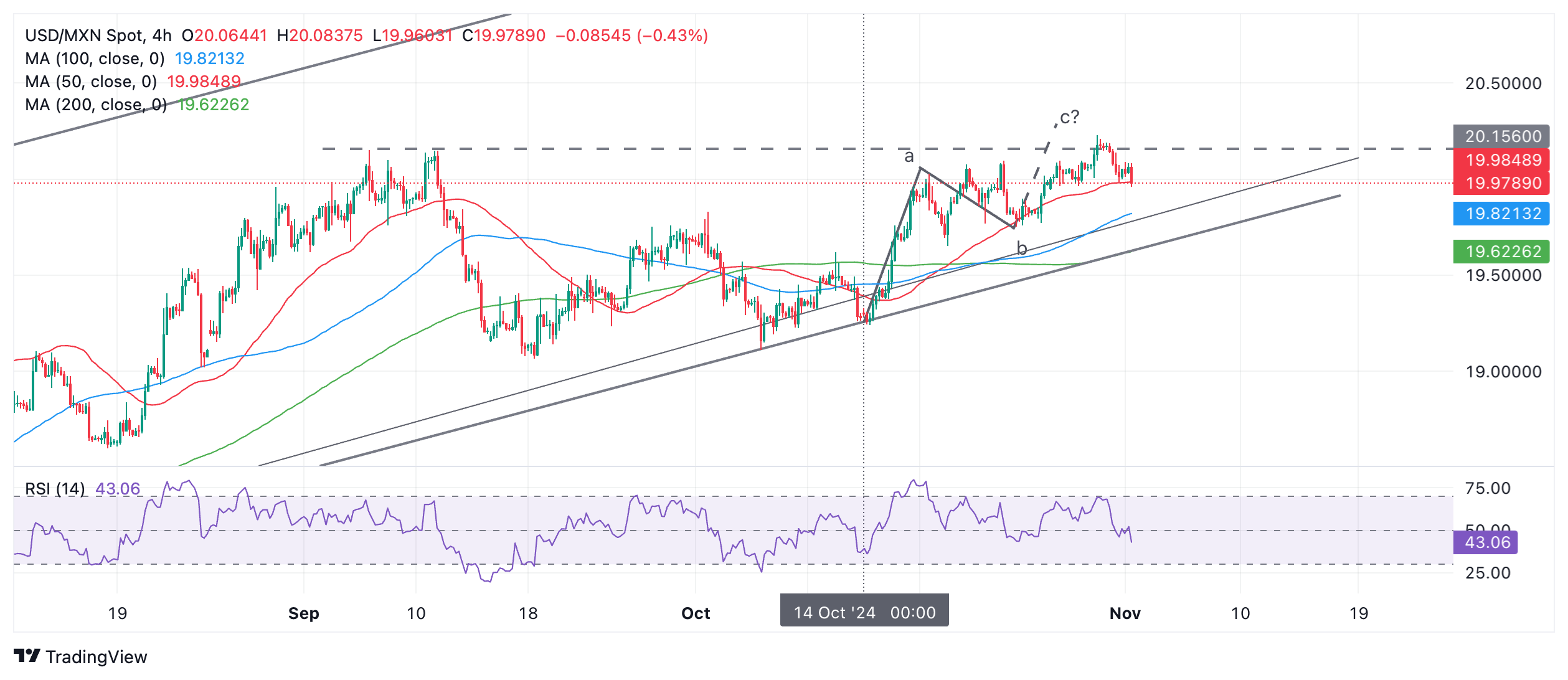
USD/MXN is probably still in an uptrend on a short, medium and long-term basis and it is trading in a rising channel. Given the technical dictum “the trend is your friend,” the odds favor a continuation higher. Thus, a resumption higher is still possible.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.

