EUR/USD descends to lower 1.0700s after strong US data
- EUR/USD is selling off after the release of more positive data from the US.
- The data suggests the Federal Reserve could delay cutting interest rates, supporting USD.
- The ECB continues to target June as the first month to cut interest rates.
EUR/USD falls to the lower 1.0700s on Tuesday after more strong US macroeconomic data supports the US Dollar (USD), pushing down the probability of the US Federal Reserve (Fed) cutting interest rates by June to close to 50%. The maintenance of higher interest rates is good for the USD as it attracts more capital inflows.
In Europe, slower growth and lower inflation mean rate-setters at the European Central Bank (ECB) are not as cautious about cutting interest rates to help stimulate the wheels of growth. This divergence of trajectories between both central banks is negative for EUR/USD.
EUR/USD declines as US data bears up
EUR/USD takes another step lower, breaching the key 1.0800 level over the Easter weekend, as some firm US data suggests the Fed will have to delay reducing interest rates as inflation is likely to remain stubbornly above target.
On Good Friday, the inflation metric favored by the Fed, the core Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCE) in February, came out at 2.8%, exactly as expected, if below the 2.9% of January. It showed price pressures remain buoyant and well above the Fed’s 2.0% target.
US Manufacturing data on Easter Monday was also overall quite positive, with the ISM Manufacturing PMI for March vaulting over 50 – the dividing line between expansion and contraction – from a previous level of 47.8. The result was well above expectations of a rise to 48.4. It was the first result denoting expansion in the US manufacturing sector since November 2022.
The Euro was kept under pressure, meanwhile, by another ECB rate setter joining the chorus line for a June rate cut. ECB Governing Council member and Austrian Central Bank Governor Robert Holzmann said that the ECB could cut interest rates before the Fed, and in regards to when, “will depend largely on what wage and price developments look like by June.”
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD continues pushing lower
EUR/USD extends the dominant short-term downtrend that started at the March 8 high. It is currently on its way down to key support at the 1.0694 year-to-date (YTD) lows.
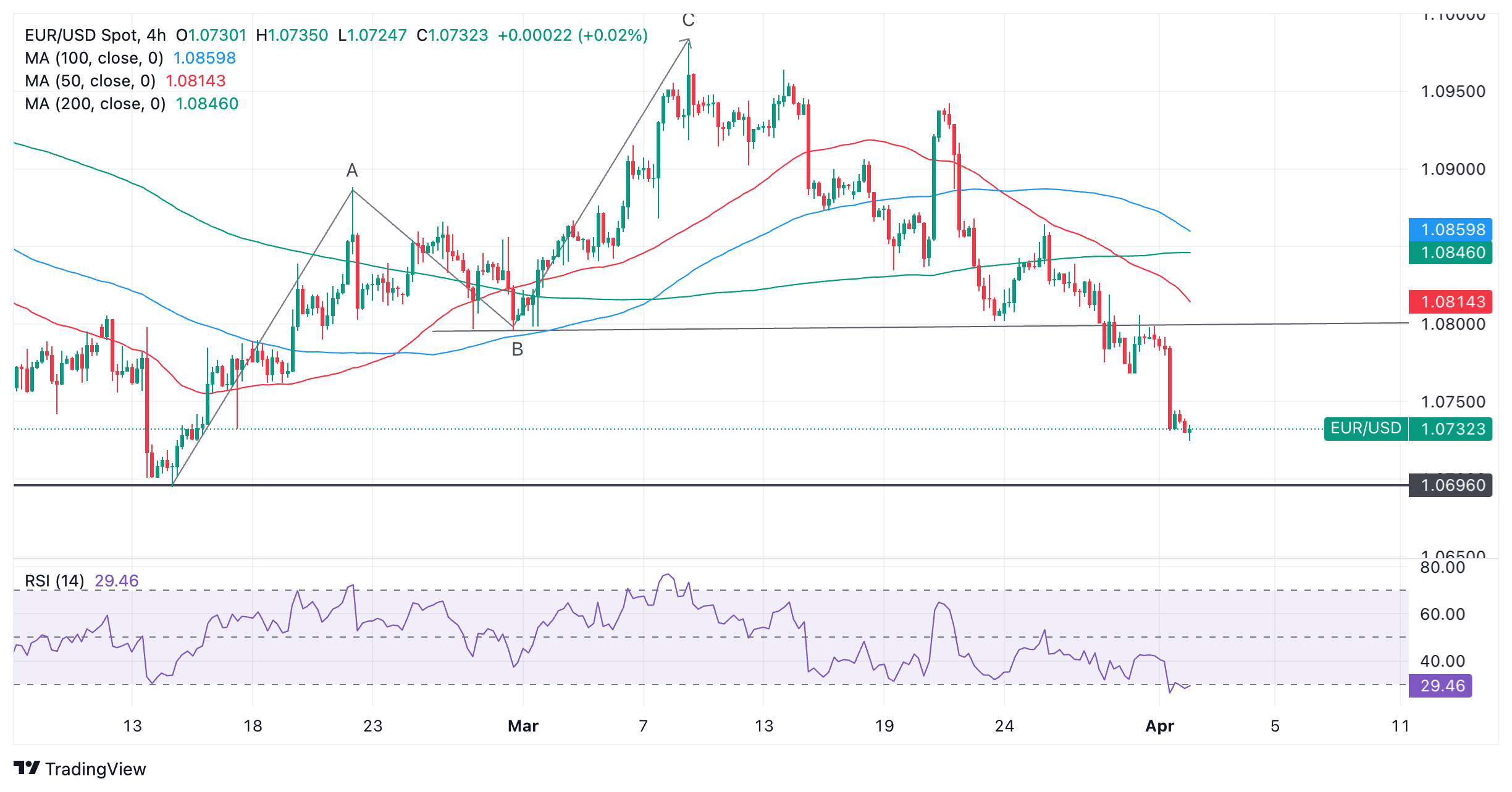
Euro versus US Dollar: 4-hour chart
The pair is oversold according to the Relative Strength Index (RSI) momentum indicator. This is a signal for sellers not to add any more shorts to their positions. If the indicator rises out of oversold (above 30), it will be a signal to close all short positions and open longs. This could lead to a pullback, although the precedence of the downtrend suggests an eventual capitulation.
The 1.0694 February and YTD lows are likely to present substantial support and a bounce off that level is likely at the first test. A decisive break below, however, would usher in another bout of weakness, and target the 1.0650s.
A decisive break is one characterized by a long red down candle breaking cleanly through the level and closing near its low, or three consecutive red candles breaching the level.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

