The Australian Dollar appreciates as Trump postpones the implementation of reciprocal tariffs.
The AUD may face headwinds as the RBA maintains its rate-cut stance following a fresh inflation outlook.
The US Dollar weakens amid declining US yields, despite persistent concerns over a global trade war.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) strengthens for the second consecutive day on Friday, driven by US President Donald Trump’s decision to postpone the implementation of reciprocal tariffs. Additionally, the AUD/USD pair appreciates as the US Dollar (USD) weakens amid falling US yields across the curve, despite ongoing concerns about a global trade war. Investors now await the release of US Retail Sales data later in the day.
The AUD may face headwinds as expectations of a Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) rate cut remain intact following fresh inflation outlook data. Consumer inflation expectations climbed to 4.6% in February from 4.0% in January, reaching their highest level since April 2024. This comes ahead of the RBA’s first monetary policy meeting of the year next week, with market odds indicating a 95% probability of a rate cut to 4.10%, as recent data suggests underlying inflation is cooling faster than anticipated.
The upside of the AUD/USD pair could be limited as strong US inflation data reinforces expectations of prolonged Federal Reserve (Fed) rate holds. Fed Chair Jerome Powell recently reiterated that the central bank is in no rush to cut rates further, citing a resilient economy and persistently high inflation.
Australian Dollar appreciates as US Dollar loses ground despite a hawkish Fed
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the US Dollar’s value against six major currencies, extends its losses and trades around 107.00 at the time of writing.
US Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 3.0% year-over-year in January, exceeding expectations of 2.9%. The core CPI, which excludes food and energy, increased to 3.3% from 3.2%, surpassing the forecast of 3.1%. On a monthly basis, headline inflation jumped to 0.5% in January from 0.4% in December, while core CPI rose to 0.4% from 0.2% over the same period.
Stronger US inflation could strengthen expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will maintain interest rates at 4.25%-4.50% for an extended period. According to the CME FedWatch Tool, the probability of a Fed rate cut in June has dropped to nearly 30% following the latest inflation data.
In his semi-annual report to Congress, Fed’s Powell said the Fed officials “do not need to be in a hurry" to cut interest rates due to strength in the job market and solid economic growth. He added that US President Donald Trump's tariff policies could put more upward pressure on prices, making it harder for the central bank to lower rates.
A Reuters poll of economists now suggests the Federal Reserve will delay cutting interest rates until next quarter amid rising inflation concerns. Many who had previously expected a March rate cut have revised their forecasts. The majority of economists surveyed between February 4-10 anticipate at least one rate cut by June, though opinions on the exact timing remain divided.
The US Dollar receives support as the US Federal Reserve (Fed) is now expected to keep interest rates steady this year, following January’s jobs report released on Friday, which indicated slowing job growth but a lower Unemployment Rate.
US President Donald Trump decided to expand steel and aluminum tariffs by 25% to include all imports, nullifying trade agreements with key US allies, including Australia. The White House confirmed that all import tax exclusions had been removed and indicated that further action on microchips and vehicles would be considered in the coming weeks.
Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland President Beth Hammack stated on Tuesday that keeping interest rates steady for an extended period will likely be appropriate. Hammack emphasized that a patient approach will allow the Fed to assess economic conditions and noted that the central bank is well-positioned to respond to any shifts in the economy, according to Reuters.
Technical Analysis: Australian Dollar rises above 0.6300 toward eight-week highs
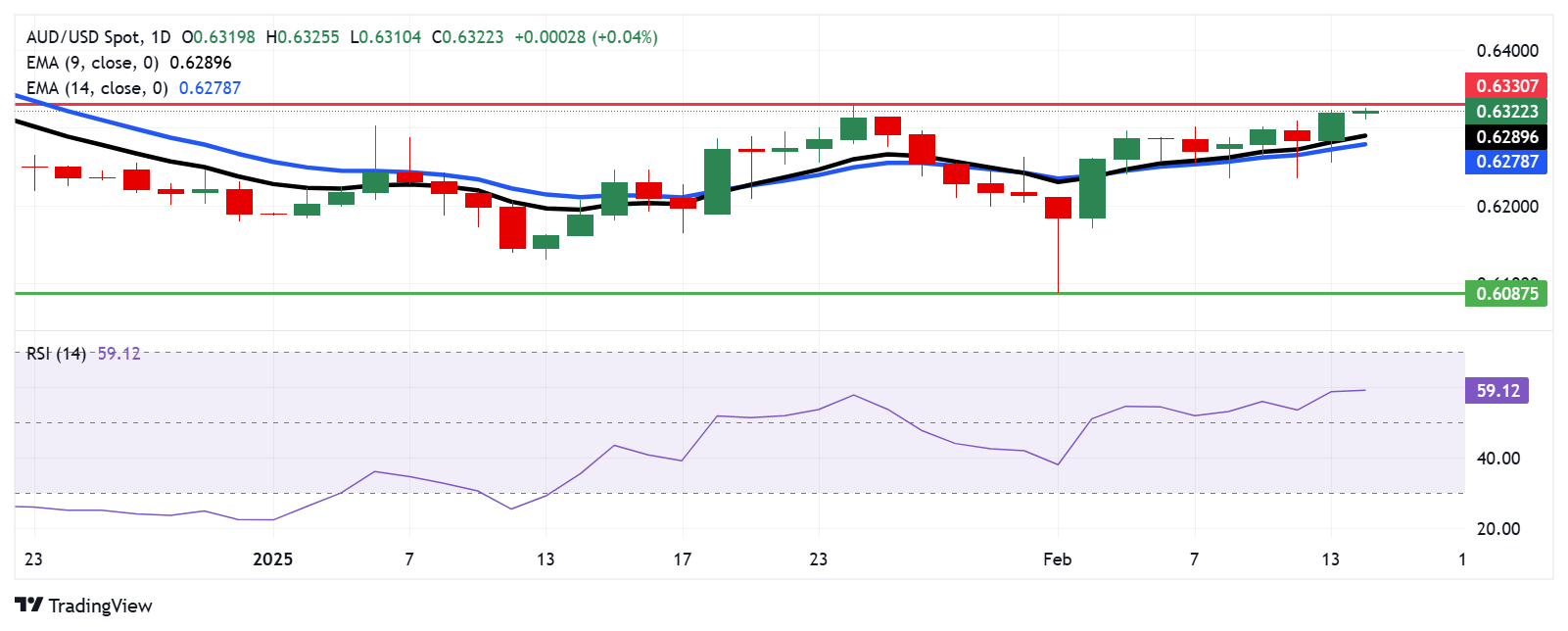
The AUD/USD pair hovers near 0.6320 on Friday, rising above the nine- and 14-day Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) on the daily chart. This suggests that short-term price momentum is strengthening. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) maintains its position above the 50 mark, reinforcing a bullish bias.
On the upside, the AUD/USD pair may test the eight-week high of 0.6330, which was last reached on January 24. A break above this level could support the pair to approach a psychological level of 0.6400.
The AUD/USD pair could fall toward primary support at the nine-day EMA of 0.6290 level, followed by the 14-day EMA of 0.6279. A decisive break below these levels could weaken the short-term price momentum, potentially pushing the pair toward the psychological level of 0.6200.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Australian Dollar PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies today. Australian Dollar was the strongest against the Euro.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.02% | -0.04% | -0.09% | -0.01% | -0.03% | -0.11% | -0.00% | |
| EUR | -0.02% | -0.06% | -0.11% | -0.03% | -0.06% | -0.14% | -0.03% | |
| GBP | 0.04% | 0.06% | -0.06% | 0.03% | 0.00% | -0.07% | 0.04% | |
| JPY | 0.09% | 0.11% | 0.06% | 0.07% | 0.04% | -0.04% | 0.08% | |
| CAD | 0.00% | 0.03% | -0.03% | -0.07% | -0.04% | -0.10% | 0.00% | |
| AUD | 0.03% | 0.06% | -0.00% | -0.04% | 0.04% | -0.08% | 0.03% | |
| NZD | 0.11% | 0.14% | 0.07% | 0.04% | 0.10% | 0.08% | 0.11% | |
| CHF | 0.00% | 0.03% | -0.04% | -0.08% | -0.01% | -0.03% | -0.11% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Australian Dollar from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent AUD (base)/USD (quote).a from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.
* The content presented above, whether from a third party or not, is considered as general advice only. This article should not be construed as containing investment advice, investment recommendations, an offer of or solicitation for any transactions in financial instruments.