Canadian Dollar pares recent gains as trade war rhetoric heats up
- The Canadian Dollar fell 0.32% against the Greenback on Thursday.
- Loonie markets are recoiling as Canada and the US gear up for a messy trade war.
- USD/CAD returns to familiar technical territory near 1.4300.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) shed weight on Thursday, paring away recent gains against the US Dollar (USD) as trade war rhetoric between the US and Canada ramps up. World leaders are quickly growing tired of US President Donald Trump’s constant waffling on tariffs he is, then isn’t, imposing across the board. Market nerves have completely frayed from reacting to President Trump’s ham-handed trade policy approach, and investors are pulling into a wait-and-see period ahead of Donald Trump’s self-imposed April 2 deadline to impose a sweeping package of tariffs.
Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney struck back against recent tariff headlines, cautioning that Canada is prepared to take retaliatory measures against the US. President Trump’s self-imposed deadline of April 2 to impose a sweeping tariff policy handbook that includes “reciprocal” tariffs, additional tariffs on Copper, even more additional tariffs on Canadian lumber specifically, and yet even more tariffs on countries that buy Crude Oil from Venezuela.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar eases as Canada hearse up for tariff fight
- The Canadian Dollar gave up recently gained ground on Thursday, falling roughly one-third of one percent against the Greenback.
- Canadian PM Mark Carney: We will fight the US tariffs with actions of our own.
- Headway on possible tariff concessions which US President Trump may or may be willing to grant on a per-case basis remains difficult.
- As noted by Canadain PM Carney, nobody is really clear on what tariffs the US plans to actually enact, nor has the Trump administration been clear on what they want in exchange for tariff relief.
- Key US inflation figures are due on Friday. Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index inflation comes just ahead of the Trump administration’s self-imposed tariff deadline of April 2.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
The Canadian Dollar’s Thursday walkback saw the Loonie shed some 45 pips against the US Dollar. Market flows continue to favor the Greenback on a near-term basis as risk-off flows begin to ramp up.
USD/CAD remains pinned to the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.4320 as near-term momentum continues to grind sideways. The pair has remained trapped in a choppy sideways channel as the congestion grind that started four months ago continues unabated.
USD/CAD daily chart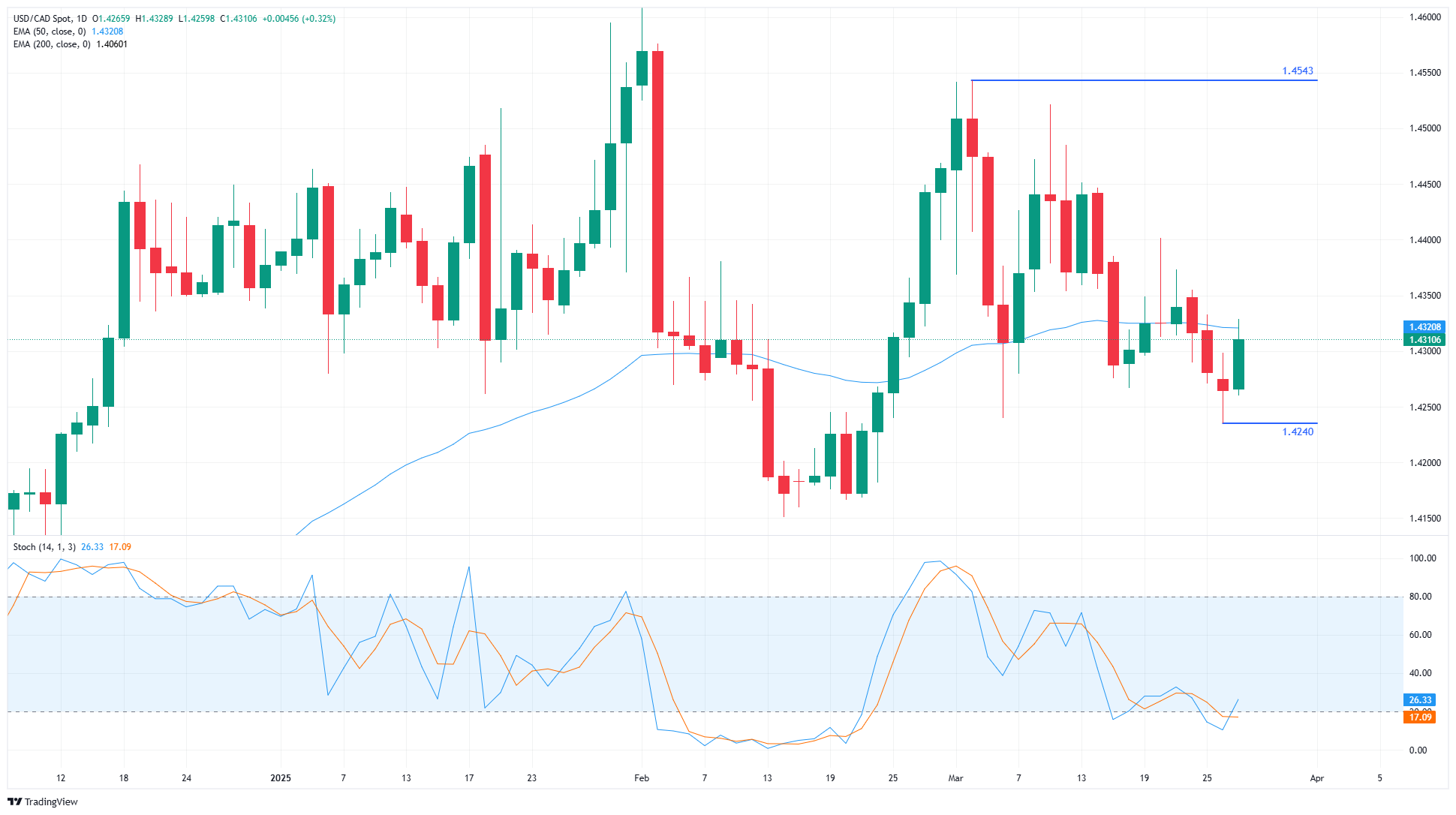
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

