USD/INR remains subdued despite stronger US Dollar, rising Oil prices
- The Indian Rupee remains stable, with USD/INR hovering near a seven-week low of 86.20.
- The INR faces potential headwinds from rising crude Oil prices amid ongoing geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
- The US Dollar strengthens as risk aversion rises due to concerns over tariff policies.
The Indian Rupee (INR) remains stable against the US Dollar (USD) during the Asian trading hours on Friday, with USD/INR holding near a seven-week low of 86.20, recorded on Thursday. However, further downside of the pair may be limited as the Greenback gains strength amid rising risk aversion driven by concerns over US tariff policies.
The INR also faces potential headwinds from rising crude Oil prices amid ongoing geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, as India, the world’s third-largest Oil consumer, remains sensitive to energy costs. Israel has launched a new ground operation in Gaza, breaking a two-month ceasefire, while the US continues airstrikes against Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen.
Indian equities advanced on Thursday, buoyed by expectations that higher liquidity and relaxed financial conditions will support economic growth. Tech stocks led the rally, mirroring gains in US markets, while banking stocks maintained their upward momentum this month, supported by slower inflation, which has allowed the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to adopt a more accommodative stance toward the Indian Rupee.
The RBI recently implemented its first rate cut in nearly five years, aligning with market expectations. With liquidity concerns persisting in the Indian financial system, the central bank is expected to continue easing to support growth. India’s GDP expanded by 6.5% in the current financial year, down from 8.2% in the previous period.
Indian Rupee could appreciate as US Dollar struggles amid declining bond yields
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the USD against six major currencies, is trading higher near 103.90. However, the US Dollar may face challenges as US bond yields decline, with investors seeking safety in Treasuries amid economic uncertainties.
- Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell downplayed the inflationary impact of tariffs, calling it temporary, but acknowledged the challenges in assessing broader effects. While recession risks have risen, Powell suggested they remain relatively low for now.
- US Initial Jobless Claims increased to 223K for the week ending March 15, slightly missing estimates of 224K and exceeding the previous week's revised figure of 221K (from 220K). Additionally, the Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Survey for March eased to 12.5 MoM, down from February’s 18.1. This marked the second consecutive monthly decline, though the drop was less severe than the expected 8.5.
- US President Donald Trump urged the Federal Reserve (Fed) to lower interest rates, citing the economic impact of tariffs. Trump posted on the Truth Social platform that the Fed would be better off cutting interest rates as US tariffs begin to take effect in the economy. He added, "Do the right thing," "April 2nd is Liberation Day in America!"
- The Reserve Bank of India has likely been "opportunistically" absorbing USD inflows in recent sessions, possibly to rebuild foreign exchange reserves used to support the INR in recent months, according to reports.
- The yield on the 10-year Indian G-Sec dropped to 6.68%, its lowest level in three years, as expectations of lower interest rates grew. The RBI recently implemented its first rate cut in over four years, with lower-than-expected inflation in February reinforcing prospects for further easing this year.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR could test nine-week lows near 86.00
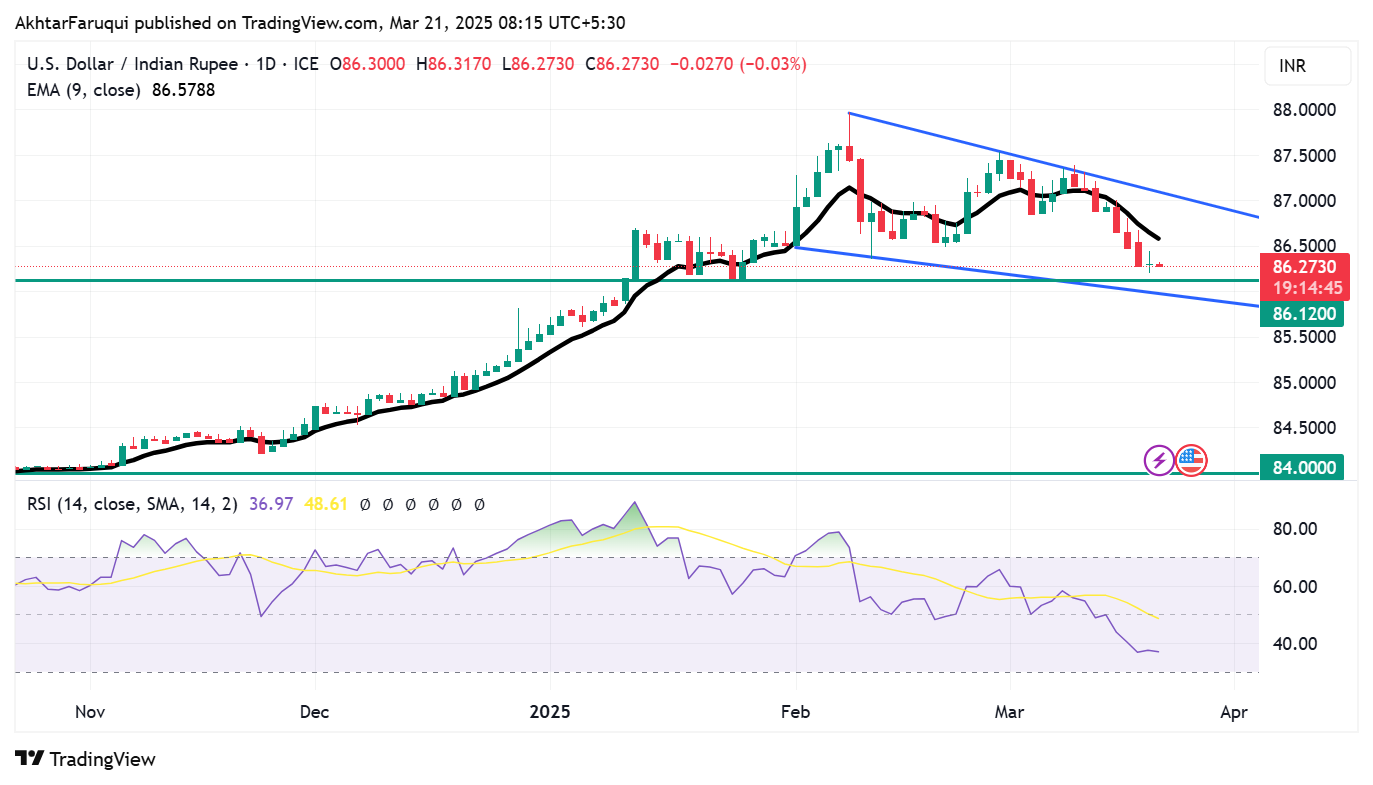
The Indian Rupee (INR) remains stable, with the USD/INR pair trading around 86.30 during Asian hours on Friday. Technical analysis of the daily chart suggests a strengthening bearish bias, as the pair remains within a descending channel pattern. Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is positioned slightly above the 30 mark, reinforcing the bearish outlook. A break below 30 could indicate an oversold condition, potentially triggering an upward correction.
The USD/INR pair could find immediate support at a nine-week low of 86.14 level, recorded on January 13, followed by the lower boundary of the descending channel near the psychological level of 86.00 level.
On the upside, the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 86.57 could act as the initial barrier. A break above this level could improve the short-term price momentum and support the USD/INR pair to explore the area around the descending channel’s upper boundary near the 87.10 level.
USD/INR: Daily Chart
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



